and the distribution of digital products.
DM Television
Understanding MultiversX: A Comprehensive Overview
- MultiversX is a Layer-1 blockchain launched in 2020. Its network offers a scalable, highly secure, and developer-friendly alternative to smart contract platforms like Ethereum.
- MultiversX uses adaptive state sharding to divide the blockchain network into smaller units called shards. These shards process their own subset of transactions, smart contracts, and states in parallel, increasing the system’s overall throughput.
- In Q2 2024, MultiversX announced the Sovereign Chains SDK, enabling developers to deploy a custom L2 or app chain natively interoperable with the MultiversX ecosystem. The protocol plans to launch Sovereign Chains in Q4 2024.
- MultiversX recently passed the Spica protocol upgrade, introducing onchain 2FA, cost-effective relayed transactions, and dynamic NFTs.
Since its inception, Ethereum has been the leading force for programmability in the blockchain space. However, like other blockchains, Ethereum still faces several challenges, particularly regarding scalability, interoperability, user experience, and developer tooling.
Ethereum's throughput is around 12 transactions per second, leading to high fees during peak activity, which restricts access for smaller users. Interoperability is also a challenge, as many blockchains operate in isolation, causing fragmentation and limiting collaboration. Solutions like cross-chain bridges exist, but they introduce complexity and risks. Additionally, blockchain platforms still lag behind Web2 in terms of user experience and developer accessibility, making onchain interactions less intuitive.
These challenges highlight the broader obstacles that blockchain and smart contract technology face in achieving widespread adoption. MultiversX seeks to tackle these issues by leveraging adaptive state sharding, providing a more intuitive user and developer experience, and introducing its Sovereign Chain SDK — all aimed at overcoming scalability, usability, and interoperability hurdles.
BackgroundMultiversX, launched initially as Elrond, was founded in 2017 by Beniamin Mincu, Lucian Mincu, and Lucian Todea, with a vision to create a highly scalable, efficient, and developer-friendly blockchain platform. In 2019, the company raised $1.9 million in a private investment round and an additional $3.25 million in a successful ICO on Binance Launchpad.
Elrond solves the challenges of existing blockchain architecture, including scalability, high transaction cost, low latency, and developer flexibility. Elrond's novel approach to blockchain infrastructure was defined by its use of Adaptive State Sharding. This method improved throughput by splitting the network into shards, each capable of parallel processing transactions and smart contracts. This enabled Elrond to achieve high scalability, with the ability to process up to 15,000 TPS. Additionally, Elrond introduced a Secure Proof-of-Stake (SPoS) consensus mechanism, combining security, decentralization, and efficiency while reducing energy consumption compared to Proof-of-Work systems.
In November 2022, Elrond rebranded to MultiversX. The rebrand signaled a strategic realignment toward its vision of creating an immersive digital experience that could appeal to a large audience of Web2 and Web3 users.
The rebrand also coincided with the launch of three products: xFabric, an open-source content management system (CMS) for businesses and brands in Web3; xPortal, a non-custodial crypto wallet with fiat and crypto; and xWorlds, a suite of tools for creating and navigating the metaverse. The team has paused xFabrics and xWorlds to focus on other dApps, such as xPortal, xExchange, and xMoney.
In Q2 2024, MultiversX released the Sovereign Chain SDK. The product allows developers to launch a custom L2 or appchain that is interoperable with the MultiversX ecosystem. MultiversX aims to become a Layer-0 (L0) interoperability layer for other networks, with Sovereign Chains benefiting from the prime chain’s security and liquidity using the EGLD token.
TechnologyMultiversX differentiates itself through two features: adaptive state sharding and the Secure Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. Along with the SpaceVM, which executes smart contracts on MultiversX, these properties define the network's architecture and solution for achieving global scalability, fast finality, and high resiliency to malicious attacks.
