and the distribution of digital products.
State of LayerZero Q4 2024
- The ZRO market cap increased by 9.7% QoQ to $556.3 million, supported by Sybil filtering during the token launch, which ensured airdrop recipients were more likely to be long-term holders.
- The average value transferred per message was $1,590 (up 598% YoY). Compared to pre-Sybil filtering levels, this reflected durable users conducting higher-value transactions.
- The first onchain fee switch referendum was held by LayerZero Foundation, though it fell short of a quorum. This marked a key step in LayerZero’s efforts to decentralize governance and incentivize ZRO holders.
- lzRead primitive was introduced, enabling omnichain applications to access and compute cross-chain and historical data, streamlining governance, DeFi, and other use cases.
- LayerZero expanded its network integrations to 120 supported blockchains, with applications like Pudgy Penguins ($PENGU), Ondo and PayPal USD leveraging omnichain standards like OFT for token distribution and interoperability.
Though blockchains are designed to be secure, facilitating safe communication between networks is challenging. LayerZero is an interoperability protocol that allows secure communication between 120 networks for omnichain applications, such as tokens.
It sends and receives messages via an immutable set of Endpoints, with verification and execution facilitated by a permissionless set of decentralized verifier networks (DVNs) and Executors. Executors carry out a message's instructions in the destination chain, while DVNs ensure the end-to-end validity of messages. The security stack, including executors and DVNs—along with block confirmations—can be configured by each independent application built on LayerZero, depending on the level of security required for sending and receiving messages.
LayerZero is a standardized communication protocol, allowing omnichain applications to communicate on distinct networks. Its primary use case is transferring arbitrary data between these networks, with asset transfer being the most popular type of data moved. Other use cases include any application that might need to send messages between multiple chains, including gaming, cross-chain governance, identity solutions, restaking, and enterprise products.
LayerZero Labs is the initial developer and core contributor to the LayerZero protocol. In April 2023, it raised a $120 million Series B. LayerZero V2 went live in January 2024, featuring a common messaging system and common security properties to simplify cross-network communication and improve the developer experience. LayerZero launched its native token, ZRO, in June 2024. For a full primer on LayerZero, refer to our Initiation of Coverage.
Website / X (Twitter) / Discord
Key Metrics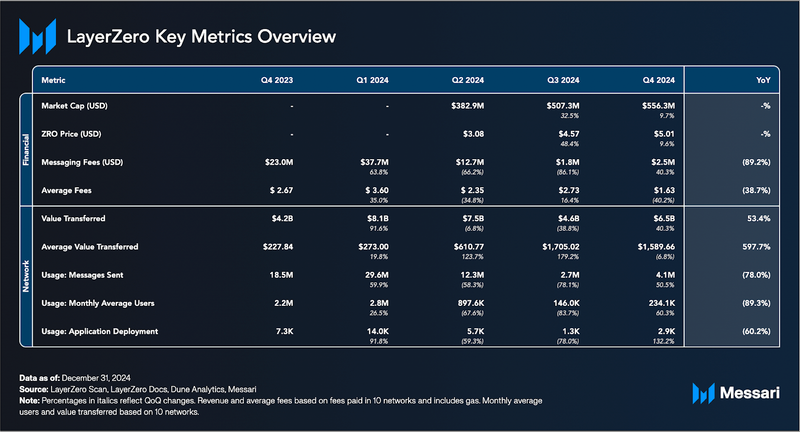 Performance AnalysisFinancial OverviewMarket Capitalization and Token Price
Performance AnalysisFinancial OverviewMarket Capitalization and Token Price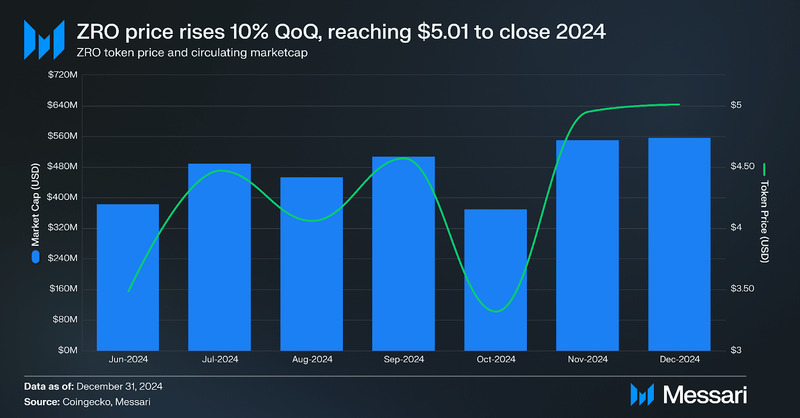
On June 20, 2024, the LayerZero Foundation launched ZRO, the native token of the LayerZero protocol. As an Omnichain Fungible Token (OFT), ZRO grants holders governance control over a protocol fee switch, a permissionless mechanism that can collect fees on each message sent through LayerZero and burn ZRO fee tokens.
