and the distribution of digital products.
What is a smart contract? Why do we need them, and how do they work?
traditional agreement explained, smart contracts, blockchain technology, automated agreements, digital contracts, decentralized applications
 Background
BackgroundImagine a society in which contracts are carried out automatically without the need for human interaction. No lawyers, no intermediaries, just trustless automation. Welcome to the realm of smart contracts—a revolutionary technology at the heart of blockchain innovation.
Smart contracts are reshaping industries by eliminating inefficiencies in traditional agreements. But what exactly are they, and how do they work? This blog will demystify smart contracts, showing you why they matter and how they could transform the way we interact digitally.
Before we go further, let’s talk about agreements.
What is an agreement?Agreements are foundational elements in both personal and professional relationships, serving as formalized understandings between parties. At their core, agreements establish expectations and responsibilities, fostering a sense of trust that is essential for collaboration and cooperation.
In various contexts—such as business contracts—agreements outline the terms under which parties operate together. They can address a wide range of issues, including deliverables, timelines, payment structures, and confidentiality.
 Challenges and Limitations of Traditional Agreements
Challenges and Limitations of Traditional AgreementsTraditional agreements, while foundational to business and personal interactions, often come with significant drawbacks.
One of the primary issues is reliance on intermediaries. Whether it’s a bank overseeing a financial transaction or a lawyer drafting a contract, these third parties add layers of complexity, time, and cost to the process. Their involvement often creates bottlenecks, delaying outcomes and increasing expenses.
Another challenge is the potential for disputes and ambiguities in traditional contracts. Without clear enforcement mechanisms, parties may face prolonged legal battles, leading to uncertainty and wasted resources. Furthermore, traditional agreements are prone to human error, whether in drafting, interpretation, or execution, increasing the likelihood of conflicts.
Security is another critical concern. Paper-based agreements or centralized digital contracts are susceptible to tampering, fraud, or data breaches. The lack of transparency and accountability in many traditional systems can erode trust between parties.
These limitations highlight the need for a more efficient, secure, and reliable alternative to traditional agreements—an alternative that smart contracts aim to provide.
Smart Contracts: A Solution to Traditional ChallengesSmart contracts address many of the shortcomings of traditional agreements by leveraging the power of blockchain technology. They eliminate the need for intermediaries by automating processes through self-executing code. This automation not only reduces costs but also accelerates transactions, enabling near-instant execution once conditions are met.
Transparency is another key advantage. The terms of a smart contract are encoded on a blockchain, making them visible and verifiable by all parties. This openness fosters trust and minimizes disputes, as the code itself enforces the agreed-upon terms without bias.
Smart contracts are inherently secure, benefiting from the cryptographic protections of blockchain networks. Once deployed, they cannot be altered, ensuring the integrity of the agreement. Their decentralized nature reduces the risk of tampering or fraud by eliminating single points of failure.
Geographical barriers are also minimized. Smart contracts operate on global blockchain networks, making cross-border transactions seamless and efficient. Whether transferring funds internationally or managing supply chain logistics across continents, smart contracts provide a unified and streamlined solution.
By addressing the inefficiencies, vulnerabilities, and constraints of traditional agreements, smart contracts are revolutionizing how we interact and transact in the digital age. Their ability to automate, secure, and simplify complex processes positions them as a cornerstone of the Web3 ecosystem.
Definition of Smart Contract & Key CharacteristicsSmart contracts are self-executing programs where the terms of the agreement are directly written into lines of code. Operating on decentralized blockchain networks like Ethereum, these contracts ensure transparency, security, and automation. Key characteristics include:
- Self-Executing: The contract automatically enforces the agreed terms when specific conditions are met.
- Decentralized: Unlike traditional agreements, smart contracts are hosted on blockchain networks, eliminating central authority control.
- Immutable: After deployment, the code and conditions cannot be changed, ensuring the integrity of the agreement.
- Transparent: All participants can verify the terms and conditions encoded in the contract.
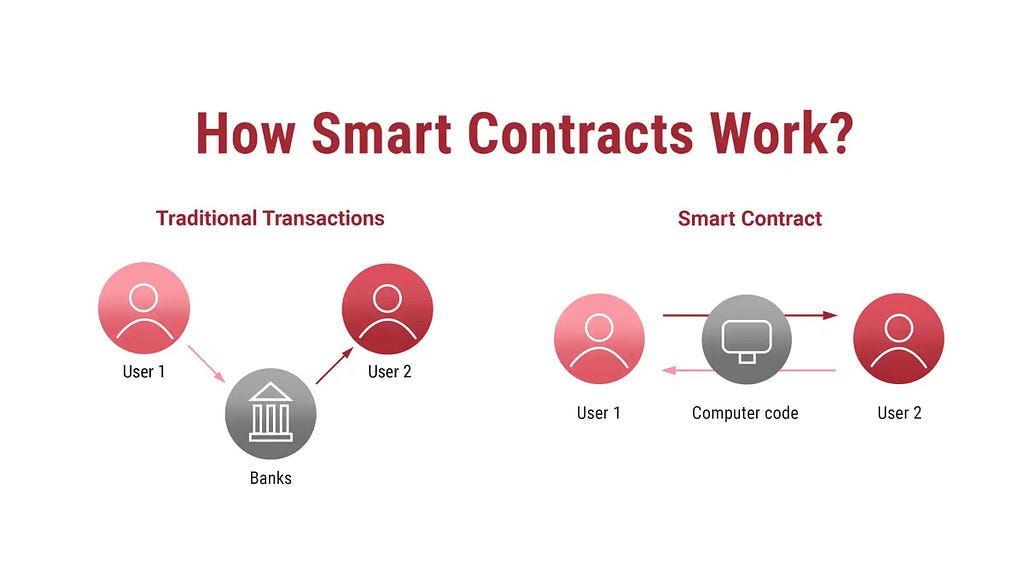 How Smart Contracts Work
How Smart Contracts WorkSmart contracts operate through a straightforward process:
- Coding: Developers write the contract’s terms using programming languages like Solidity (popular in Ethereum).
- Deployment: The contract is deployed on a blockchain, where it resides as a distributed and unalterable entity.
- Triggering Events: When predefined conditions are met (e.g., a payment or delivery confirmation), the contract executes the agreed-upon actions.
- Execution: The blockchain verifies and enforces the transaction, ensuring all steps are followed as coded.
Smart contracts have gained traction across various industries:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Automating loans, insurance, and decentralized exchanges without banks or brokers.
- Supply Chain Management: Ensuring transparency by tracking goods through blockchain, from production to delivery.
- Digital Identity: Managing personal data securely while granting selective access to organizations or platforms.
- Real Estate: Facilitating property sales and rental agreements without requiring escrow services or agents.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Enabling secure ownership and transfer of digital art, collectibles, and in-game assets.
- Efficiency: By automating tasks, smart contracts save time and reduce errors.
- Cost Savings: They eliminate intermediaries, cutting associated fees.
- Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic nature ensures robust protection against tampering.
- Trustless Transactions: No need to rely on third parties; the code governs the agreement.
- Transparency: Open to audit by all parties, ensuring accountability.
Despite their advantages, smart contracts face challenges:
- Coding Vulnerabilities: Flaws in the code can lead to exploits and financial loss.
- Scalability Issues: High gas fees and network congestion on popular blockchains like Ethereum.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Legal frameworks around smart contracts are still evolving.
- Limited Flexibility: Once deployed, smart contracts cannot be easily updated or modified.
What is a smart contract? Why do we need them, and how do they work? was originally published in Coinmonks on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.