Adaptive State ShardingAdaptive state sharding is central to MultiversX’s network architecture. Sharding is a method that divides the blockchain network into smaller, manageable units called "shards." Each shard processes its own subset of transactions, smart contracts, and states in parallel, significantly increasing the system’s overall throughput. Compared to Ethereum’s dank sharding, which focuses on data availability, adaptive state sharding splits data and states across shards. As a result, each shard acts like a mini blockchain, executing and storing transactions independently, while the main chain keeps track of shards and ensures cross-communication.
MultiversX takes sharding a step further with adaptive state sharding, which combines state sharding, transaction sharding, and network sharding into a single, more efficient solution:
- State Sharding involves distributing the blockchain’s state (account balances, smart contract states, etc.) across multiple shards, reducing the storage and computational load on individual nodes.
- Transaction Sharding ensures that transactions are assigned to different shards based on predefined rules, enabling parallel processing and horizontal capacity scaling.
- Network Sharding splits the network's nodes into distinct groups, each responsible for a specific shard. This ensures efficient communication and coordination between nodes.

Source: MultiversX
Adaptive state sharding also allows for dynamic shard resizing, which lets the network adjust the number of shards automatically based on demand. This enables the protocol to scale horizontally, adjusting throughput to meet demand. This feature ensures the system maintains high performance even during fluctuating network activity. Currently, one shard can process up to 10,000 transactions per second (TPS). The network can expand through horizontal scaling to support additional activity far surpassing legacy blockchain networks.
MultiversX shuffles the nodes between shards at the end of each epoch to reduce the risk of collusion or targeted attacks on specific nodes. This process ensures that validators cannot predict or manipulate which shard they will be assigned. Node shuffling occurs regularly, making the system more resilient to attacks and improving overall security. The nodes are chosen to be shuffled at random, which adds to the integrity of the selection and redistribution process.
Secure Proof-of-Stake (SPoS)Building upon traditional Proof-of-Stake (PoS) models, Secure Proof-of-Stake (SPoS) selects validators in a highly secure and decentralized manner, ensuring fast consensus and block finality. Key features of SPoS include:
- Improved Validator Selection Process: Similar to conventional PoS, SPoS randomly selects a subset of validators for each shard at the beginning of each round. In addition to the stake factor generally used in PoS architectures as a sole decision input, MultiversX includes an additional weight factor called rating. The node’s probability of being selected in the consensus group considers both stake and rating, adding another layer of security by promoting meritocracy.
- Low Latency Block Finality: SPoS achieves fast block times with minimal latency — currently around six seconds per block. For comparison, the average block time for Ethereum PoS is around 12 seconds. MultiversX hopes to achieve sub-second finality through several design upgrades on its roadmap, with testing measuring 600ms in 99.9% of instances.
- Stake-Based Incentives: Similar to PoS, validators are required to stake tokens to participate in consensus. Rewards are provided for honest behavior, and penalties (slashing) are issued for malicious activity. This economic incentive aligns validators' interests with the security of the network.
Through adaptive state sharding and SPoS, MultiversX can maintain decentralization without compromising scalability or speed, making it a competitive option across Layer-1s.
MultiversX WASM Virtual MachineMultiversX’s technology stack also features a WebAssembly (WASM) Virtual Machine (VM), a specialized environment designed for executing smart contracts. WebAssembly has a flexible, high-performing, and developer-friendly design, addressing several pain points faced by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Key aspects of the MultiversX WASM VM (SpaceVM) include:
- Multi-language Support: Unlike Ethereum’s EVM, which primarily supports Solidity, SpaceVM supports smart contract development in multiple programming languages, including Rust, C/C++, and others.
- Improved Performance: The SpaceVM is designed to offer superior performance, executing smart contracts faster and more efficiently than many traditional virtual machines. WASM’s near-native execution is possible using Wasmer, an execution engine that allows programs written in WASM to run on any device.
- Stateless Design: SpaceVM is stateless, meaning it doesn’t retain previous states. Each time the VM executes a smart contract, it does so without remembering any past data, relying solely on the input provided during that execution. This reduces potential attack vectors.
