and the distribution of digital products.
State of The Graph Q4 2024
- Demand for data on The Graph reached an all-time high of over 5.9 billion queries in Q4, up 13% QoQ from 5.3 billion. Additionally, demand-side fees in USD grew by 4.3% QoQ to an all-time high of $215,000.
- At the end of the fourth quarter, there were more than 11,200 active Subgraphs on The Graph, an increase of 8% QoQ from 10,400.
- In November, Geo, a core developer team for The Graph, proposed GRC-20, a knowledge graph standard that aims to establish a unified, interoperable data structure for decentralized applications in Web3.
- Indexing rewards increased 2% QoQ from $16.1 million to $16.5 million in USD, while in GRT terms they grew by an approximately equivalent amount of 1.8% QoQ to 77.5 million GRT.
- Since Q3’24, The Graph has integrated multiple networks, including Boba, Unichain, and Mantra, extending its support to more than 100+ chains.
The Graph (GRT) is an indexing protocol that provides onchain data — such as DeFi transactions and liquidity pool data — from various sources. The Graph removes the need for data consumers (e.g., app developers) to build complicated infrastructure to get onchain data. Instead, data consumers pay to query custom APIs — called “Subgraphs” — of onchain data via the GraphQL API. Subgraphs define a data schema to be indexed, making that data queryable. Subgraphs can be developed and queried by anyone.
The Graph Network uses its native utility token GRT to incentivize data indexing and consumption:
- Indexers process and store onchain data from Subgraphs. They usually have advanced technical knowledge of node operation. Indexers receive query fees in GRT from data consumers and indexing rewards from new GRT issuance.
- Curators are incentivized to analyze and signal which Subgraphs are valuable to index. Curators earn a 10% portion of the GRT query fees generated by Subgraphs.
- Delegators do not employ resources to index onchain data; instead, they delegate The Graph's native utility token GRT to Indexers. The amount of GRT query fees and indexing rewards a delegator receives is proportional to the amount of GRT delegated, less an Indexing Reward Cut (commission). There is also a 0.5% delegation tax each time a wallet delegates GRT.
In June 2024, The Graph completed its Sunrise of Decentralized Data initiative to upgrade all Subgraphs to its distributed network of approximately 100 independent Indexers. At the end of Q4’24, over 11,000 Subgraphs have either launched on the decentralized network or successfully transitioned from the hosted service. Following this milestone, The Graph has had consecutive quarters of all-time high query fees due to the increasing demand for data indexing.
Website / X (Twitter) / Discord
Key Metrics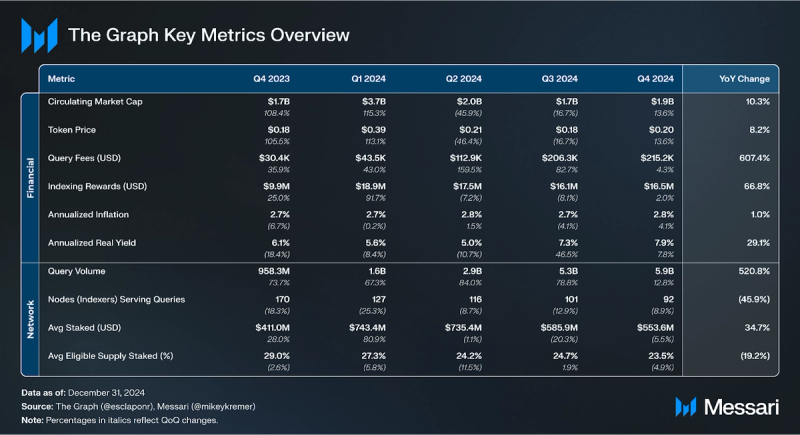 Performance Analysis
Performance AnalysisThe Graph Network is used by developers and data consumers who pay to query data. The network's performance can be measured by the growth of the volume of queries serviced, the active Subgraphs serving queries, and the accrual of query fees.
