and the distribution of digital products.
State of The Graph Q3 2024
- Demand for data on The Graph Network reached an all-time high of over 5.3 billion queries in Q3’24, up 79% from 2.9 billion in Q2’24. Additionally, demand-side fees in USD grew by 83% QoQ to an all-time high of $206,000 in Q3’24.
- All subgraphs are upgraded to The Graph Network. As of the end of Q3’24, over 10,400 subgraphs were published to the decentralized network, up 42% QoQ.
- To improve network performance and reduce costs, The Graph transitioned from Ethereum L1 to Arbitrum L2. Over 3,000 subgraphs were created on Arbitrum in Q3’24.
- Indexing rewards decreased 8% QoQ to over $16 million in Q3’24, due to the depreciation in the USD price of the GRT token. In GRT terms, however, indexing rewards actually grew by 4% QoQ to 76 million GRT in Q3’24.
- In Q3’24, The Graph collaborated with Sony's Soneium project, and integrated with multiple networks, including IoTeX, Moonbeam, Neo X, and Solana.
The Graph is an indexing protocol that provides onchain data — such as DeFi transactions and liquidity pool data — from various sources. The Graph removes the need for data consumers (e.g., app developers) to build complicated infrastructure to get onchain data. Instead, data consumers pay to query custom APIs — called “subgraphs” — of onchain data via the GraphQL API. Subgraphs define a data schema to be indexed, making that data queryable. Subgraphs can be developed and queried by anyone.
To ensure the protocol runs correctly and efficiently, The Graph Network incentivizes several key roles within its ecosystem of both technical and non-technical participants:
- Indexers process and store onchain data from subgraphs. They usually have advanced technical knowledge of node operation. Indexers receive query fees from data consumers and indexing rewards from new token issuance.
- Curators are incentivized to analyze and signal which subgraphs are valuable to index. Curators earn a 10% portion of the query fees generated by subgraphs.
- Delegators do not employ resources to index onchain data; instead, they delegate The Graph's native utility token GRT to Indexers. Delegators earn a portion of query fees and indexing rewards without running nodes themselves.
The Sunrise of Decentralized Data is The Graph’s initiative to upgrade all subgraphs to its distributed network of over 100 independent Indexers. As of the end of Q3’24, over 10,000 subgraphs had successfully transitioned from the hosted service to the decentralized network. This transition corresponded to an all-time high in query fees due to the increasing demand for data indexed by The Graph Network.
Website / X (Twitter) / Discord
Key Metrics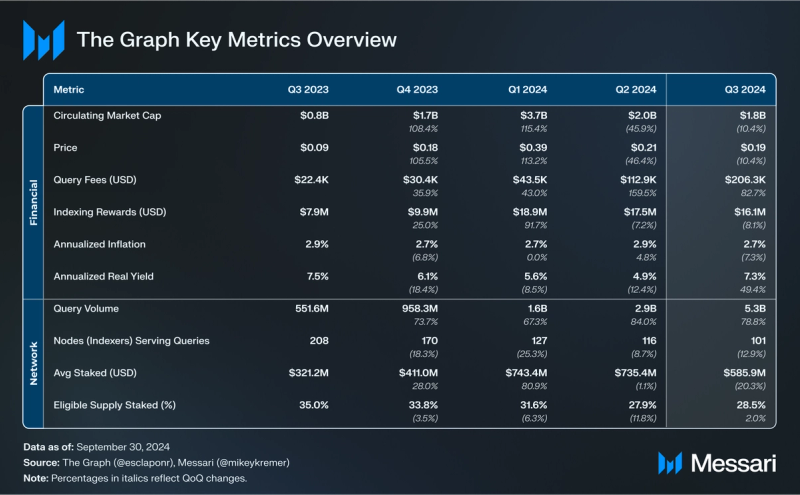 Performance Analysis
Performance AnalysisThe Graph Network is used by developers and data consumers who pay to query data. The network's performance can be measured by the growth of the volume of queries serviced, the active subgraphs serving queries, and the accrual of query fees.
