and the distribution of digital products.
State of Tezos Q3 2024
- Tezos saw a 46% increase in network activity, with 8.6 million transactions in Q3, as Layer-1 and Etherlink adoption drove a 192% increase in daily transactions across the ecosystem.
- Etherlink saw a 272% increase in fees collected, highlighting its rapid growth and adoption due to lower fees and faster transactions.
- The Etherlink ecosystem has 100+ projects developing on the network.
- ‘Q’ Upgrade Proposals: Two competing protocol upgrade proposals were announced in Q3. The Quebec proposal reduces block time to 8 seconds (16-second finality), improves the staking mechanism, and adjusts Adaptive Issuance. The Qena proposal is a clone of Quebec, but without the Adaptive Issuance adjustment.
- Manchester United, Rarible, oobit and Battlerise launched applications on Tezos and Etherlink. Manchester United launched Fantasy United, a fantasy football game utilizing digital trading cards of their players And continued with 'Devil Rewards' Manchester United’s results based reward campaign. Battlerise and Rarible launched their RPG game and NFT marketplace, respectively.
Tezos (XTZ) is a Liquid Proof-of-Stake (LPoS) blockchain network known for its strong focus on security, upgradeability, and democratic community governance. Its smart contracts on Layer-1 are implemented using the Michelson language, designed to facilitate formal verification while also offering Ethereum virtual machine (EVM)-compatibility through Etherlink, a community-supported Layer-2. The network features on-chain governance and self-amending functionality, enabling stakeholders to adopt protocol upgrades without requiring a network hard fork. Recent upgrades on Tezos have focused on scalability and performance through Smart Rollups and a Data Availability Layer (DAL). The Mumbai upgrade introduced Smart Rollups, a Layer-2 scaling solution that enables throughput beyond 1 million TPS and customization to adapt to specific use cases, such as implementing new coding environments. The Paris upgrade reduced Layer-1 block time from 15 to 10 seconds, bringing 20-second finality. It also introduced the DAL, a data-availability solution that boosts Smart Rollup scalability and is part of the Tezos protocol. Finally, the Paris upgrade implemented a new staking mechanism and Adaptive Issuance, which adjusts token issuance based on the staked ratio of XTZ. In Q3, developer