Network OverviewQuery Volume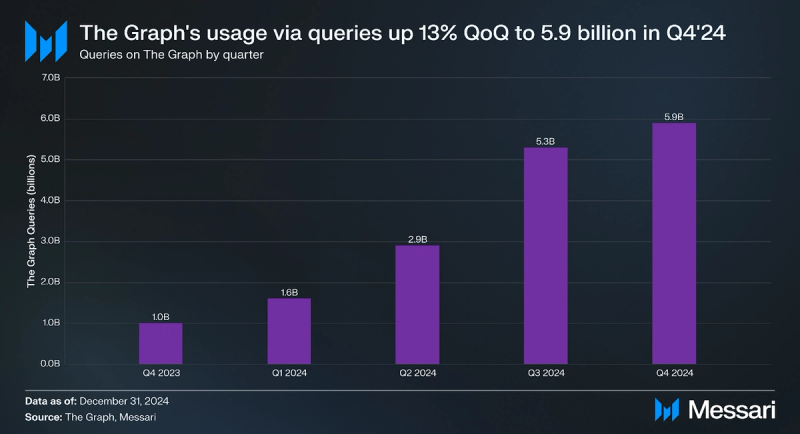
Demand for data on The Graph reached an all-time high of over 5.9 billion queries in Q4, up 13% QoQ from 5.3 billion. The Ethereum Mainnet led the way with 1.3 billion successful queries (22% of the total of 5.9 billion queries) in Q4, followed by Arbitrum One 983.5 million (16.5%), Polygon 1.0 billion (14.4%), BNB Smart Chain 854.6 million (14.4%), and Base 480.7 million (8.1%). Notably, query volume decreased by 23% QoQ on Ethereum, increased by approximately 15% QoQ on each of Arbitrum One, Polygon, and BNB Smart Chain, and increased by 203% QoQ on Base.
In terms of Subgraphs with the largest query volume, Graph Network Arbitrum (5% of total queries) led the way, followed by QuickSwap V3 (4%), and UNCX Lockers V3 and V2 on BNB Chain, both of which had 3% of query volume respectively. Notably, query volumes have seen an upward trend over the past six quarters. While the initial growth in query volumes was likely driven by a recovery of crypto activity throughout 2023, there were other recent contributing factors to the increase in query volume, including:
- a free query plan of 100,000 queries per month introduced in March 2024, as well as
- the increase in Subgraphs published to the decentralized network, as detailed below.
To bootstrap The Graph, a hosted service was initially created. This service hosted Subgraphs as the protocol gradually transitioned to its decentralized network. The hosted service was free (subsidized by The Graph ecosystem) and offered indexing infrastructure run by Edge & Node, the initial team behind The Graph.
The first decentralized Subgraph launched on the decentralized network in Q1'21. In October 2023, the project introduced its Sunrise of Decentralized Data to upgrade all Subgraphs to its distributed network of independent Indexers in three phases: Sunray, Sunbeam, and Sunrise.
The first phase of the upgrade — Sunray — was completed in March 2024. Sunray brought more chains, free queries, and improved billing, including a free query plan of 100,000 queries per month. This helped developers get started on the network and scale their development.
The second phase — Sunbeam — was concluded in June 2024. Sunbeam focused on upgrading hosted service Subgraphs to The Graph Network. The third phase of the upgrade — Sunrise — retired hosted service endpoints and was completed in June 2024.
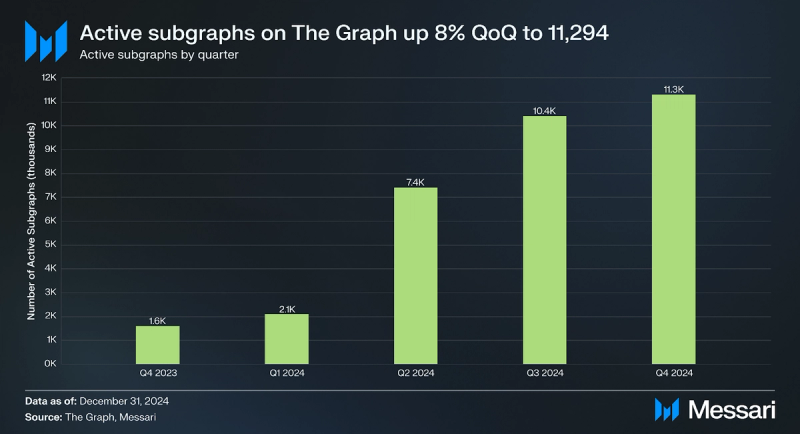
As a consequence, the number of deployed Subgraphs on The Graph’s Network has steadily increased. As of the end of Q4’24, 11,294 active Subgraphs have either launched on The Graph’s distributed network of independent data indexers or successfully transitioned from hosting services to it (+8% QoQ).