Network OverviewQuery Volume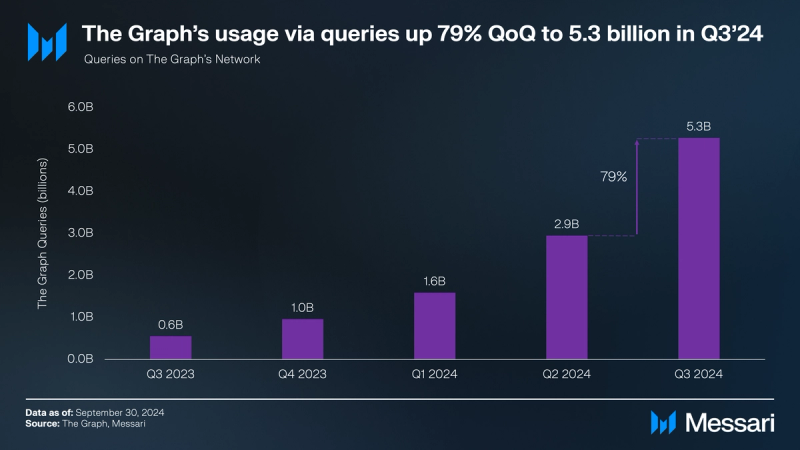
Demand for data organized by The Graph reached an all-time high of over 5.3 billion queries in Q3’24, up 79% from 2.9 billion queries in Q2’24. The Ethereum Mainnet led the way with 1.7 billion successful queries (32% of the total of 5.3 billion queries) in Q3’24, followed by Polygon with 1.0 billion queries (19%) and Arbitrum One with 780 million queries (15%).
In terms of subgraphs with the largest query volume, Quickswap V3 (9% of total queries) led the way, followed by Uniswap V3 (7%) and ENS (6%). Notably, query volumes have seen an upward trend over the past six quarters. While the initial growth in query volumes was likely driven by a recovery of crypto activity throughout 2023, there were other recent contributing factors to the increase in query volume, including:
- the introduction of a free query plan of 100,000 queries per month, as well as
- the increase in subgraphs published to the decentralized network, as detailed below.
To bootstrap The Graph, a hosted service was initially created. This service hosted subgraphs as the protocol gradually transitioned to its decentralized network. The hosted service was free (subsidized by The Graph ecosystem) and offered indexing infrastructure run by Edge & Node, the initial team behind The Graph.
The first decentralized subgraph launched on the decentralized network in Q1'21. Since then, the Sunrise of Decentralized Data has been on a course to upgrade all subgraphs to its distributed network of independent Indexers in three phases: Sunray, Sunbeam, and Sunrise.
The first phase of the upgrade — Sunray — was completed in March 2024. Sunray brought more chains, free queries, and improved billing, including a free query plan of 100,000 queries per month. This helped developers get started on the network and scale their development.
The second phase — Sunbeam — was concluded in June 2024. Sunbeam focused on upgrading hosted service subgraphs to The Graph Network. The third phase of the upgrade — Sunrise — retired hosted service endpoints and was completed in June 2024.
As a consequence, the number of deployed subgraphs on The Graph’s Network has steadily increased.
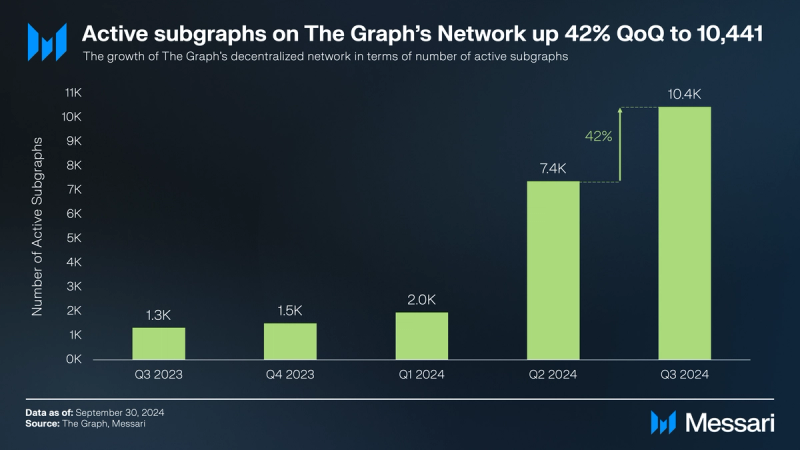
Over 10,400 active subgraphs successfully transitioned from hosting services to The Graph’s distributed network of independent data indexers as of the end of Q3’24. This translates into a 42% QoQ.