teams Nomadic Labs, Trilitech, and Functori proposed the Quebec upgrade, aiming to reduce block time to 8 seconds, enhance staking, and adjust Adaptive Issuance to curb inflation. TezCapital also proposed Qena, identical to Quebec but without the Adaptive Issuance adjustment. By the end of Q3, Qena was selected for exploration via on-chain governance. In Q2, Tezos launched Tezos X, a proposed roadmap for boosting the blockchain’s performance, composability, and interoperability, with the goal of delivering a "cloud-like" developer experience. Leveraging Smart Rollup technology and the data-availability layer, it enables developers to build complex, scalable applications using mainstream programming languages, with improved connectivity across the ecosystem.
Website / X (Twitter) / Discord
Key Metrics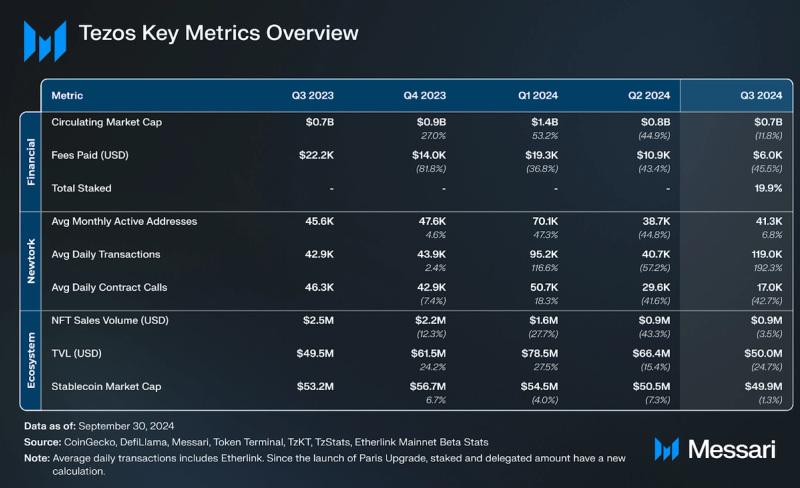 Financial Overview
Financial Overview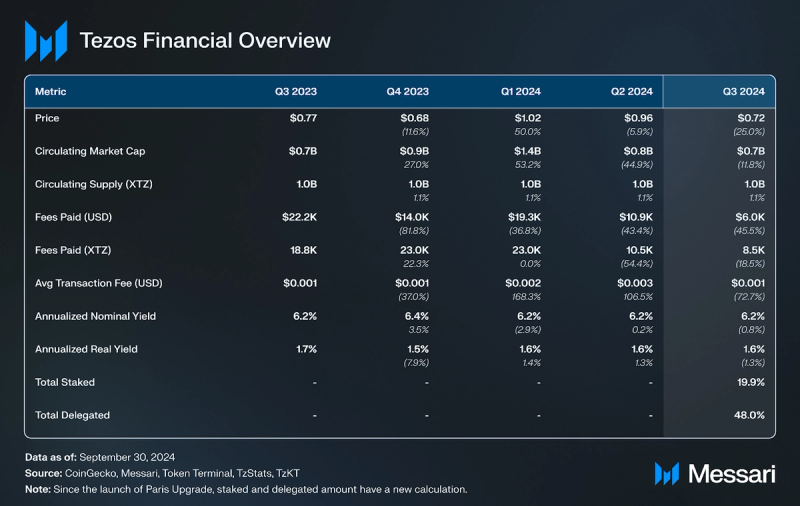 Revenue
Revenue 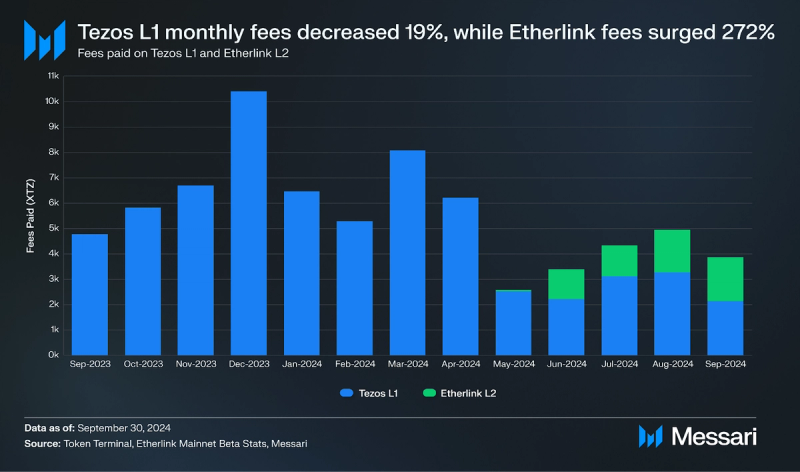
In Q3 2024, Tezos L1 transaction fees dropped to 8,500 XTZ ($6,000), a 45% (19% )QoQ decline, while Etherlink saw a 272% surge, totaling 4,617 XTZ ($3,300). The drop in L1 fees may be driven by the introduction of Smart Rollups, particularly the launch of Etherlink Mainnet Beta, Tezos' first EVM-compatible non-custodial Smart Rollup, which shifted activity to the more cost-efficient Layer-2, reducing overall L1 fees.
Supply and Market CapitalizationNative token, XTZ is used as a medium of exchange and for staking, delegating, and facilitating governance. As of the end of Q3, the circulating supply was 1.0 billion XTZ. The Mumbai upgrade adjusted the block time to 15 seconds and reduced block rewards to 20 XTZ to maintain the annual inflation rate. The Paris upgrade introduced Adaptive Issuance, a dynamic mechanism that adjusts staking rewards to maintain network security with minimal inflation and further reduced block time to 10 seconds. This system targets a 50% staking ratio of the total Tezos supply, adjusting rewards to encourage more or less staking as needed, thereby reducing inefficiencies and aligning Tezos with real-world use cases. The annualized real yield for validators remained at 1.6%, with a QoQ increase of 0.5%.
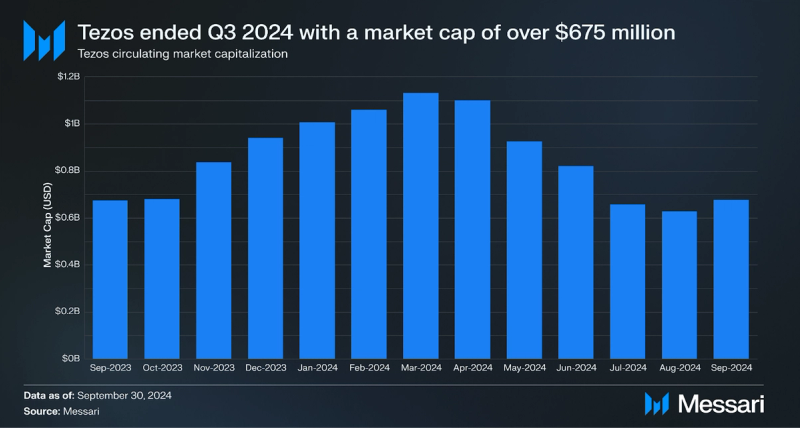
Tezos' market cap dropped to $675 million, down 4.7%, due to the lower value of XTZ to USD and reflecting the broader cooling in the crypto market during Q3.