- Asynchronous calls between contracts: Due to adaptive state sharding, a smart contract may be called another smart contract stored by a different shard. Smart contracts on MultiversX can communicate using asynchronous calls to address this, allowing seamless interaction across shards. When contracts are on the same shard, they execute instantly (synchronously). If they’re in different shards, the system automatically handles the switch to asynchronous mode, sending the call to the correct shard, executing it, and returning the result.
In 2024, MultiversX implemented two major network upgrades — Vega and Spica. The Vega upgrade, which had 33.7% network participation, introduced Staking V4, making it easier for validators to join the network by eliminating the staking queue. Additionally, Vega included a dynamic slot auction mechanism and a chain simulator for isolated testing and development.

Source: MultiversX
The Spica upgrade, which had 27.9% network participation, focused on enabling cost-effective relayed transactions and improving ESDTs (enabling dynamic NFTs and multi-ESDT transfers). It also introduced new crypto VM endpoints and simplified onchain access with passkeys. These upgrades have collectively contributed to a more efficient and developer-friendly ecosystem.
User SafetyGuardians is an onchain two-factor authentication (2FA) standard introduced in 2023 to combat crypto scams and protect compromised wallets. It requires an additional signing layer for transactions and lets users set up popular 2FA methods, such as authenticator apps, to help secure their accounts.
Enabling 2FA costs a one-time fee of $0.02, and no guarded wallets have reported a compromise. Approximately 20% of accounts have opted to use Guardians.
ESDT StandardThe MultiversX network natively supports the issuance of custom tokens, unlike Ethereum, which uses the ERC-20 token standard. In other words, a token issued on MultiversX does not need a dedicated smart contract, and as a result, token transactions do not require the Virtual Machine. Instead, transaction logic is handled at the core level without executing code on a separate VM, allowing for faster transactions and removing smart contract risk for the user.
The eStandard Digital Token (ESDT) is MultiversX's standard for managing fungible, semi-fungible, and non-fungible tokens at the protocol level. ESDTs can be issued, owned, and held by any account on the MultiversX network.
Sovereign Chains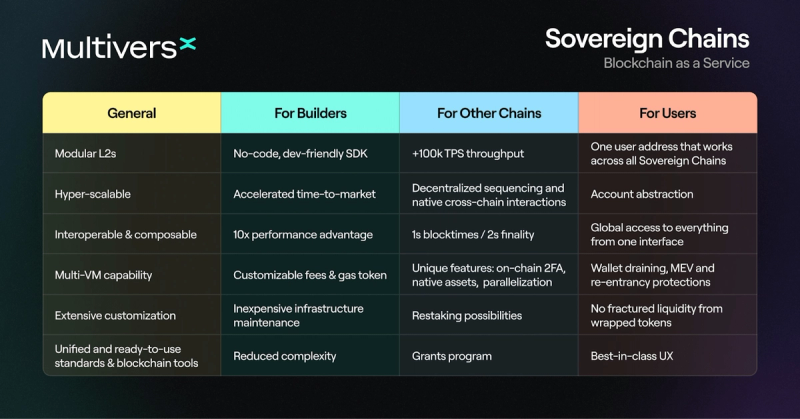
Source: MultiversX
In Q2 2024, MultiversX introduced the Sovereign Chains SDK, enabling developers to launch custom L2 or appchains interoperable with the MultiversX ecosystem. Currently, Sovereign Chains support Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, and Move-based chains, with more coming. MultiversX aims to redefine itself as an L0 interoperability layer for large blockchains while keeping the mainnet and current smart contracts live.
Sovereign Chains inherit SPoS consensus from the main chain. They benefit from the security and economic trust of the main chain and easier bootstrapping for validation. A minimum of 1,000 EGLD must be staked to launch a sovereign chain. Each validator node requires a stake of 100 EGLD, with a minimum of 20 nodes needed. Validators will use EGLD as gas, which helps maintain the connection to the main chain.