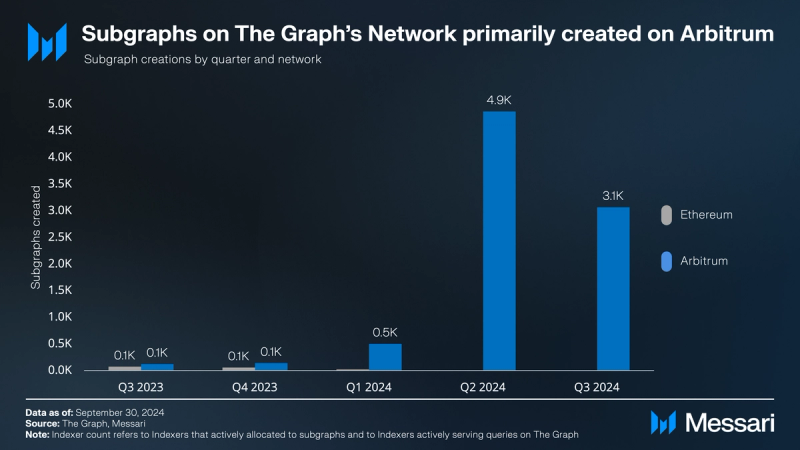
To improve performance and reduce costs, The Graph transitioned from Ethereum Layer-1 to Arbitrum Layer-2. As a result, approximately 80% of the active subgraphs (8,000 of the total of over 10,000 active subgraphs) were created on Arbitrum over the past two quarters.
Ecosystem ParticipationSubgraphs provide an arena for both technical and non-technical ecosystem participants to interact symbiotically:
- Indexers operate Graph Nodes to process and store onchain data. Data consumers can then query this data via GraphQL, an open-source language for The Graph’s APIs.
- Curators signal to Indexers which subgraphs are worth indexing. Curators also often act as subgraph developers.
- Delegators delegate their GRT tokens to Indexers. Delegation enables anyone to participate in the protocol regardless of their technical know-how.
Staked GRT is required for indexing subgraphs. As Indexers get more GRT delegated, they increase their capacity to index more subgraphs on The Graph Network. Indexers monetize their indexing and query processing services on The Graph's query market by staking GRT.
The minimum stake for an Indexer is currently set at 100,000 GRT (approximately $19,000 as of September 30, 2024). In addition to this minimum, Indexers can also receive delegated stake from other ecosystem participants. Delegators can increase their total stake up to 16x an Indexer's personal stake.
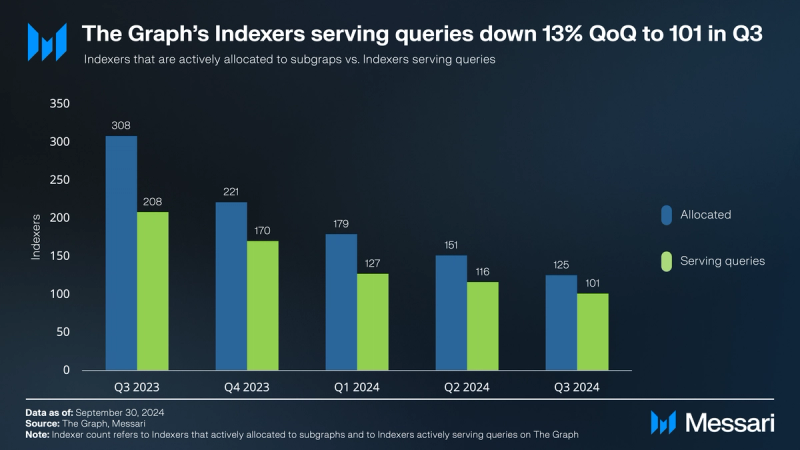
Indexers actively serving queries on The Graph Network decreased 13% to 101 at the end of Q3’24 from 116 at the end of Q2’24. This continues a downward trend in Indexers actively serving queries ever since Q1’23, explained by the end of The Graph’s Multi-Chain Incentivized Program at the end of Q1’23 and by some Indexers simultaneously un-staking their GRT. Notably, this drop in the number of Indexers has not resulted in performance drops of Indexers covering a larger number of subgraphs, testing The Graph Network's resilience.