Network Overview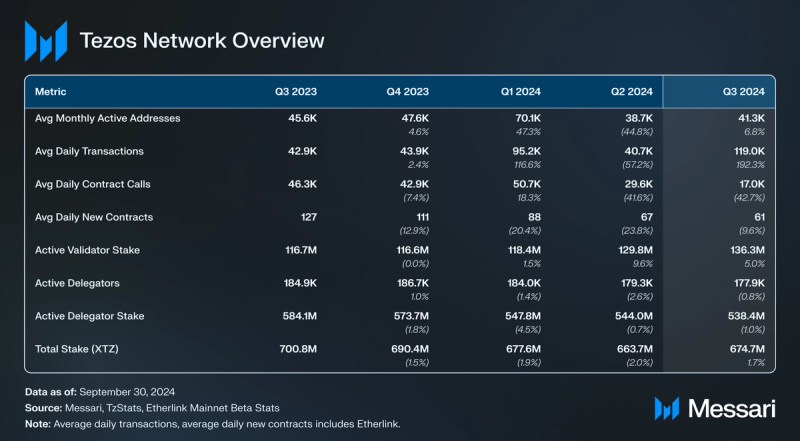 Usage
Usage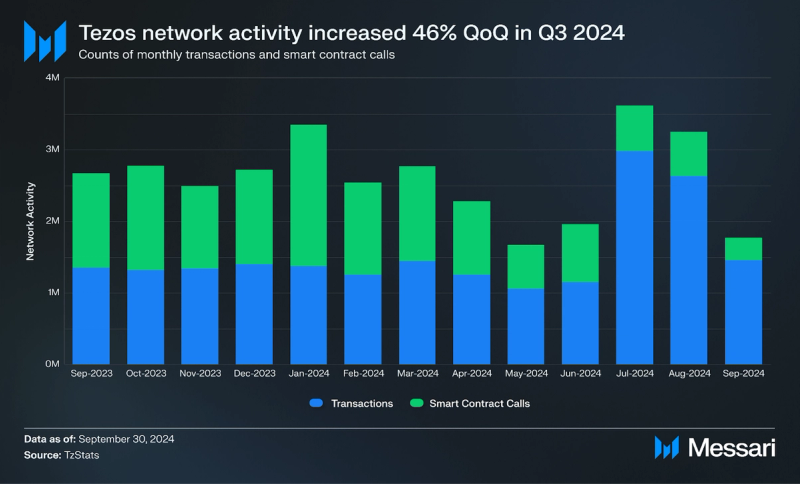
In Q3 2024, overall network activity on Tezos increased by 46% QoQ, with average monthly transactions and contract calls reaching 2.9 million. This growth was fueled by a 104% QoQ rise in transactions, totaling 8.6 million over the quarter.
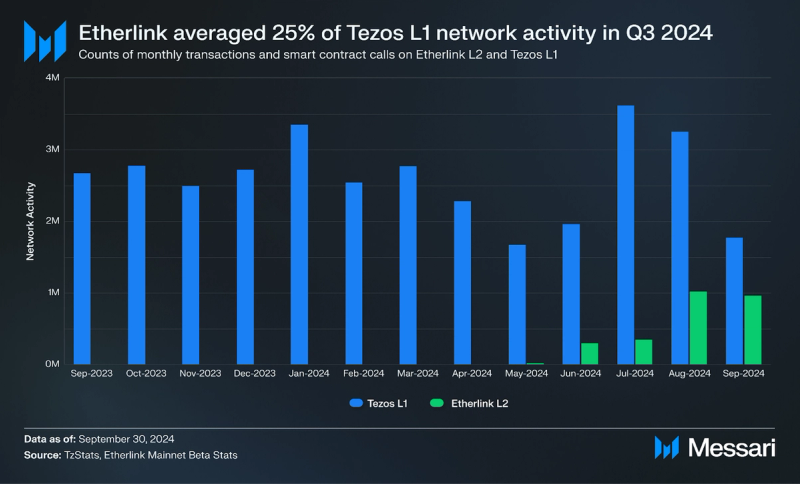
In Q3 2024, network activity on Etherlink averaged over 770,000 transactions per month, accounting for 25% of Tezos L1's activity, highlighting rapid growth in Etherlink's usage just months after its launch.
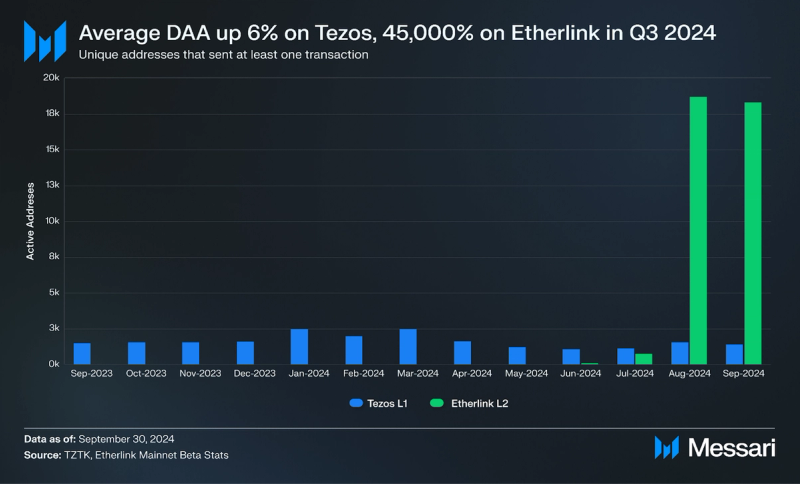
In Q3 2024, Tezos saw a 6% QoQ increase in daily active addresses (DAA), averaging 1,400, while Etherlink’s DAA surged by 45,000% to over 12,000. Since May 2024, Etherlink has over 100,000 unique wallets. Suggesting that faster transaction speeds and lower fees of the L2 is driving a shift in usage from Tezos L1 to Etherlink.
Network UpgradesSmart RollupsThe Q1 2023 Mumbai upgrade introduced Smart Rollups, enabling development of rollups using any programming language that can be compiled into WebAssembly (WASM), such as Rust, C/C++, and Go. Etherlink, an EVM-compatible non-custodial Smart Rollup, is one example of how it has enabled developers to build on Tezos using new programming languages and virtual machines.The Q2 2023 Nairobi upgrade expanded the capabilities of Smart Rollups, such as internal Layer-2 messages allowing it to sync with Tezos protocol upgrades. The Q1 2024 Oxford 2 upgrade introduced Private Rollups, which allow developers to choose between public and permissioned L2s.