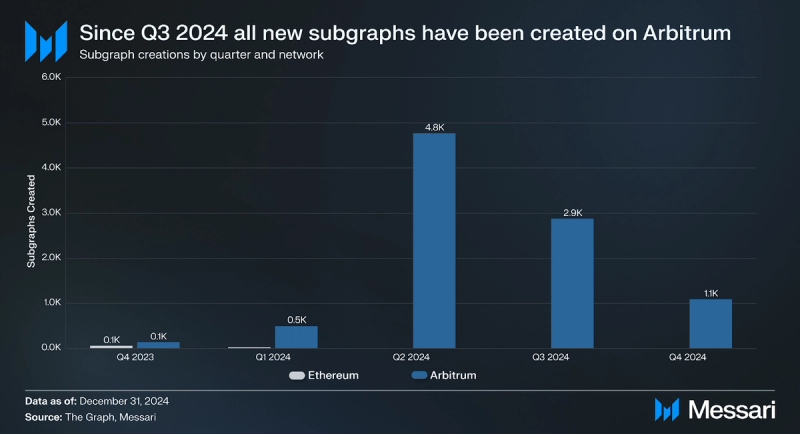
To improve performance and reduce costs, The Graph completed its migration from Ethereum Mainnet to Arbitrum, a Layer-2 scaling solution, on June 28, 2024, with 100% of indexing rewards on Arbitrum One from that day forward. This date also marked the beginning of the deprecation of The Graph’s deployment on Ethereum Mainnet, which was completed in December. In line with this transition, all new Subgraphs have been created on Arbitrum since Q3’2024.
Ecosystem ParticipationThe Graph’s protocol economic design coordinates participation from both technical and non-technical participants to meet supply and demand for data indexing and consumption:
- Indexers operate Graph Nodes to process and store onchain data. Data consumers can then query this data via GraphQL, an open-source language for The Graph’s APIs. Indexers receive query fees in GRT from data consumers and indexing rewards from new GRT issuance.
- Curators signal to Indexers which Subgraphs are worth indexing. Curators also often act as Subgraph developers. Curators earn a 10% portion of the GRT query fees generated by Subgraphs.
- Delegators delegate their GRT tokens to Indexers in exchange for a portion of an Indexer’s GRT query fees and indexing rewards. The amount of GRT query fees and indexing rewards a delegator receives is proportional to the amount of GRT delegated, less an Indexing Reward Cut and Query Fee Cut (commissions). There is also a 0.5% delegation tax each time a wallet delegates GRT.
Staked GRT is required for indexing Subgraphs and processing queries. As an Indexer stakes and is delegated more GRT, its capacity to process queries increases.
The minimum stake for an Indexer is currently set at 100,000 GRT (approximately $20,000 as of Dec. 31, 2024). In addition to this minimum, Indexers can also receive delegated stake from other ecosystem participants. Collectively, a maximum of 16x an Indexer’s personal stake can be delegated to a given Indexer.
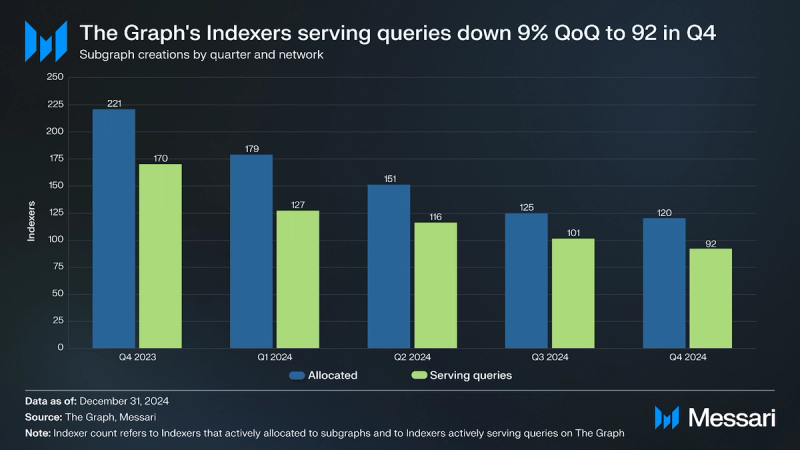
Indexers actively serving queries on The Graph decreased 9% QoQ from 101 to 92 at the end of the fourth quarter. Q4’24 marks the eighth consecutive quarter of a downtrend in Indexers actively serving queries. This trend began in Q1’23 following the end of The Graph’s Migration Infrastructure Providers incentivization program at the end of Q1’23 and some Indexers simultaneously unstaking GRT. Notably, the decline in the number of Indexers has not resulted in a decline in Indexer performance as these Indexers cover more Subgraphs, highlighting the network’s resilience.