Financial OverviewThe GRT token follows the Stake-for-Access model, also known as a utility token model. Participants in The Graph's ecosystem earn revenue in GRT by performing indexing and querying services on the decentralized network. Both services require GRT to be staked. An Indexer’s stake comprises their own GRT tokens (i.e., self-stake) and GRT delegated toward them (i.e., delegated stake).
Both indexing rewards and query fees are funneled through Indexers, who then distribute them to Delegators and Curators. Every Indexer is free to define their own individual cut of query fees and indexing rewards based on the supply-and-demand dynamics of the open marketplace. According to this individual cut, each Indexer then distributes the indexing rewards and query fees with Delegators. In contrast, the Curators earn a 10% portion of the query fees generated by particular subgraphs.
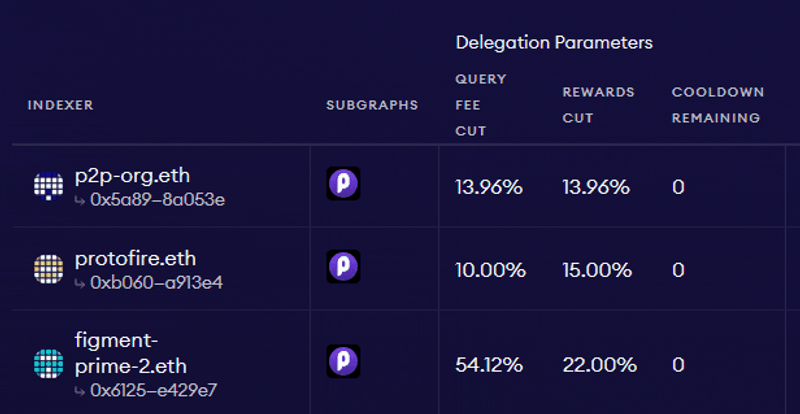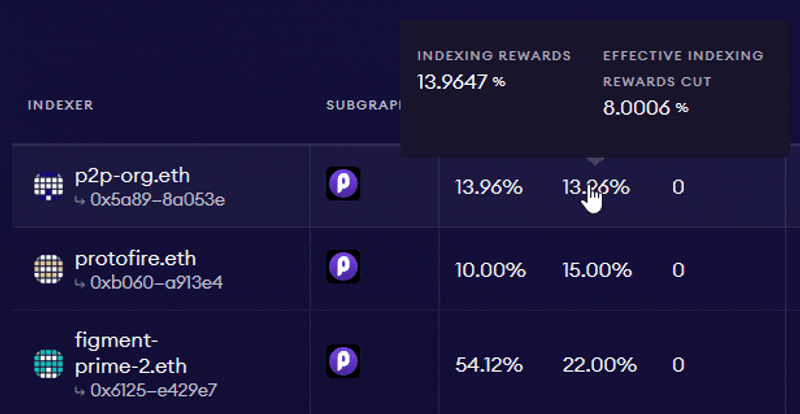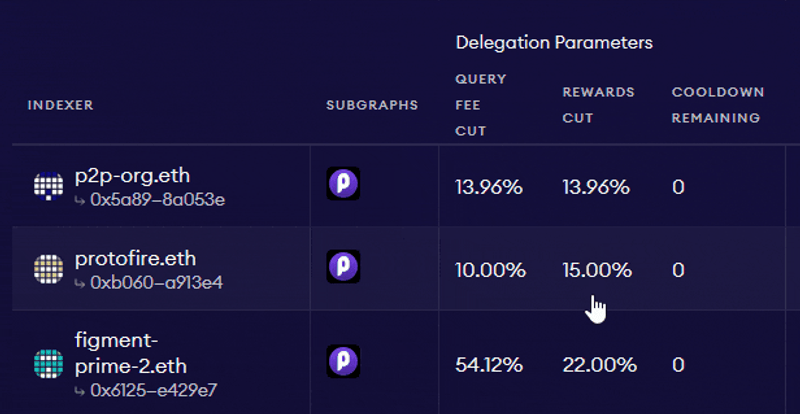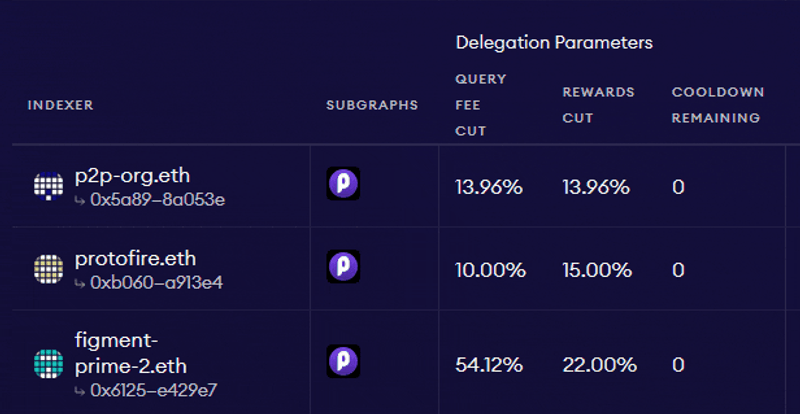
Source: The Graph: Choosing Indexers
