and the distribution of digital products.
Using LUA Scripts in Redis with Node.js: Why It’s Beneficial
Games, financial services, social media, IoT, and many other areas actively use Redis today due to its high performance and ease of use. Redis is often chosen for its ability to handle millions of requests per second with sub-millisecond latency. However, without a thorough understanding of its data structures, commands, and how it works, we may not be able to fully leverage its performance capabilities.
We face these challenges all the time:When using Redis, most applications involve more complex logic than simply performing GET/SET operations. The most common challenges we face implementing the logic, involve supporting atomic operations and reducing network round trips.
Atomic operations:An atomic operation is one that is completed in a single, indivisible step. This is crucial when performing operations on multiple keys that must be executed atomically to ensure data consistency.
\ Let's imaging, we want to increment the total number of devices and save the device state only if the device is not already registered and the threshold of registered devices has not been reached.
PSEUDOCODE: “Check for IoT in the database” “Get the current number of registered IoT “ IF ( “IoT does not exist” AND “Current number of registered IoT” < 100) THEN “Save IoT state in a database” “INCR the number of registered IoT” RETURN 1 END RETURN 0\ Obviously, such logic requires locks to prevent race conditions, avoid idempotency issues and ensure data consistency.
Network Round Trips:Network round trips refer to the complete cycle of sending a request to a server and receiving a response. Fewer round trips result in less waiting time for responses, which leads to faster application performance.
\ Let’s imaging, we want to retrieve multiple values, make a computation, and then store the result as another value.
PSEUDOCODE: “Get user salary” “Get user bonus” “Get user discount” “Computation(User salary + User bonus – User discount)” “Save computation to DB” RETURN ComputationThis logic would normally require 4 network round trips, causing latency.
\ ==In both two cases Lua scripting can be a valuable tool.== Lua scripting in Redis is a powerful feature that should be used when we need to perform complex operations requiring atomicity, efficiency, and reduced latency.
Using Lua with Redis in Node.jsRedis supports Lua scripting via the EVAL and EVALSHA commands. The application should first load the script with SCRIPT LOAD command and then call EVALSHA once more to run the cached script by its SHA1 sum. Most of Redis' clients already provide utility APIs for doing that automatically. In this article I will use ioredis for Node.js as a Redis client.
\ Let's take the example described in the Atomic Operations sub-section above and solve it entirely using a LUA script.
- Create a directory and name it whatever you want.
- Inside the created directory, run npm install ioredis to install the Redis client.
- Create files: createDevice.lua, service.js
\
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
- Create a script in the createDevice.lua file:
\
- Define the script as a command in the service.js:
\
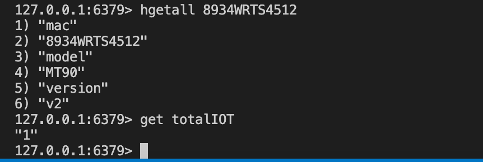
Run node server.js to register a hardcoded IoT device (MAC: 8934WRTS4512)
Let’s check the result in redis-cli:
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
What we achieved:- Minimize the amount of data sent over the network. Instead of sending multiple calls, we send a single call to the Redis.
- Out data is consistency. Lua script allows to bundle multiple operations into a single atomic unit.
- The code in the service is clear. We use only one command to invoke a sctipt that encapsulates all the logic.
- Avoid using Lua scripts for operations that might take a long time to complete, as Redis is single-threaded, and a long-running script will block all other operations.
- If the logic becomes too complex or difficult to debug, it might be better to handle it within the application code rather than in a Redis Lua script.
- Complex, not optimized Lua scripts can block a Redis instance.
- Writing and maintaining Lua scripts requires knowledge of the language, and this can lead to development overhead.
- There is no way to work with keys from multiple buckets in a Lua script.
- Debugging and testing takes time.
When using Redis, we face many challenges related to achieving optimized performance and solving problems such as idempotency or race conditions. But the most common ones are ensuring atomicity and reducing network roundtrips. This article provides an example of using LUA to solve these two problems.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.