Sovereign Chains can design their own tokenomics that align with their specific needs. While this offers more potential for customization, independence, and innovation, Sovereign Chains must rely on their own set of validators and stakes for security. Sovereign Chains can participate in MultiversX’s dual staking system to aid in bootstrapping security. Dual staking increases network security for the sovereign chain, providing additional yield/incentives for all contributing users.
Several other blockchains offer similar interoperability structures. Avalanche allows developers to create application-specific L1 blockchains, known as Avalanche L1s, that operate independently from the main network. Each Avalanche L1 must secure itself independently, which can be challenging and costly for smaller networks. Polkadot’s parachain architecture connects independent blockchains to a central relay chain, which secures the network and facilitates interoperability. However, the scalability of parachains is limited by the relay chain's capacity. Additionally, L2s like Optimism, Polygon, and Arbitrum all offer interchain optionality with varying tradeoffs and benefits.
MultiversX’s Sovereign Chains stand out for their horizontal scaling and frictionless experience, although the chain abstracts the complex sharding technology for users. For instance, users can conduct transactions across chains without specifying shards. Moreover, these chains benefit from shared security, allowing them to maintain their own token incentives while leveraging the main chain for quicker bootstrapping.
Tokenomics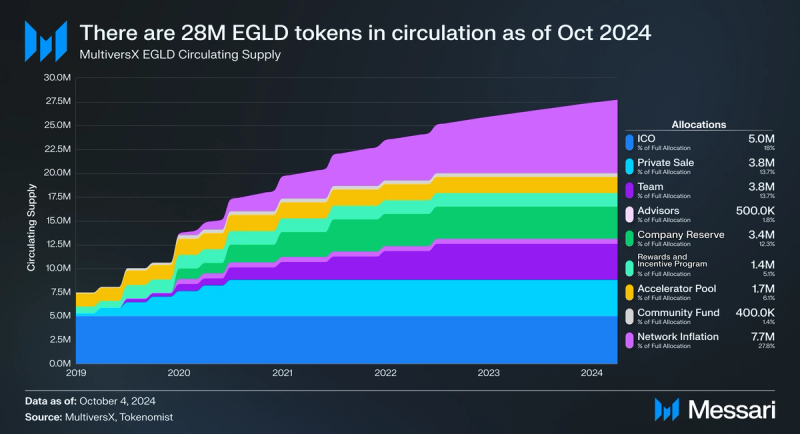
MultiversX's tokenomics is designed to support the ecosystem’s functionality and incentivize active participation from all stakeholders. The MultiversX blockchain economy is designed around eGold (EGLD), which is critical in securing the network, facilitating transactions, and enabling governance. The distribution of EGLD did not change when the company rebranded from Elrond to MultiversX.
For the initial distribution, 20 million EGLD tokens were allocated across eight different areas:
- 5.0 million EGLD (17.3% of the supply) was allocated to the ICO, which took place on July 1, 2019. The ICO was available to eligible users through the Binance Launchpad. At the time, this was equivalent to $3.25 million.
- 3.8 million EGLD (19%) was allocated in a private sale. The company raised $1.9 million in a private investment round. Tokens reserved for the private sale were fully vested by January 2021.
- 3.8 million EGLD (19%) was allocated to the team. Tokens reserved for the team were fully vested by January 2023.
- 0.5 million EGLD (2.5%) was allocated to advisors. Tokens reserved for advisors were fully vested by July 2020.
- 3.4 million EGLD (17%) was allocated to the Company Reserve (Treasury). Tokens reserved for the treasury were fully vested by January 2022.
- 1.4 million EGLD (7%) was allocated to the Rewards and Incentive Program. Tokens reserved for the program were fully vested by January 2020.
- 1.7 million EGLD (8.5%) was allocated to a pool, specifically Marketing, Grants, and an Accelerator. Tokens reserved for the pool were fully vested by July 2020.
- 0.4 million EGLD (2%) was allocated to a Community Fund. Tokens reserved for the fund were fully vested by July 2020.