As per the above example, if an Indexer sets the query fee cut to 13.96%, their Delegators would receive the remaining 86.04% of the fee revenue proportional to their stake. While Delegator stake cannot be slashed, Delegators should still consider several factors when staking GRT with Indexers. These include:
- Indexer choice, i.e., choosing effective Indexers with the most optimal balance between reward payouts and “skin-in-the-game” from allocation of self-stake.
- Unbonding period, i.e., no GRT transfers or rewards are possible within a 28-day window after un-delegation.
- Delegation tax of 0.5%, i.e., calculating how long it takes to earn back the 0.5% tax on delegation.
Indexing rewards come from a GRT annual inflation below 3% (2.7% on average in Q3’24), derived from the GRT issuance rate. Rewards are distributed to staked Indexers in return for providing indexing and querying services on The Graph’s open marketplace.
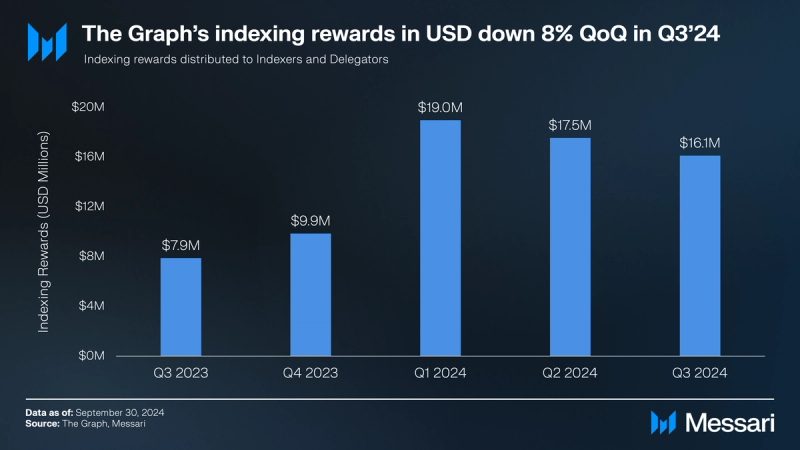
Indexing rewards decreased 8% QoQ to over $16 million in Q3’24, due to the depreciation in the USD price of the GRT token. In GRT terms, indexing rewards grew by 4% QoQ to 76 million GRT in Q3’24.