Financial OverviewThe GRT token follows the Stake-for-Access model, also known as a utility token model. Participants in The Graph's ecosystem earn revenue in GRT by performing indexing and querying services on the decentralized network. Both services require GRT to be staked. An Indexer’s stake comprises their own GRT tokens (i.e., self-stake) and GRT delegated toward them (i.e., delegated stake).
Both indexing rewards and query fees are funneled through Indexers, who then distribute them to Delegators and Curators. Each Indexer sets a cut (commission) on both GRT query fees and indexing rewards generated from delegated GRT with the remainder distributed proportionally according to the amount of GRT delegated. These cuts (commissions) do not apply to Curators, who earn a fixed 10% portion of the query fees generated by particular Subgraphs.
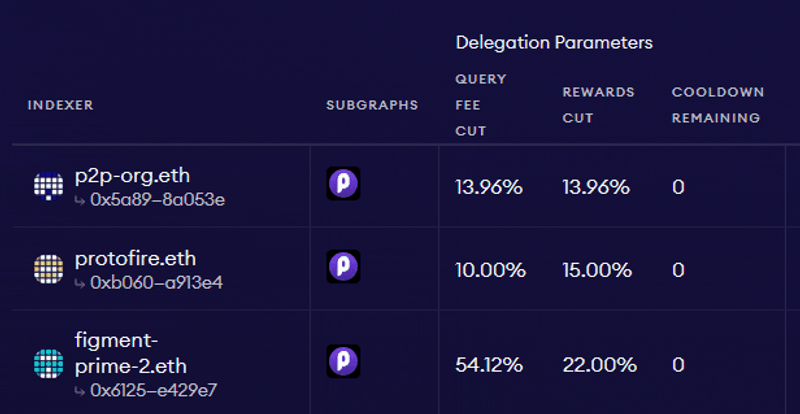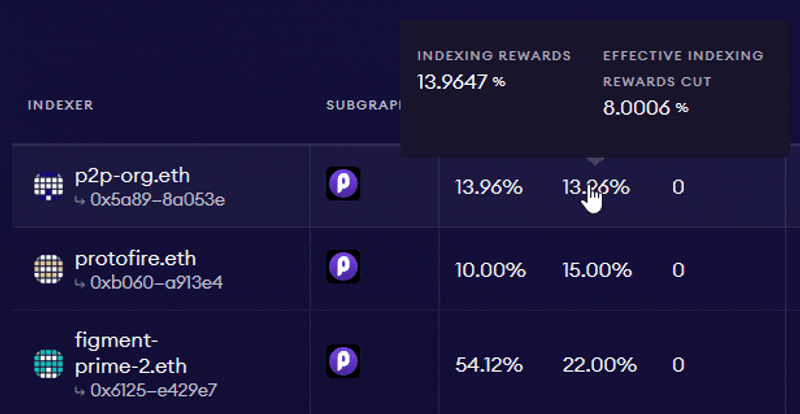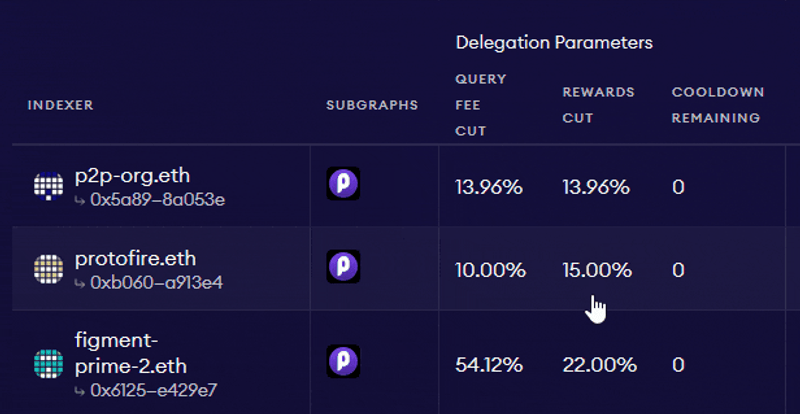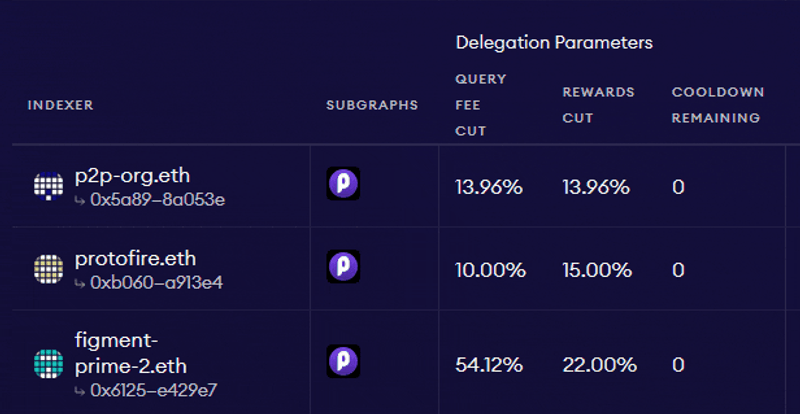
Source: The Graph: Choosing Indexers
As per the above example, if an Indexer sets the query fee cut to 13.96%, its Delegators would receive the remaining 86.04% of the fee revenue proportional to their stake. While Delegator stake cannot be slashed, Delegators should still consider several factors when staking GRT with Indexers. These include:
- Indexer choice, i.e., choosing effective Indexers with the most optimal balance between reward payouts and “skin-in-the-game” from allocation of self-stake.
- Unbonding period, i.e., no GRT transfers or rewards are possible within a 28-day window after un-delegation.
- Delegation tax of 0.5%, i.e., calculating how long it takes to earn back the 0.5% tax on delegation.
Indexing rewards come from new GRT issuance set by technical protocol governance. In Q4’24, annualized inflation from new GRT issuance averaged 2.76%. GRT rewards are distributed to Indexers staking GRT in return for providing indexing and querying services on The Graph’s open marketplace.
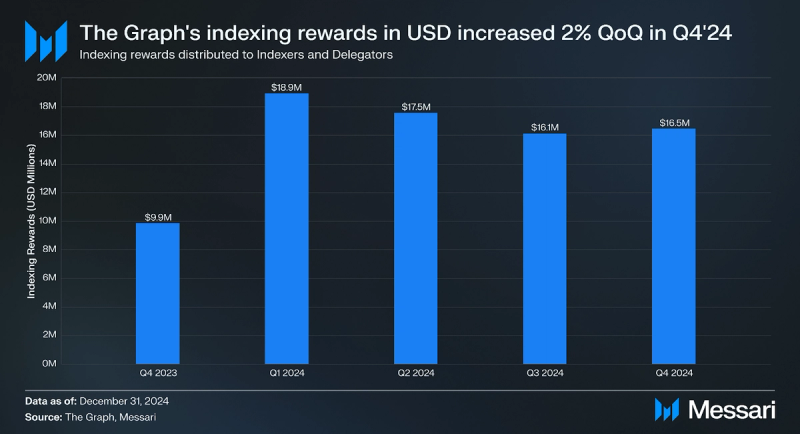
Indexing rewards increased 2% QoQ from $16.1 million to $16.5 million in Q4’24. In GRT terms, indexing rewards grew by an approximately equivalent amount of 1.8% QoQ to 77.5 million GRT.
Query Fees (Network Usage Fees)Data consumers (e.g., app developers) pay query fees for Indexers to fetch and organize data. As of Q4’24, The Graph delivers data to projects like Polygon, Art Blocks, and Loopring. Query fees are determined by market demand and distributed to Curators, Indexers, and Delegators.