ZRO closed Q4 with a market cap of over $556 million and a token price of $5.01, reflecting a 9.7% increase in market cap and a 9.6% increase in price QoQ. The price of ZRO has remained strong for months since launch, which may be attributed to Sybil filtering, which excluded Sybil addresses from the airdrop. Its assumption that durable users selected for the airdrop are more likely to be long-term holders has held true for 6+ months. By the end of 2024, ZRO ranked among the top four cross-chain messaging protocols by market cap.
Messaging FeesMessaging fees are collected in the native token of the source chain. These fees serve three purposes:
- To distribute to DVNs and Executors for verification and execution, respectively.
- To pay for gas on the destination chain.
- To burn on the source chain if the protocol fee accrual is activated, a decision controlled by tokenholder governance.
Revenue generated from these fees by DVNs and Executors pays for security. Each application chooses its own configurations of DVNs for validation. Simultaneously, Executors are also selected to deliver messages accurately. If the fee switch is activated, protocol fee accrual reduces the circulating supply of ZRO through a burn mechanism. This control over supply and market capitalization aims to incentivize ZRO holders to engage in governance.
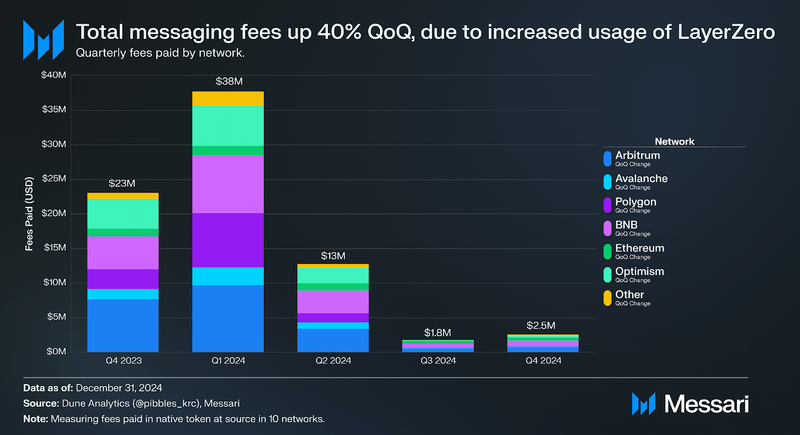
Total messaging fees paid by users increased by 40% QoQ to $2.5 million in Q4’24. The top source chains for messaging fees were BNB Chain ($771,000), Arbitrum ($675,000), Ethereum ($477,000), and Optimism ($201,000). This increase was driven by increased protocol usage rather than higher costs, as average fees per message—defined as the fees collected per message sent on the network—dropped 40% QoQ. The decline in average fees reflects a higher message volume and cost reductions from upgrades like EIP-4844. The majority of these fees go toward paying gas on the destination chain, in Q4, the chain with the largest inflows was Ethereum, which also has the highest fees.
Value TransferredLayerZero has over 58,000 contracts using its omnichain communication protocol and is live on over 120 different networks, including Ethereum, Optimism, Arbitrum, Polygon, Solana, BNB Chain, TRON, and Base. These contracts use LayerZero messaging for various use cases, supporting over 350 user-facing applications.
Transferring assets between distinct networks (bridging) is one of the most common use cases for LayerZero. Other use cases include gaming, cross-chain governance, and identity solutions.
