and the distribution of digital products.
Crypto arbitrage guide: How to make money as a beginner
Cryptocurrency arbitrage is a type of trading that exploits differences in prices to make a profit. These price differences commonly referred to as “arbitrage spreads”, can be used to buy a cryptocurrency at a lower price and then sell it at a higher price.
For example, if BTC (Bitcoin) is being sold for $8,050 on Coinbase Pro and $8,200 on Binance. You could buy some amount of BTC at a lower price and sell it at a higher price.
There are different types of arbitrage that exploit price differences in different ways. However, they all involve finding these spreads and quickly acting on them.
In 2020 the types of crypto arbitrage spread anywhere from 0.2%-4%. Sometimes upwards of 20% will appear but they’re rare.
Try Pionex’s arbitrage bot which gives a 30-50% yearly return.
If you can act on arbitrage spreads enough times in a day though, it can be worth your time. Arbitrage is a great tool when prices aren’t moving much in a day and other crypto day trading strategies, such as swing trading, aren’t entirely viable.
Table of contents- What is crypto arbitrage?
- Different types of arbitrage
- How to find crypto arbitrage opportunities
- How to submit arbitrage trades and take advantage of a spread
- Good luck!
A common misconception with arbitrage is that you must buy crypto on one exchange, transfer it another, then sell it.
While this is one approach, it’s not your only option and there are other ways of crypto arbitrage trading that don’t rely on waiting for a potentially slow and expensive transfer.
Spatial arbitrage – Transferring between exchanges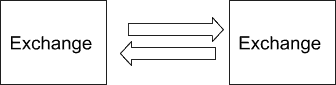
This involves buying crypto on one exchange, transferring it to another exchange where it’s being traded for a higher price, and then selling it.
This isn’t a realistic way to make a profit because spreads (price differences) may only exist for a couple of seconds.
Therefore, by the time you transfer the crypto to another exchange, the price will probably have changed again.
Transfer fees are also being incurred in addition to trading fees.
Pros
- Easy to execute
Cons
- Transfers are slow and expensive
- The spread might not exist anymore by the time the transfer is done
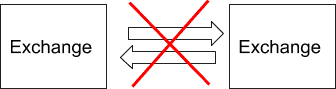
This spatial arbitrage approach eliminates the step of transferring crypto between exchanges.
Therefore, you can immediately act on a spared without having to wait on a slow transfer or pay a transfer fee.
That difference makes it a better option for crypto day trading compared to the transfer method.
To do this, you hold a balance on two exchanges and submit a buy and sell order at the same time on both.
For example, let’s say you’ve seen some spreads on the BTC-USD market when buying on Coinbase Pro and selling on Binance.
You would move your USD to Coinbase Pro and your BTC to Binance, then wait for a spread. When a price difference appears, say it’s 1.2% more on Binance, you would trade buy BTC with your USD on Coinbase Pro, and at the exact same time sell BTC for USD on Binance.
Breaking down the example further, if you had bought 0.1 BTC at a rate of $8,050 on Coinbase pro you’d have spent $805 USD.
And if you’d sold 0.1 BTC at the same time on Binance at a rate of $8,200 you’d have sold it for $820.
So in an instant, you bought 0.1 BTC and sold 0.1 BTC, neither losing nor gaining BTC. But you spent $805 to buy it and sold it for $820, yielding a profit of $15 (before trading fees).
You could keep waiting for spreads to appear like this and act on them as they come. Order books are changing constantly so prices are always fluctuating and spreads can appear fairly regularly.
Pros
- You can realize a profit immediately
- No transfer times or fees
Cons
- It can be difficult to submit two accompanying trades quickly at the same time
- One order might fill while the other doesn’t mean that you won’t get the price you wanted, you can’t guarantee you’ll be fast enough to fill both orders first
This approach is different because it can be done entirely on one exchange. Instead of exploiting differences in prices between exchanges, triangular arbitrage takes advantage of differences between trade pairs.
For example, you could trade ETH for BTC, BTC for XRP, and XRP back to ETH. If the differences in prices were advantageous you would end up making a profit.
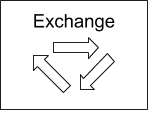
Pros
- It can be done on a single exchange
- You can realize a profit immediately
- No transfer times or fees
Cons
- The more orders you’re submitting, the more chances there will be for other people to fill that order instead of you, meaning that you won’t get the price you wanted
For example, we’ll look at how to find spatial arbitrage opportunities. This involves looking for price differences between two exchanges where the spread is large enough that you can make a profit even after trading fees.
You might want to start by checking which coins have had a decently high volume for liquidity, or price volatility. However, that will be up to you to find what works best each day.
There are four important factors to consider when looking for spreads:
1. FeesThe spread must be large enough that you’ll make a profit after trading fees. If you’re paying 0.2% on your buy and 0.25% on your sell, you won’t make a profit if the price difference was only 0.1%. Therefore, you may want to only search for spreads above some threshold, say 1%.
2. Ask and bid ratesYou want to be looking at the top of the order book on each exchange. When buying you’ll be filling the ask order on that exchange. Therefore, you look at the ask order’s rate and amount. When selling you’ll be filling the bid order on that exchange. Therefore, you look at the bid order’s rate and amount.