Query Fees (Network Usage Fees)Data consumers (e.g., app developers) pay query fees for Indexers to fetch and organize data. As of Q3’24, The Graph delivers data to projects like Polygon, Art Blocks, and Loopring. Query fees are determined by market demand and distributed to Curators, Indexers, and Delegators.
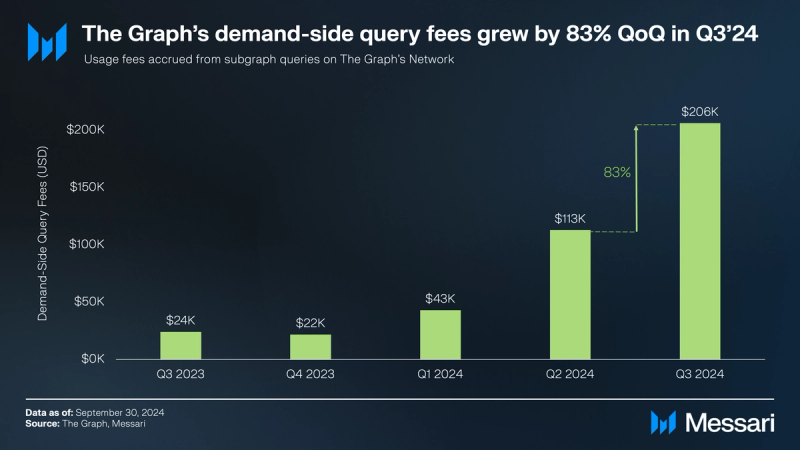
Total query fees increased 83% QoQ in USD terms to an all-time high of $206,000 in Q3’24. This increase in demand-side revenue in USD was primarily driven by the increase in query volume and the number of subgraphs on the decentralized network. In terms of the chains that drove the most revenue from query fees throughout Q3’24, the Ethereum Mainnet led the way with nearly $66,000 (32% of the total fees from query fees in Q3’24), followed by Polygon with over $40,000 (19%) and Arbitrum One with nearly $31,000 (15%).
For The Graph, the Q3’24 total query fees (over $206,000) comprised nearly 1.3% of the total indexing rewards (approximately $16.1 million). This distribution indicates that The Graph’s network participants still rely on indexing rewards to sustain their day-to-day operations.
Qualitative AnalysisKey DevelopmentsLayer-2 TransitionThe Graph transitioned from Ethereum's Layer-1 to Arbitrum's Layer-2 to address the challenges of high gas fees and slower transactions on Ethereum's mainnet. As part of this transition, The Graph has proposed a plan to deprecate its L1 protocol, known as GGP 0044. This proposal, approved by The Graph Council, outlines a six-month deprecation process for the L1 protocol by the end of 2024. The transition is expected to reduce transaction costs and increase processing speed.
Advanced Data ServicesIn response to the growing complexity of blockchain data environments, The Graph has introduced advanced data services to complement the existing subgraph services. These new services include:
- Firehose: Offering real-time data streams, enabling developers to access blockchain data with increased speed and efficiency.
- Substreams: Providing granular data access, allowing for more detailed and specific querying of blockchain information.
- AI capabilities: Enabling AI-driven applications opens up new possibilities for data analysis and prediction within the blockchain space.
These additions expand The Graph's functionality beyond traditional subgraph indexing, positioning it as a comprehensive onchain data service provider. For Indexers, this means the potential for higher earnings and a broader range of service offerings, allowing them to specialize in areas such as real-time data processing, granular onchain data analysis, or AI-driven insights.
Performance OptimizationsThe Graph focuses on optimizing the performance of dApps. One such optimization, implemented using Graph-Client, focuses on pausing queries on inactive browser tabs. This addresses the issue of excess queries during periods of inactivity in decentralized applications, conserving resources and improving overall efficiency. By limiting active queries to only when the browser tab is in use, developers can reduce unnecessary requests and optimize their dApp's interaction with onchain data.