On June 4, 2024, the Paris protocol upgrade was activated, marking the 16th major enhancement to the Tezos blockchain. This upgrade introduced key improvements, including reducing block times to 10 seconds and implementing the Data Availability Layer (DAL) on the mainnet to boost throughput for Smart Rollups. It also refined Tezos' Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism to achieve stronger network security while keeping XTZ inflation at a minimum.
Jstz: Java Script RollupIn July 2024, Tezos developer Trilitech introduced Jstz, an early-stage Smart Rollup that enables developers to build and deploy smart contracts using JavaScript, the world’s most widely used programming language. Jstz provides a familiar Web2 development experience by supporting JavaScript standards, enabling developers to leverage the vast ecosystem of tools and libraries they already use, like npm. Unlike many blockchain platforms that require developers to learn new languages, Jstz enables developers to use the same JavaScript environments they are accustomed to, such as server-side JavaScript runtimes like Deno and Cloudflare Workers. Development of Jstz is underway with the first release expected in the coming months.
By offering a Web2-like development experience while incorporating Web3 features such as smart contracts, identity, wallets, and payments, Jstz aims to bridge the gap between traditional web development and blockchain technology. This will be the second L2 rollup and a significant step toward Tezos' larger vision for Tezos X, creating a cloud-like, blockchain-based backend for various applications.
‘Q’ Upgrade ProposalsSeptember 2024 saw the announcement of two competing ‘Q’ protocol upgrade proposals.
The Quebec protocol upgrade proposal was announced first, by developer teams Nomadic Labs, Trilitech, and Functori. Quebec contains a reduction of block time from 10 to 8 seconds, enhancing Layer-1 transaction finality (to 16 seconds) and improving the overall user experience with faster transaction speeds. Quebec also contains the Adaptive Maximum, a new component of the Adaptive Issuance mechanism which aims to better balance network security with minimal inflation. The Adaptive Maximum prevents scenarios where issuance could become high despite the staking ratio being close to the target.
Quebec also modifies how a baker's minimal delegated balance is computed, resolving an issue with delegation rights assignment introduced in the Paris upgrade. Finally, Quebec reduces the weight of delegated funds in baking power calculations to promote more active staking and decentralization.
Shortly after Quebec’s announcement, an alternative proposal, Qena, was announced by developer team TezCapital. Qena is a clone of Quebec, but without the Adaptive Maximum feature. By the end of Q3, the Qena proposal was selected by the Tezos community as the proposal to move forward for exploration.
Development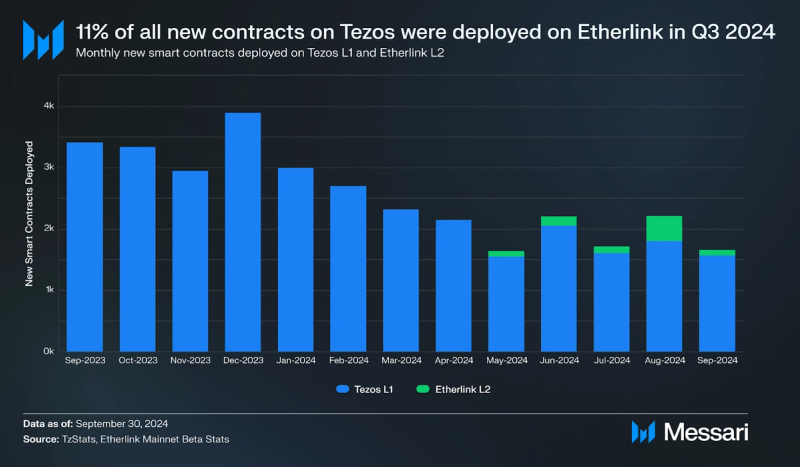
In Q3 2024, nearly 5,000 contracts were deployed on Tezos L1, reflecting a 14% QoQ decrease. Meanwhile, over 600 new contracts were deployed on Etherlink, representing 11% of all contracts in the Tezos ecosystem, indicating a shift by developers toward moving user application development from L1 to L2.
Tezos XTezos X is a proposed roadmap for combining the best characteristics of modular and monolithic blockchains into a unified “modu-lithic” design for Tezos. Introduced at TezDev 2024, Tezos X is meant to enhance the blockchain's utility and competitiveness within three key areas: performance, interoperability, and composability.
For performance, the goal is sub-second latency and a throughput of 1 million TPS or more.
Interoperability involves adding more programming environments and enabling Tezos to connect with other blockchains and non-blockchain systems. This "plug'n'play" approach allows developers to use their preferred languages and tools to build applications, and to let them interact with different platforms and systems.
Composability is about enabling applications to interact across environments — in other words, a smart contract written in Solidity can interact with one written in Python and pass results to another in JavaScript, all within the same transaction in the same rollup.
Key to enabling these improvements is the canonical rollup. Based on Smart Rollup technology, the canonical rollup is designed for high scalability while supporting multiple execution environments in parallel. The DAL provides the necessary network bandwidth for the increased transaction data, while preserving verifiability through integration with Tezos’ layer 1.
Secret Builders’ Program
The Secret Network launched its first Secret Builders' Program in collaboration with Etherlink. This program is designed to support startups and Web2 businesses looking to integrate decentralized confidential computing (DeCC) into their decentralized applications (dApps). The program offers financial modeling, developer support, and mentoring to help participants incorporate privacy-focused features, leveraging both the Secret and Etherlink ecosystems. Five selected startups will participate in this program, which includes grant opportunities and technical planning assistance. To date 35+ startups have submitted applications.