3. Avoiding slippageSlippage occurs when you don’t get the price you expected. If the latest ask is for 0.1 BTC at a rate of $8,050 but you buy 0.15 BTC, you’ll get 0.1 at the rate of $8,050. And the other 0.5 BTC at a worse rate because you’ll be filling the next order in the order book. To avoid slippage your orders can’t be larger than the smallest of either the ask or bid orders that you’ll be filling.
4. Potential profitIf a spread of 30% exists but the ask order that you’ll be filling is only for $1 worth of the asset, your max profit won’t be more than $0.30.
So let’s say we want price differences that are >= 1% and have an order size that will allow at least $10 in profit.
You can either open up multiple exchange websites and try to calculate price differences and check order sizes manually. Or you can use some sort of software tool to help in the process.
Realistically since arbitrage spreads may only exist for a second or less you’ll probably want to use a tool to assist with the process.
There are a few options out there but the one we’ll be using for an example today is Coygo Terminal, which provides a real-time crypto arbitrage scanner for a number of crypto exchanges and allows you to filter by spread percent and possible profit.
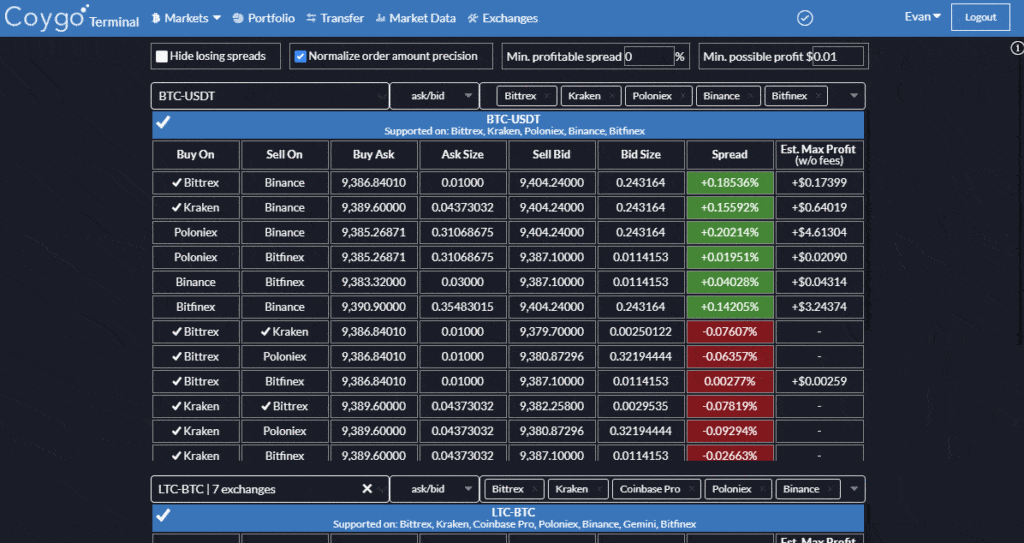 Coygo – Crypto arbitrage tool
How to submit arbitrage trades and take advantage of a spread
Coygo – Crypto arbitrage tool
How to submit arbitrage trades and take advantage of a spread
As stated above, for our example we’re doing spatial arbitrage without transferring between exchanges.
Let’s say you’ve been watching the arbitrage scanner and you’ve seen profitable spreads pop up a few times on the ETH-USDT market when buying on Kraken and selling on Bittrex.
You already have some ETH and USDT, so hoping that this trend will continue, you can send your USDT to Kraken and your ETH to Bittrex.
Steps to submit crypto arbitrage Trade- Move your USDT to Kraken
- Move your ETH to Bittrex
- Wait for a profitable spread to appear
- Find the smallest order amount to avoid slippage. For this example, if the bid order you’re filling is for 0.1 BTC and the ask order that you’ll be filling is for 0.05 BTC, the largest amount you can order is for 0.05 BTC.
- Now you have to place both orders at the same time on each exchange, one buy and one sell. For both orders, you’ll be using the amount you determined, 0.05 BTC in this example. You can open two limit orders and specify the exact price you want by using the ask and bid rate for that order you’re filling, or you can just open market orders.
- If you were able to place both orders quickly enough that you filled them before either was canceled or someone else filled them, you’ve just realized an immediate profit.
- Go back to step #3 and start again.
Arbitrage spreads may only exist for a second or less, so it can be difficult to quickly fill out these orders.
Speed is the key to the game with arbitrage, you’re racing to be faster than other traders and bots that are trying to do the same thing.
Your best option for being quick enough is to use a tool that can help you quickly act on spreads as they appear.
Mentioned previously, Coygo Terminal can also help in this area with its One-Click-Trading interface, which helps automatically pre-configure your order sizes and rates and submit orders to multiple exchanges with one click.
Good luck!Arbitrage can be a great approach to day trading crypto, but it comes with its own set of benefits and downsides.
The ability to realize an immediate profit without waiting and watching charts is certainly appealing to some, but the prospect of competing against other traders and bots to be the first to fill an order can be intimidating to beginners. Best of luck!
Attribution
This article is provided by Coygo Terminal, a crypto arbitrage solution. You can read Coygo reviews on CoinCodeCap.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.