Using bridges built on LayerZero, assets can be transferred by swapping native assets on source chains for native assets on destination chains (e.g., Stargate) or via LayerZero’s token standards — called Omnichain Fungible Tokens (OFTs) and Omnichain Non-Fungible Tokens (ONFTs). The standard OFT is burned on the source chain and minted on the destination chain. Examples of native bridges using standard OFTs are Aptos Bridge, Core DAO, and Harmony Bridge. For existing native tokens, bridges can adopt the OFT standard by locking the tokens on the native chain and minting equivalent tokens on the destination chain. Tokens are received by the destination chain by issuing new tokens, with 1:1 for each token locked or burned.
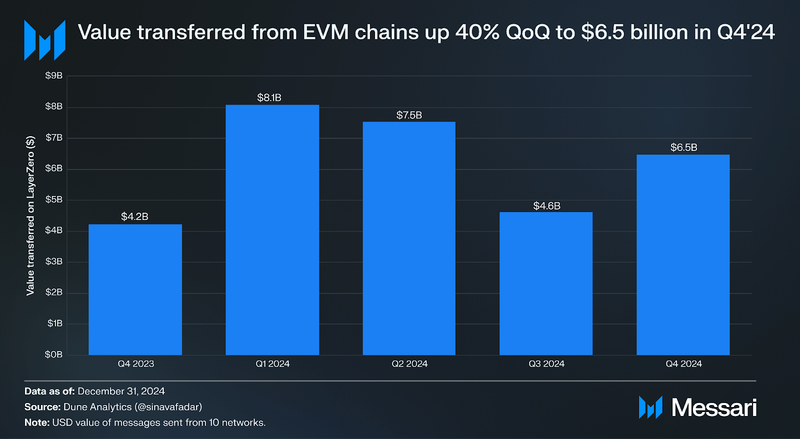
In Q4’24, the value of assets transferred via LayerZero bridge applications across 10 EVM networks totaled $6.5 billion, a 40% increase QoQ. This aligns with the overall growth in bridge volume observed across all protocols this quarter. Notably, this figure excludes Solana, which is supported by LayerZero and recorded the second-largest net inflows at $1 billion during Q4.
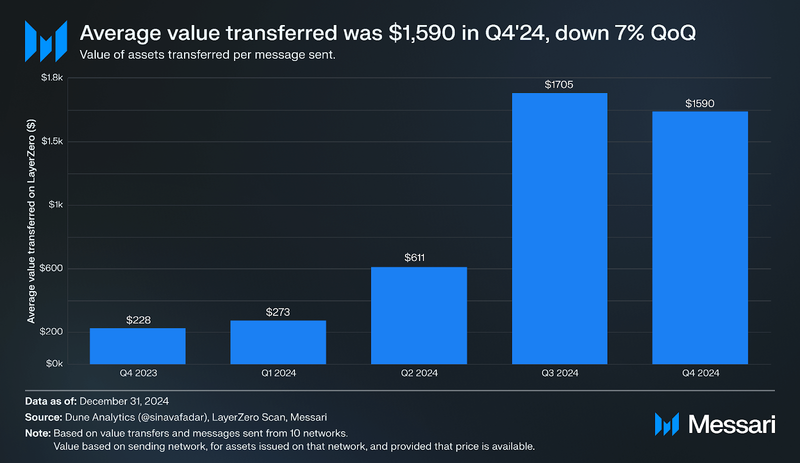
By deterring Sybil farming, onchain data reflects durable users rather than inflated numbers from entities using multiple wallets (defined as clusters of 20 addresses linked to the same individual by the LayerZero Foundation ahead of the TGE). The average value per message decreased 7% QoQ to $1,590 in Q4 but was up 598% compared to levels before the announcement of Sybil filtering. This suggests that genuine users leverage the LayerZero protocol for higher-value transactions than industrial Sybil farmers.