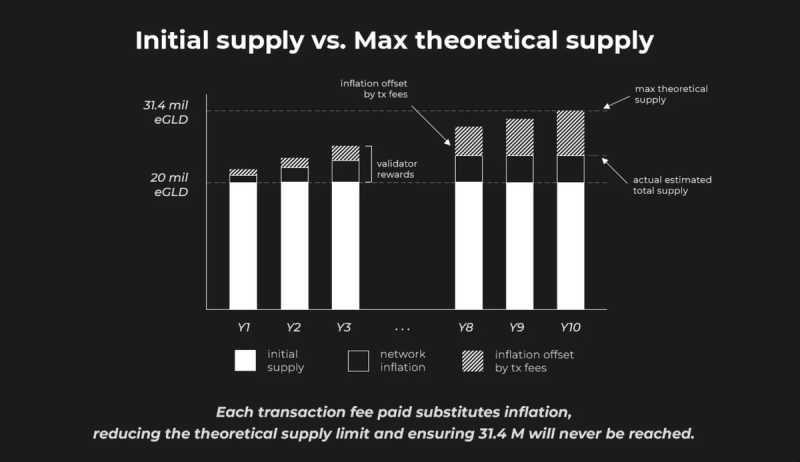
Source: MultiversX Docs
The remaining tokens enter through inflation that lasts 10 years following the initial bootstrapping phase. The max theoretical supply is 31.4 million EGLD, and the network offsets any remaining tokens entering through inflation with the total transaction fees collected. For example, if the scheduled inflation for a given year is 100,000 EGLD, and the transaction fees collected during that year amount to 75,000 EGLD, only 25,000 new EGLD tokens will be created and added to the circulating supply. The token offset differs from a burn mechanism since tokens removed from scheduled inflation were never created; they were just scheduled to be created. This mechanism increases token scarcity as adoption grows, strengthening incentives for validators and stakers.
Of all tokens that enter due to inflation, 90% go to validators and delegators, and 10% go to the treasury.
Economic Sustainability and Incentives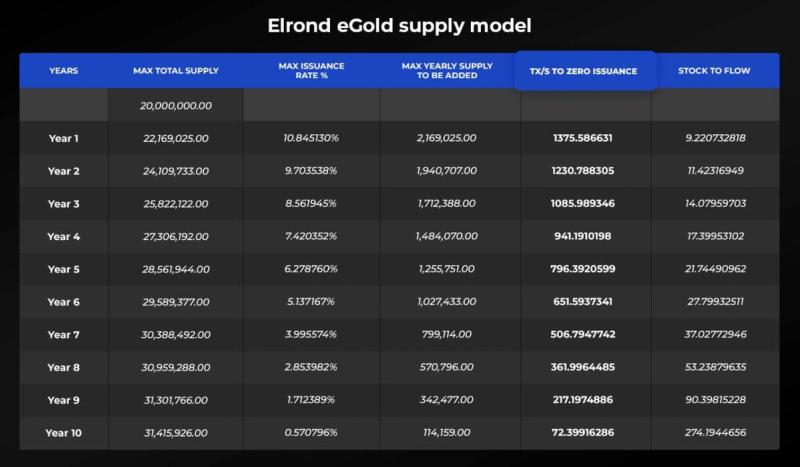
Source: MultiversX Economics Paper
The team designed MultiversX's tokenomics to ensure long-term sustainability by balancing rewards with responsible token supply management. MultiversX has a gradually decreasing inflation. The numbers in the "TX/S to zero issuance" column represent the transaction throughput necessary to replace the need for new token issuance (inflation) with transaction fees, allowing the system to continue rewarding participants without further inflating the supply.
“Stock to flow” refers to how scarce the supply of EGLD becomes over time as new issuance decreases. A higher stock-to-flow ratio indicates greater scarcity, as the flow (new issuance) represents a smaller fraction of the total stock (existing supply).
Governance and Decision-MakingEGLD holders participate in the onchain governance of the MultiversX network. Governance activities include proposing and voting on key protocol changes that shape the future direction of the ecosystem. By staking their tokens, holders gain voting power, ensuring that those with a vested interest in the network's success are involved in decision-making processes. This governance model aims to be transparent and community-driven.