Multichain IntegrationsOn Aug. 20, 2024, The Graph announced the integration of Arbitrum Nova mainnet into its Subgraph Studio, marking an advancement for developers within the Arbitrum ecosystem. This integration allows for the creation of fast, performant frontends for Nova dApps. It enhances the capabilities of decentralized applications built on Arbitrum's Layer-2 solution.
Moreover, The Graph has integrated with Moonbeam and partnered with IoTeX 2.0, serving as the Indexing module for DePINs to process and display real-time information from physical devices.
Furthermore, The Graph announced its integration with Neo X, a sidechain of the Neo blockchain, on Aug. 29, 2024. This partnership enables Neo X developers to access The Graph's Studio for building, publishing, and utilizing subgraphs, enhancing the efficiency of data access and query capabilities within the Neo ecosystem.
In a development for the Solana ecosystem, The Graph introduced new enhancements to support Solana, offering faster and more efficient access to Solana data. These updates include new tooling, a smoother developer experience, and ready-to-use Substreams-powered subgraphs.
Other notable multichain integrations include: Chilliz integration, Unichain testnet integration, and Boba Network integration. These integrations allow developers to build subgraphs to power their dApps on Chiliz Chain.
Strategic PartnershipsOn Aug. 28, 2024, Sony launched Soneium, an Ethereum Layer-2 network developed by Sony Block Solutions Labs (Sony BSL), with The Graph as a technology partner. This partnership showcases The Graph's capabilities in supporting large-scale, enterprise-grade onchain initiatives. Another notable collaboration was established with NEAT Protocol, aiming to enhance the decentralized indexer network for AI applications on the NEAR network. Launched on July 22, 2024, this partnership aims to bridge artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technologies.
Timeline Aggregation Protocol (TAP)The Graph announced the mainnet launch of the Timeline Aggregation Protocol (TAP), a micro-payment system. TAP enables Indexers to handle receipts offchain and later redeem them using Receipt Aggregate Vouchers (RAVs) onchain. While the exact completion date for the transition to TAP has not been explicitly stated, Indexers are encouraged to begin migrating to TAP.
CommunityDeveloper Education and SupportRecognizing the role of developers in the ecosystem's growth, The Graph has expanded its educational resources and support channels. A notable initiative in this direction was the launch of @GraphDevs, a dedicated Twitter account serving as a hub for developers. This resource offers technical content including "technical tutorials, subgraph best practices, code tips, tricks, optimizations, and much more technical content designed to help you get the most value out of The Graph."
Key GovernanceDeprecate the L1 (Mainnet) Protocol (GGP 0044)This successful proposal resulted in deprecating the Layer-1 (mainnet) protocol following GIP 0052 and the migration of all indexing rewards to Arbitrum. The motivation behind the deprecation is to lower potential user costs and eliminate potential confusion regarding running two protocols in tandem. By Dec. 28, 2024: The stake, delegation, curation, and subgraph transfer tools will be removed. The L1 protocol will be officially deprecated, with contracts earmarked as "end of life." Any remaining GRT may still be withdrawn from the L1 contracts.
Deploying GRT Token to Base (GGP 0047)This ongoing proposal aims to formally recognize the GRT token on Base as the canonical version. If approved, this deployment will enable Coinbase users to withdraw GRT via Base.
Closing SummaryDemand for data on The Graph Network reached an all-time high of over 5.3 billion queries in Q3’24, up 79% from 2.9 billion in Q2’24. Additionally, demand-side fees in USD grew by 83% QoQ to an all-time high of $206,000 in Q3’24. All subgraphs are upgraded to The Graph Network. As of the end of Q3’24, over 10,400 subgraphs were published to the decentralized network, up 42% QoQ.
Key developments this quarter include the strategic transition to Arbitrum's Layer-2 solution, which promises enhanced scalability and cost-effectiveness, and the introduction of advanced data services like Firehose and Substreams.
In Q3’24, The Graph expanded its ecosystem and integrated with multiple networks including IoTeX, Moonbeam, Neo X, and Solana. Collaborating with Sony's Soneium project broadens the protocol's utility across various ecosystems.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.