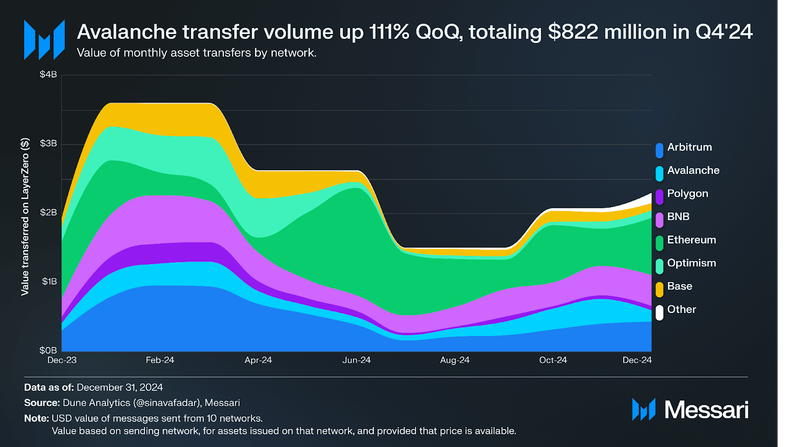
In Q4’24, Ethereum ($2.2 billion), BNB Chain ($1.2 billion), and Arbitrum ($1.2 billion) ranked as the top three source networks by transfer volume for bridges built on LayerZero. Avalanche experienced the most immense growth, transferring $822 million in assets—a 111% QoQ increase. This surge could be attributed to the launch of Avalanche 9000, a significant network upgrade that likely drove increased bridging activity and messaging to and from the network.
Protocol OverviewUsageMessages (packets of data) sent are a key indicator of LayerZero's total usage since they are user-initiated and used in all use cases, such as bridging (e.g., Stargate), token issuance (e.g., PancakeSwap and ether.fi), cross-chain liquidity (e.g., Orderly Network) governance (e.g., Angle), gaming (e.g., Nine Chronicles), cross-chain identity (e.g., Clusters), and fee/rewards distribution (e.g., Pendle). By excluding Sybil farmers from the token launch, LayerZero adjusted onchain usage metrics to reflect durable users instead of inflated numbers from entities using multiple wallets. Data from this quarter represents actual protocol usage.
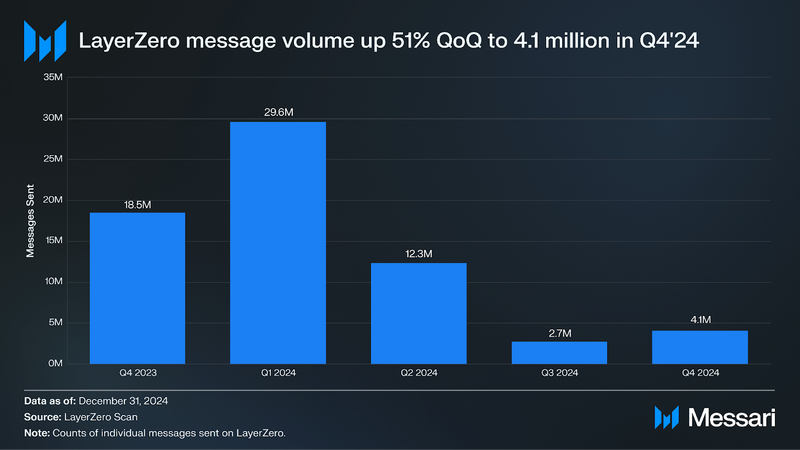
The number of messages sent on LayerZero was 4.1 million in Q4’24, up 51% QoQ. On September 25, 2024, LayerZero's daily messages surged to 98,000, marking a 433% increase following the announcement of a redistribution of unclaimed ZRO tokens from LayerZero's original airdrop. This surge reflects LayerZero's effort to incentivize ongoing user engagement by rewarding active participants while excluding previous airdrop claimants who showed no activity afterward. The airdrop's 30-day claim window sustained this increase in activity, in part resulting in this surge in activity in Q4.