Additional DevelopmentsSelect development updates from Q3 include:
- TezDev 2024: The largest Tezos developer conference, took place in Brussels, Belgium, in July. The one-day event featured over 15 industry-leading speakers and showcased 20+ projects building on Tezos.
- Magic Labs: Magic SDK provides streamlined tools for integrating applications onto blockchains. In Q3, it surpassed 50,000 npm downloads for Tezos, with Etherlink becoming the second most visited developer documentation.
- Cube3: Web3 incubator and accelerator announced a partnership with Nomadic labs to support developers building on Tezos.
- Tezos on AWS: At TezDev, Tezos demonstrated the ability to launch Tezos nodes using the AWS Cloud Blockchain Node Runner, simplifying node deployment and management on the cloud.
- The Rollup Day: Hosted by Zeeve RaaS (rollups as a service) featured talks from Tezos , Arbitrum, Polygon Labs, and zkSync. Zeeve currently supports smart rollups on Tezos.
- Tezos Realm: Hosted by TZ APAC at Token2049, showcased 15 projects building on Tezos and Etherlink. Among them were several supported by the Fortify Labs accelerator, including akSwap, Ladder, OnChainVision Labs, Questflow, Renora, TaskOn, and YourD.
- Oobit: The payment platform went live on Tezos allowing users globally to pay via Mastercard, Visa, ApplePay and GooglePlay.
Grant Programs and Investments: The Tezos Foundation supported various development projects, including infrastructure and tooling enhancements. Some investments from Q3 include:
- The Graph: A decentralized indexing protocol that is building on Etherlink.
- Explorus: developer tool created by Functori that offers detailed insights into the Tezos blockchain.
- 3Route: A DEX-aggregator that optimizes liquidity across multiple Tezos DEXs and finds the best trade route for users.
- Subsquid: a decentralized data lake, adding support for their tools on Etherlink, including their Subquid SDK.
- Rarible: A leading decentralized NFT marketplace, currently live on Etherlink.
According to Electric Capital’s report, Tezos had 72 full-time developers and 228 monthly active developers on July 1, 2024.
Security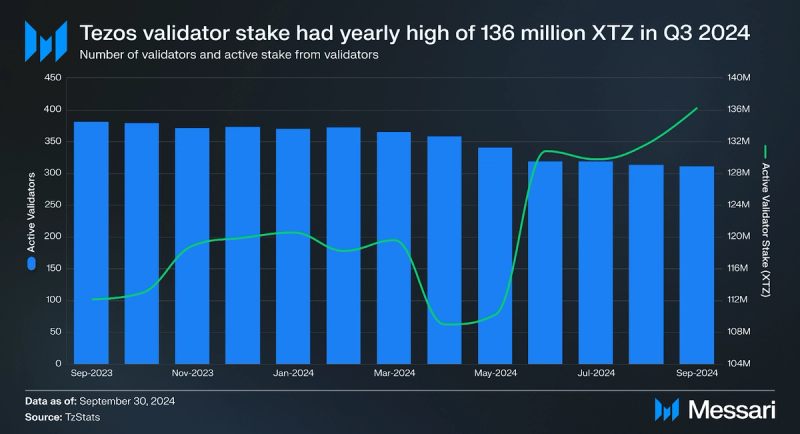
Tezos uses a Liquid Proof-of-Stake mechanism, which requires validators (known as “bakers” in the Tezos ecosystem) and delegators to stake XTZ as collateral to secure the network. Rewards and fees collected from transactions are paid to validators and delegators for maintaining the network. Active validators and active validator stake have remained consistent over the last three quarters. In Q3, active validators saw a 2% decrease, but active stake increased by 5%, QoQ. Active validator stake reached a yearly high of 136 million XTZ at the end of Q3.
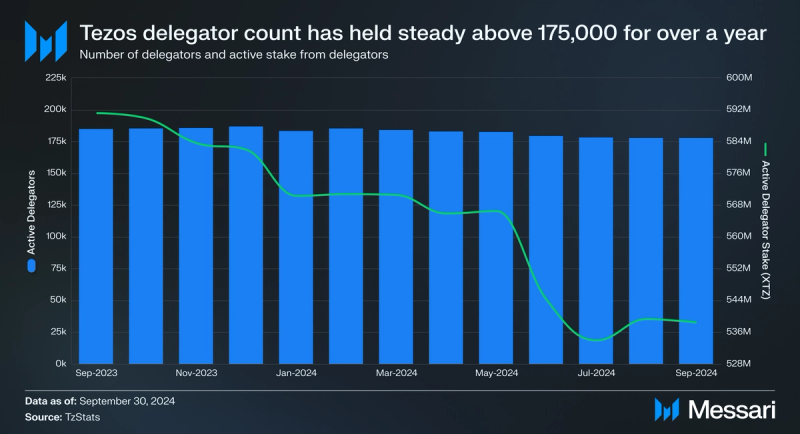
Delegators stake XTZ on active validators and receive a portion of fees and rewards collected. Active delegators and stake from delegators decreased in Q3, by 0.8% and 1% QoQ, respectively.