State of MultiversXDespite a challenging market environment in 2024, MultiversX has made progress on several fronts:
DeFi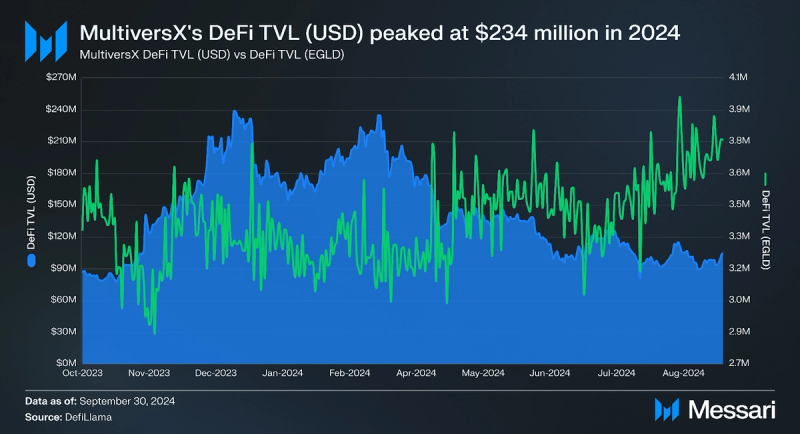
In 2024, DeFi TVL on MultiversX peaked at $234.9 million in 2024, ultimately ending Q3 at $163.6 million. xExchange, the top DEX on MultiversX, recorded $645.4 million in trading volume YTD. In Q3, MultiversX lagged behind some competitors like Avalanche ($260.8 million) and NEAR ($260.8 million) while outperforming others like Zilliqa ($1.6 million). Several dApps on MultiversX contributed to their TVL and DEX volume:
- xExchange was built by the MultiversX team and designed to be a fast, user-friendly experience. In 2023, xExchange introduced energy, an attribute that scales with the number of tokens time-locked on the DEX, entitling users to higher APRs. In Q3 2024, xExchange launched its V3 upgrade, including several user experience improvements tailored towards onboarding an audience of Web2 and Web3 users.
- Hatom, the leading lending protocol, recorded an all-time high TVL of $236.4 million in March. Hatom is non-custodial and aims to energize the MultiversX landscape through various products, including a newly developed liquid staking protocol and USH, a native overcollateralized stablecoin.
- xLaunchpad, managed by the MultiversX team, is a launchpad for new projects on MultiversX. It assists founders in community-building, raising funds, and developing new technologies. So far, xLaunchpad has raised over $13 million for seven startups.
- xPortal is a non-custodial crypto wallet and payments app built by the MultiversX team. The team has announced they’re planning the first fundraising round for xPortal.
- xMoney, a major MultiversX venture, is a crypto payments app enabling businesses to accept crypto or fiat at competitive rates. Users can invoice in crypto and receive fiat. Launched as UTRUST with token $UTK, it was acquired by MultiversX in 2022 and deployed as an ESDT. xMoney has served 302,000 users, supports payouts in 35 currencies, and operates carbon-neutrally. As part of Tether’s Plan B in Lugano, xMoney facilitates crypto payments throughout the city. In January 2024, Liechtenstein began accepting EGLD and other cryptocurrencies for state services through xMoney. Recently, the platform appointed new leadership and is finalizing an investment round for growth.
MultiversX natively supports NFTs by adding metadata and attributes to the fungible ESDT. New NFTs decreased by 47.6% YoY from 1.1 million to 0.6 million. Of these new NFTs, 3.8% were SFTs, with the rest being non-fungible. NFTs are primarily purchased on XOXNO, an NFT marketplace, launchpad, and ticketing platform.
RoadmapOver the past few years, MultiversX has sought to rebrand its image and reimagine how users and developers interact with its network.