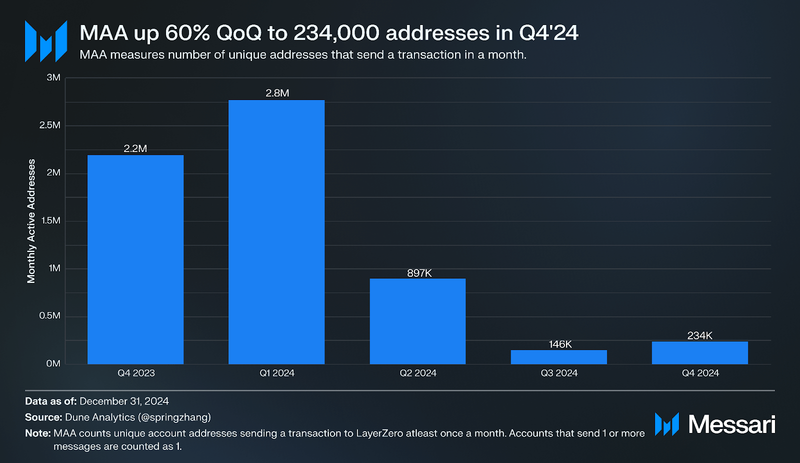
Since its launch in 2022, over 6 million unique wallets have interacted with LayerZero. This quarter, monthly active addresses (MAA) on EVM chains increased 60% QoQ to 234,000 users, correlating with the rise in messages sent and reflecting durable protocol usage. Given Solana’s position as the second-largest source of net inflows last quarter, a similar surge in MAA likely occurred on connected non-EVM networks.
Application DeploymentApplications that send and receive messages over LayerZero are called Omnichain Applications (OApps). These applications consist of deployed smart contracts on either source or destination networks. OApps connect to LayerZero via endpoint contracts on their respective networks. These applications can have various functions, including asset/token transfers, voting in governance, distribution of fees/rewards, and items for gaming.
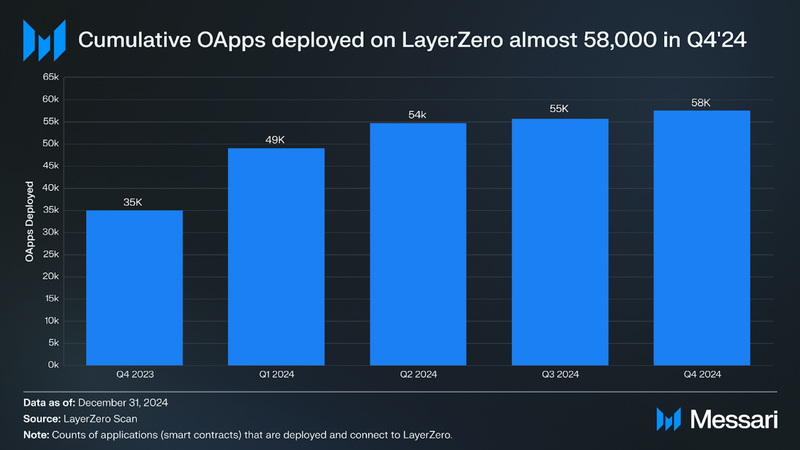
This quarter, the LayerZero protocol neared 58,000 OApps deployed, up 65% YoY. One of the incentives driving the consistent growth in 2024 was that teams were invited to submit proposals and deploy OApps for the ZRO token. Over 200 developer teams submitted applications for ZRO allocations and deployed their own OApp. The number of developers in the RFP alone was more than that of some major blockchains. Teams included GMX, Solidly Labs, DeFi Kingdoms, and Merkly.
Qualitative AnalysisKey DevelopmentsLzReadOne of LayerZero’s key product developments this quarter was lzRead, a data primitive designed to help developers of omnichain applications request and retrieve data from all supported EVM chains across any time period. Traditionally, smart contracts are restricted to accessing the current state of their native blockchain, which creates inefficiencies in a fragmented ecosystem. lzRead addresses this limitation by enabling applications to access and compute data from multiple blockchains—both current and historical—using a single function call in standard smart contract languages.
To utilize lzRead, developers deploy a compatible Omnichain Application (OApp), configure Decentralized Verifier Networks (DVNs), and create Read Requests. Each Read Request specifies the blockchains to query, the data required (along with time parameters), and any computations or transformations to be performed by the DVNs before returning the data. LayerZero’s initial DVN partners include BCW, Nethermind, LayerZero Labs, Animoca, Blockdaemon, and Gelato. By offloading these computations to DVNs, lzRead reduces the processing burden for onchain applications, streamlining data handling and accessibility.