Adaptive Issuance dynamically adjusts the issuance of XTZ based on the proportion of staked tokens to the total supply. At the end of each blockchain cycle, the issuance rate is modified to target a protocol-defined staking level, currently set at 50%. This mechanism incentivizes staking to provide stable security for the network.
The Tezos network has shown consistent year-over-year stability in the number of validators and delegators, as well as in staked XTZ. This stability is crucial for secure and scalable Layer-2 growth. Validators in the ecosystem are also decentralized geographically and by host service providers, further ensuring the network's resilience and security.
GovernanceTezos utilizes a Liquid Proof-of-Stake mechanism, enabling staked XTZ to be used for both network security and governance. The network's self-amending blockchain reduces the need for hard forks by employing onchain governance for protocol upgrades. Users delegate their XTZ to validators who participate in stake-weighted voting. The governance process is divided into five periods, spanning approximately 2 months and 10 days.
To complement protocol governance, Tezos Commons established the Tezos Ecosystem DAO, which manages and allocates XTZ for community projects. The DAO’s initial funding came from NFT sales on Objkt and donations from ecosystem participants.
Etherlink follows an onchain governance model similar to Tezos Layer-1, ensuring fairness and transparency. Governance for Etherlink is self-amending (meaning no hard fork), controlled by Layer-1 bakers, and pilots both upgrades and the sequencer operator. The governance process fully happens on Tezos Layer-1 through dedicated smart contracts, and consists of three stages: a Proposal period, a Promotion period, and a Cooldown period. The Etherlink governance periods are synchronized with Layer-1 governance periods. The first upgrade for Etherlink was implemented successfully shortly after launch.
Ecosystem Overview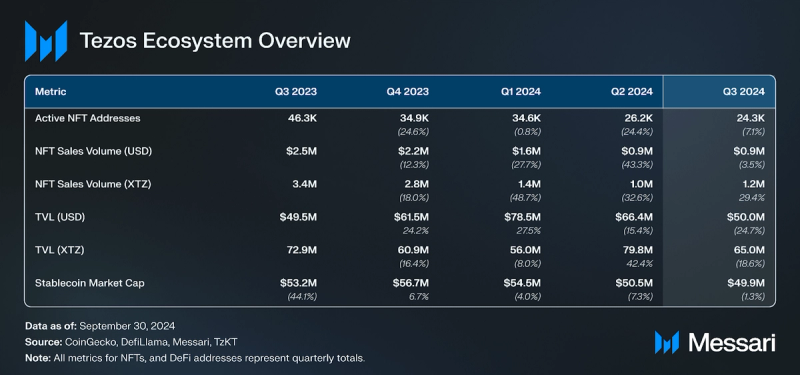 Etherlink Adoption
Etherlink AdoptionEtherlink, the first EVM-compatible non-custodial Smart Rollup on Tezos, entered mainnet beta in May 2024. It facilitates the deployment of EVM-based contracts on Tezos and offers full compatibility with the Ethereum ecosystem (e.g., MetaMask wallet connectivity). In addition, it features low fees, low latency, and increased security with permissionless fraud proofs.
Following the launch, developers have begun building within the EVM environment, integrating their applications into the broader Tezos ecosystem. The Etherlink ecosystem currently has 100+ projects developing on the network. Q3 saw the development of various applications on Etherlink, including:
- Rarible: A decentralized NFT marketplace is currently live on Etherlink. Collections on Etherlink are currently live.
- Sugarverse: Mobile gaming developer and pioneer in Play & Earn game space is developing on Etherlink.
- Battlerise: An epic turn-based RPG launched the first gaming NFT on Etherlink.
- DappRadar: Data platform for decentralized applications announced support for Etherlink developers.
- Superlend: A decentralized lending and borrowing platform, launched on Etherlink. The protocol emerged from the Defi Catalyst Accelerator (DCA).
- Pimlico: A leading account abstraction infrastructure platform integrated with Etherlink with all the smart account standards.
- Altme Wallet: A decentralized identity and verifiable credentials platform integrated with Etherlink.
- Etherlink Ecosystem Rally: A four week event was held in Q3 educating users on DeFi, memecoins and real-world assets built on Etherlink.
- UHT: The web3 arm of GoQii successfully tested pilot application, Universal Health Token (xUHT), on Etherlink with >60,000 users on-chain
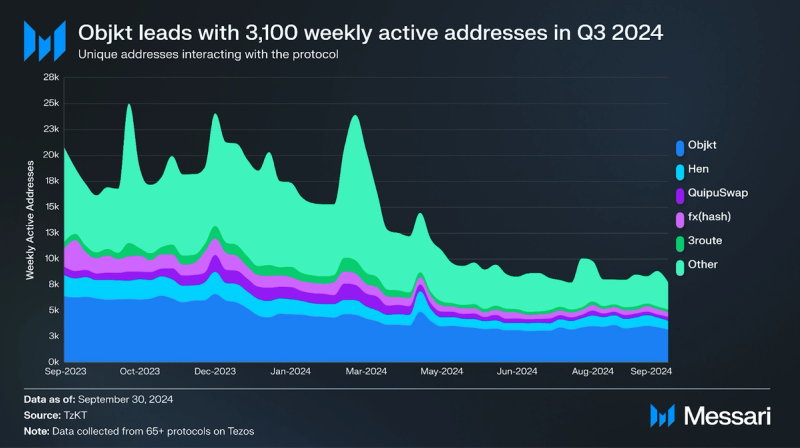
In Q3 2024, Objkt dominated the Tezos NFT market with an average of 3,100 weekly active addresses, capturing 41% of the user market share. NFT sales dropped 3.5% QoQ to $881,000, and unique active users declined 7.1% to 24,000. As NFT platforms like Rarible, launched on Etherlink in September 2024, many NFT transactions may shift to Layer-2 solutions which is set to open the door to more collectible projects.