While Elrond focused on developing the core technology, MultiversX 1.0 built a suite of internal products and tooling designed to shift focus towards consumer interests such as metaverse development. Experiments like xWorlds and xFabric were established for creators but ultimately did not find product-market fit. Other internal products like xExchange, xLaunchpad, xPortal, and xMoney were more successful and will receive more attention and funding for development from the team.
The vision for MultiversX remains the same; the future of the network lies in its ability to scale, develop new dApps, promote ecosystem growth, and capture market share. Achieving this relies on the following execution plan:
- Build a hyper-scalable blockchain network for mass adoption.
- Key drivers: Sub-second finality, Sovereign Chains, parallel execution.
- Build a powerful developer platform that enables anyone to build onchain.
- Key drivers: Simplify and refine developer tools, expand education resources, and boost dev/builder onboarding.
- Cultivate a vibrant ecosystem of apps, giving consumers and businesses a reason to be onchain.
- Key drivers: Performance-based incentive program, starter incentives, launchpad, and co-incubation program.
- Nurture deep capital markets through incentives, strategic interoperability, and native stablecoin integration.
- Key drivers: Incentive programs, strategic bridge integrations, and native stablecoin integration.
- Develop Maximum-impact marketing to drive awareness, user adoption, and capital inflows.
- Key drivers: Global awareness and brand amplification, strategic partnerships and influencer collaboration, community activation and viral growth, and business development catalyst.
The team released its official technical roadmap in early April. The team has split the roadmap into five key areas and highlighted updates for each:
- Core Network: Includes distributed transactional computation protocol updates, consensus, and performance. As of Q3, twenty tasks are done, nine are in progress (including updates from the Spica upgrade, such as EGLD multi-transfer and Relayed V3), and ten are upcoming.
- SpaceVM: Includes changes made to the MultiversX virtual machine, which is responsible for executing smart contracts. As of Q3, six tasks are done, two are in progress (restaking and timestamps as blockchain hooks), and three are upcoming.
- Developer UX: Includes developer tooling, testing frameworks, and SDKs. As of Q3, two tasks are done, nineteen are in progress (including an explorer for Sovereign Chains, a wallet for Sovereign Chains, and a Tag Builder), and six are upcoming.
- Sovereign Chains: This includes changes made to the Sovereign Chains SDK, which allows developers to create custom L2s connected to the global MultiversX network. As of Q3, ten tasks are done, eight are in progress (including an economics paper, a testing framework, and cross-chain mint and burn functionality), and three are upcoming.
- Interoperability: Includes efforts by MultiversX to connect to other blockchains. As of Q3, one task is done, two are in progress (technical support for EVM Compatible Sovereign Chains and Native IBC (Cosmos standard) Development), and six are upcoming.
MultiversX's technical roadmap intentionally leaves out abstraction because the team built the network with abstraction as a foundational concept. Since abstraction is inherent to sharding, it enables seamless interoperability between shards. MultiversX aims to offer a frictionless user experience. To achieve this, it has developed numerous in-house applications, including a DEX, wallet, exchange, content management system (CMS), and a digital payments network for merchants. It ensures a cohesive and integrated product evolution by embedding abstraction into the core vision rather than isolating it to specific upgrades.
Closing SummaryMultiversX has established itself as a scalable, developer-friendly L1 blockchain with its unique architecture and innovative features like adaptive state sharding and Secure Proof-of-Stake (SPoS). Its roadmap focuses on optimizing the core network, advancing the SpaceVM for better smart contract execution, improving developer UX, expanding Sovereign Chains for custom L2 solutions, and enhancing Interoperability with other blockchains.
MultiversX faces a saturated infrastructure market of L1s and L2s. The network’s success will come from its Sovereign Chains SDK, which gives developers an easy-to-build yet technologically advanced route to creating their own blockchain. MultiversX’s ability to capture new projects for Sovereign Chains will likely depend on the base layer’s ability to grow its ecosystem (xPortal, xExchange, Hatom, etc.). As MultiversX continues to develop, its success will hinge on executing this vision, building dApps, and expanding its ecosystem to drive adoption.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.