The applications of lzRead span a range of use cases, highlighting its versatility. For instance, Agora employs lzRead to aggregate cross-chain votes for DAOs, enabling governance without requiring token bridging. ApeChain uses lzRead to verify BAYC NFT ownership on Ethereum, creating “shadow tokens” that reflect ownership across chains. Ambient integrates lzRead for real-time proof of reserves by fetching TVL data from multiple chains. Similarly, Gelato aggregates token prices across chains for reliable cross-chain price feeds. At the same time, Wintermute uses the tool to access data across Ethereum, Arbitrum, and Base for election resolution in prediction markets.
By making cross-chain and historical data from chains like Ethereum, Base, Polygon, Avalanche, BNB Chain, Optimism, and Arbitrum accessible, lzRead unlocks new possibilities for omnichain applications in governance, DeFi, asset verification, and beyond. This tool provides developers with the ability to efficiently compose applications with external data, addressing a longstanding gap in the blockchain ecosystem.
Fee Switch ReferendumThe LayerZero Foundation conducted its first onchain fee switch referendum that ran from December 20 to December 27. The proposal sought to determine whether LayerZero would introduce a protocol fee equivalent to the total DVN and Executor fees charged for verifying and executing each LayerZero message. If implemented, the protocol fees would be used to buy back and burn the network’s native token, ZRO. For the referendum to be valid, at least 60% of the circulating supply, or approximately 66 million ZRO, was required to participate. A mechanism was established to gradually lower this quorum threshold by 5% every six months—down to a minimum of 20%—if the quorum was not met.
The referendum concluded on December 27, with 11% of the circulating supply participating, falling well short of the required quorum. As a result, the proposal was rejected. The next referendum is scheduled for June 2025, with the quorum requirement reduced by 5%.
Omnichain Use CasesThis quarter LayerZero discussed 11 ideas to build omnichain, outlining innovative use cases for omnichain technology aimed at addressing critical challenges in the fragmented blockchain landscape. This effort was to inspire developers to expand upon these ideas and create omnichain applications with real-world utility. The concepts discussed included:
- Omnichain accounts: a potential solution for managing user accounts across multiple chains. Current Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) lack programmability and require separate smart contracts for each chain, resulting in a fragmented user experience. LayerZero proposed a unified, omnichain account standard that synchronizes account states and manages keys and modules across chains. This solution would allow users to operate a single, unified account that seamlessly integrates with both EVM and non-EVM chains. Despite the technical challenges for developers, this approach could significantly improve user accessibility and engagement.
- OFT Launchpad: a solution to address the limitations of launching tokens on a single blockchain. Tokens launched on a single chain are often restricted to that chain’s users and applications, limiting adoption and usage. LayerZero’s proposed solution is a composable standard with a unified supply across multiple chains, enabling broader adoption and greater volume potential in omnichain DeFi. The OFT Launchpad would allow tokens to be deployed simultaneously across multiple chains, increasing access to liquidity for token issuers. It includes two primary methods of distribution: airdrops, which reward eligible participants based on prior activities, and fundraising, where users exchange assets like USDC for protocol tokens across chosen chains. Once live, OFTs would maintain a unified supply and could be transferred natively between chains, providing a scalable framework for token distribution. This cross-chain functionality would be a significant step forward for token management, enabling seamless interoperability across ecosystems.
- Stablecoin Yield Aggregator: an aggregator solution that would leverage LayerZero’s omnichain technology to identify high-yield opportunities, rebalance funds across chains, and simplify cross-chain transactions for users. With the proliferation of over 1,000 yield-bearing pools across various blockchains, managing and optimizing stablecoin yields has become increasingly complex. Automating these processes and potentially offering an LP receipt token for deposited stablecoins would enhance capital efficiency and reduce the manual effort required for liquidity management. This concept can potentially appeal to novice and experienced DeFi users, making yield farming more accessible and efficient.
This quarter, LayerZero expanded its network reach, adding support for over 21 new blockchains and bringing the total to 120 networks. Newly integrated networks include Ozean, Usual, Abstract, Sonic, Unichain, Movement, Arbitrum Orbit, Hedera, Lisk, Hemi, Corn, Degen, Ink, Swellchain, and PEAQ. These additions further solidified LayerZero’s position as a leading interoperability protocol for omnichain communication.