Development in the NFT ecosystem remained strong in Q3:
- NFTimbre 2.2: Launched by La Poste Groupe, France’s national postal service, is the second collection of stamps paired with twin NFTs on Tezos. La Poste has minted over 1 million NFTs on Tezos since 2023.
- Objkt Galleries: Objkt announced the upcoming cohort of partners launching Objkt galleries in the coming months including Artverse, Office Impart, Expanded Art and Galerie Data. The galleries tool allows partners to organize and curate their own selling exhibitions via an online gallery space hosted on Objkt.
- Bandog: A data analytics tool specifically designed for Artists and collectors on Tezos shared their network feature which enables users to visually map out sales or purchases network in an engaging manner.
- Community Curation: The Tezos Foundation and the Museum of the Moving Image launched “Community Curation”, the second project in a 12-month partnership. The project decentralized curation by inviting 10 advocates to select 10 artists, with the final 3 artists selected by public voting.
- Serpentine x The Art Newspaper x Tezos: Serpentine, The Art Newspaper, and Trilitech hosted an event for Judy Chicago’s “What if Women Ruled the World?” exhibition, featuring the option to mint a proof of participation token on Tezos. The event included an introduction by Hans Ulrich Obrist and a panel with The Art Newspaper's Louis Jebb, Serpentine's Chris Bayley and Kay Watson, and Trilitech's Aleksandra Artamonovskaja.
- Evening of Digital Art: Trilitech hosted an evening of digital art during London Web3 week, featuring art displays and a series of talks.
- ENTANGLED: THE EXHIBITION: Fxhash organised an exhibition at the Wintercircus in Ghent, dedicated to Bjorn Staal’s Entangled artwork. The exhibition included a series of public talks including an introduction to the Tezos blockchain and advice for building a career as a digital artist.
- Curation of Art on Tezos at Subjective Arts Festival: Victoria West curated 21 artists for The Subjective Arts Festival at Lume Studios NYC
- Agoria at Tezos Realm: Agoria performed at TzAPAC’s Tezos Realm event during Token2049 and released a surprise open-edition mint on Objkt.
- Generative Art on Objkt: Andreas Rau’s “Stairs and Stocks" was the second curated project to go live on Objkt’s generative art engine. Curated by Fakewhale, the collection sold over 300 editions for a total volume of 7.6k tez.
- Objkt in Asia: Objkt announced their role as platform partner for dialog(), a generative art exhibition that connects Tokyo, Taipei, Seoul and Beijing.
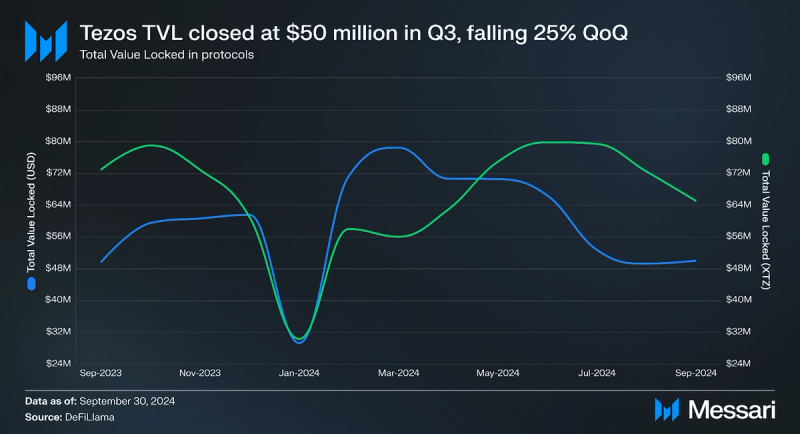
Total value locked (TVL) in USD fell by 25% QoQ in Q3 2024, closing at $50 million. This decline was driven by the drop in XTZ's price, since TVL in XTZ decreased by 19% QoQ. Etherlink has over $750,000 in TVL, growing from $10,000 in early Q3. This indicates the decrease of TVL on Tezos due to a combination of decrease in asset value, and movement of liquidity from Tezos to Etherlink, which allows users to take advantage of lower fees and faster transactions.
Most TVL in crypto exists on EVM-compatible networks. The launch of Etherlink gives developers the ability to deploy EVM-compatible protocols on Tezos, attracting new communities to the ecosystem. Etherlink’s launch expands Tezos' reach by drawing users and builders from other EVM networks, increasing its presence in the DeFi space. In Q3, over $500k in assets were bridged from other EVM chains.
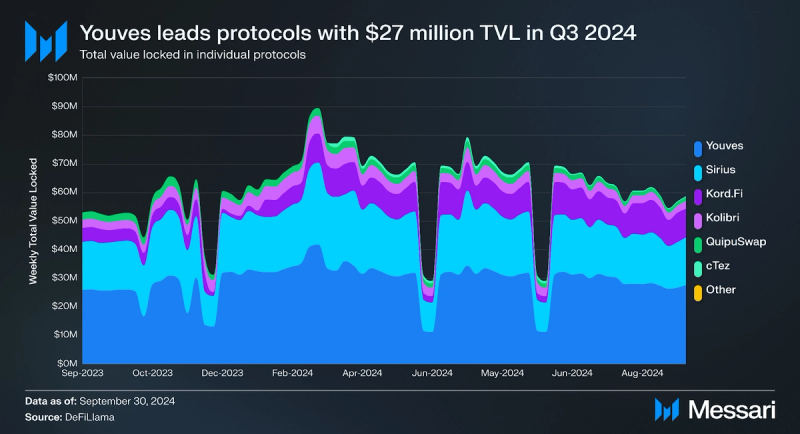
Youves, a decentralized synthetic assets application, is the largest protocol by TVL, securing $27 million in assets. Sirius, a liquidity-baking protocol for XTZ/tzBTC pools, had the second-largest TVL at over $16 million. Kord.Fi, another liquidity-baking protocol for XTZ-tzBTC, had the third-largest TVL with over $10 million. With the capital efficiency improvements in tzBTC 2.0, these liquidity-baking protocols may provide additional incentives and thus increase their TVL.
The largest protocol on Etherlink is IguanaDEX, a concentrated liquidity decentralized exchange with over $750,000 TVL and $1 million in volume. Memecoin launchpad, OrganicGrowth has accumulated over $75,000 in TVL since launch in Q3, indicating a rapidly growing memecoin economy.
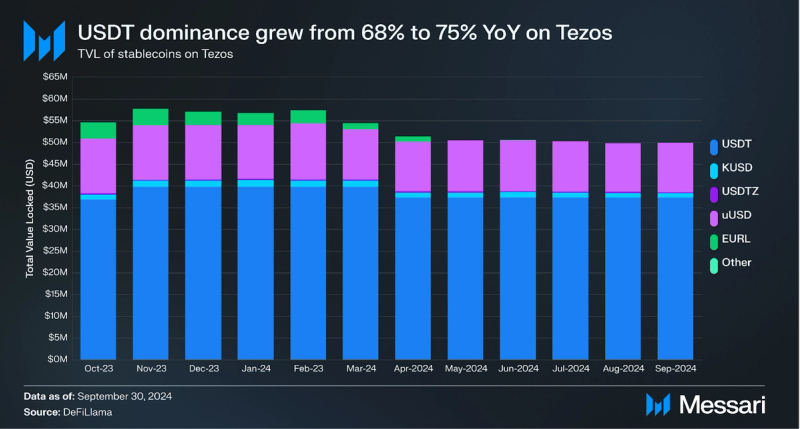
Tether’s USDT increased its dominance in the stablecoin market YoY, going from 68% to 75% of the total stablecoin supply. Tether had over $37 million in USDT issued on Tezos by the end of Q3. The largest stablecoins exclusively issued on Tezos were Kolibri’s kUSD and USDTez’s USDtz, which had over $1 million and over $270,000 in stablecoins issued, respectively. In September 2024, VNX, a leading European tokenization platform, launched VNX EUR (VEUR) and VNX CHF (VCHF) stablecoins on Tezos.
GamingQ3 2024 saw substantial progress in gaming protocols on Tezos. With Tezos X targeting 1 million transactions per second on Layer-2 and providing composable development environments, gaming developers have shown growing interest in launching their projects on the platform. Key gaming developments in Q3 include:
- Manchester United: The English Premier League football club launched Fantasy United, a fantasy football game built on Tezos, allowing users to collect unique trading cards, build squads, and earn points.
- BlockGames: Partnered with Tezos to integrate mobile games into the BlockGames ecosystem.
- TapNation: A leading publisher with over 1 billion downloads, launched Athletic Rush, in collaboration with Gaming Vertical.
As Tezos continues to evolve, several key initiatives are shaping the future of its ecosystem. Here are the major upcoming developments:
- Etherlink Development: Etherlink technical roadmap will be released in Q4 2024.
- JavaScript Rollup: Jstz, a Smart Rollup, will enable developers to build and deploy JavaScript-based smart contracts on Tezos. The first JavaScript applications are expected to launch, broadening Tezos' developer base by tapping into the vast JavaScript ecosystem.
- Tezos X Roadmap:
- 2025: Integration with the Data Availability Layer (DAL), enabling high-throughput communication between Etherlink rollups and the main sequencer, further scaling applications.
- 2025: Launch of Michelson Rollup, creating an execution environment compatible with Tezos Layer-1, with instant asset transfer to Etherlink.
- 2026: Introduction of Canonical Rollup, providing an integrated execution environment with instant cross-application transactions across different programming languages.
Q3 2024 was marked by continued innovation and significant developments across the Tezos ecosystem. The expansion of Etherlink, with a 272% surge in activity, indicates a growing shift toward Layer-2 solutions, offering users lower fees and faster transactions. The launch of Jstz, the JavaScript Rollup, signals Tezos’ commitment to expanding its developer base by tapping into the vast ecosystem of JavaScript tools, further positioning the network for widespread adoption.
Tezos maintained strong momentum in the NFTs and gaming sectors, with notable projects like Rarible, a leading decentralized NFT marketplace, launching on Etherlink, and Manchester United unveiling their Fantasy United game. These advancements underscore Tezos' expanding presence in these industries, as developers increasingly leverage the network’s scalability and cost efficiency.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.