Among the notable integrations, Sonic, a high-performance EVM-compatible L1 blockchain, partnered with LayerZero to enhance its cross-chain communication capabilities. Sonic is designed for scalable DeFi applications with a throughput of 10,000 TPS and sub-second finality. This integration enables seamless liquidity sharing and interoperability, bolstering Sonic’s appeal for developers and users.
Corn, an Ethereum L2 blockchain built on the Arbitrum Orbit stack, also adopted LayerZero to enhance its interoperability features. By integrating LayerZero, Corn enables Bitcoin holders to utilize their assets across DeFi ecosystems and multiple networks, unlocking new possibilities for Bitcoin within decentralized finance.
Application IntegrationLayerZero continued to expand its omnichain ecosystem surpassing 58,000 OApps and facilitating integrations across various applications and use cases. Notable deployments included:
- Zoth
- ApeCoin
- Avalon Finance
- EtherFi expanded its offerings by enabling its eBTC token to adopt the OFT standard, which is now operational on Base, Corn, and Arbitrum
- Tether leveraged LayerZero to launch USDT0, a 1:1 Ethereum-backed version of USDT aimed at extending accessibility across blockchains; it is now available on Ink, with launches on Berachain and MegaETH expected soon
- wBTC on Sei
- USDtb on Ethereum.
Pudgy Penguins, the second-largest NFT collection by market cap, expanded its ecosystem with Pudgy Toys and Pudgy World built on Abstract Chain, enabling PENGU bridging via LayerZero. Ondo adopted the OFT standard for its tokenized products, launching a bridging solution with features like rate limiting and emergency freezes. Initially supporting USDY transfers between Ethereum, Arbitrum, and Mantle, Ondo plans to integrate OUSG next.
Several other applications embraced LayerZero’s standards. Syrup launched on Base, making the SYRUP token accessible on the network. Aethir integrated its native token, ATH, for decentralized cloud infrastructure, enabling transfers via Stargate Finance on zkSync and Arbitrum. PYUSD adopted the OFT standard for native transfers between Ethereum and Solana, and COOK, the governance token for mETHProtocol, integrated the OFT standard to facilitate transfers between Mantle and Ethereum. Zerebro introduced ONFT integration, enabling AI-generated NFT bridging between Ethereum and Polygon. Farcana, a multiplayer arena hero shooter, and other integrations like WIF on BNB Chain further highlighted LayerZero’s expanding influence across gaming, finance, and enterprise use cases.
DVN IntegrationRecently, LayerZero Labs, in collaboration with Eigen Labs, introduced the CryptoEconomic Decentralized Verifier Network (DVN) Framework. This framework integrates cryptoeconomic security into omnichain messaging by requiring DVNs to stake assets, ensuring verifiers are financially incentivized to act honestly. The LayerZero Labs DVN, the first to use this framework, accepts ETH, ZRO, and EIGEN as staking assets. The framework supports slashing for dishonest behavior, creating a secure environment for cross-chain messaging.
LayerZero continues to offer a diverse marketplace of over 40 DVNs, which includes zk-tech verifiers like Polyhedra and enterprise solutions like Google Cloud. Adding DVN Adapters in V2 enables applications to integrate third-party validators, further expanding security options. Notable teams that started operating their own DVN this quarter included Nodekit and Superform.
Closing SummaryIn Q4’24, LayerZero continued solidifying its position as a leading omnichain interoperability protocol, achieving significant milestones across key areas. Messaging fees increased 40% QoQ, reaching $2.5 million, while total asset transfers via LayerZero bridges grew 21% to $5.5 billion across 10 EVM networks, reflecting robust protocol adoption. The successful implementation of Sybil resistance strategies ensured that onchain metrics reflected durable user engagement, with a 60% QoQ increase in monthly active addresses on EVM chains.
Notable developments included the introduction of lzRead, a powerful tool enabling cross-chain data retrieval and computation, and the first onchain fee switch referendum, which, while falling short of the quorum, marked a significant step toward decentralized governance. With integrations now spanning 120 networks and innovative proposals like omnichain accounts and the OFT Launchpad, LayerZero is shaping the future of blockchain interoperability.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.