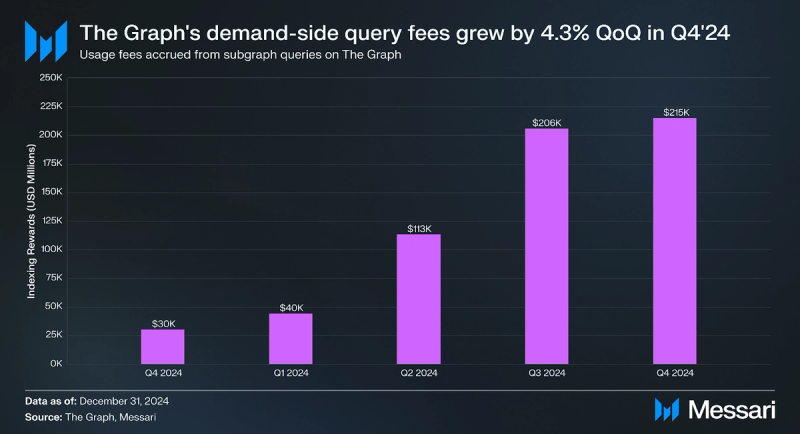
Total query fees increased 4.3% QoQ in USD terms to an all-time high of $215,000 in Q4’24. This increase in demand-side revenue in USD was primarily driven by the increase in query volume and the number of Subgraphs on the decentralized network.
By chain, Ethereum Mainnet led the way with $46,800 (21.7% of total query fees in Q4’24), followed by Arbitrum with $35,700 (16.8%), BNB Smart Chain with $32,500 (15.1%), Polygon with $31,800 (14.8%), and Base with $16,500 (7.7%). Notably, query fees decreased QoQ on Ethereum (-29%) and Polygon (-22%), and increased QoQ on BNB Smart Chain (+47%), Arbitrum (+17%), and Base (+147%).
For The Graph, the Q4’24 total query fees (over $215,000) just over 1.3% of the total indexing rewards (approximately $16.5 million), indicating that The Graph’s network participants still rely on indexing rewards to sustain their day-to-day operations.
Qualitative AnalysisKey DevelopmentsEthereum Mainnet Deprecation and L2 TransitionIn December, The Graph completed the final step in deprecating its Ethereum Mainnet (L1) protocol, with all contracts earmarked as "end of life,” though remaining GRT may still be withdrawn from the L1 contracts. This followed the successful migration on June 28, 2024, of The Graph from Ethereum's Layer-1 Mainnet to Arbitrum, an L2 scaling solution to address the challenges of high gas fees and slower transactions on Mainnet. Specifically, June 28, 2024, was the first with 100% of indexing rewards on Arbitrum One, and the beginning of the deprecation of The Graph’s Mainnet deployment, with only essential functions like the token bridge remaining operational from that date forward.
Chain IntegrationsIntegrating a chain with The Graph protocol follows three stages: Technical Integration via a forum thread, Integration Validation, and Mainnet Integration, which requires governance approval via a Graph Improvement proposal (GIP) and enables GRT indexing rewards. Since Q3 2024, The Graph has completed integrations with numerous chains, extending its support to more than 100 blockchains. Notable chains that have completed the Chain Integration Process since Q3 2024 include Boba Network (Nov. 12), Moonbeam (Jan. 24), and Mode (Feb. 11). Other notable integrations include:
- Starknet Firehose and Substreams Integration (Oct. 31) - StreamingFast, a core developer of The Graph, announced support on Starknet for Firehose, its blockchain data streaming technology, and Substreams, a parallel blockchain indexing solution.
- Solana Substreams Integration (Nov. 3) - The Graph Foundation announced support for Solana with Substreams, a parallel blockchain indexing solution.
- Other Integrations - Chiliz Chain (Oct. 8), Unichain testnet (Oct. 10), Blockscout (Nov. 11), Lens Chain (Nov. 12), Botanix (Dec. 4), Mantra (Dec. 4), Corn (Dec. 12), and 0x Loky (Dec. 20).
- GraphTally, previously Timeline Aggregation Protocol (TAP) - As of December, GraphTally, The Graph’s micropayment system, processed over 80% of payments on The Graph. To date, GraphTally processes the vast majority of payments on The Graph. GraphTally (previously TAP) mainnet launched in September and enables Indexers to handle receipts offchain and later redeem them using Receipt Aggregate Vouchers (RAVs) onchain.
- Recognizing GRT on Base as Canonical - On December 6, 2024, The Graph Council voted to officially recognize the GRT token on Base as canonical by approving (GGP-0047).
- The Graph Joins the Hypersonic Builders Alliance (HBA) - In December, The Graph announced it had joined the Hypersonic Builders Alliance (HBA) to bring blockchain data solutions to Soneium, an Ethereum Layer-2 network developed by Sony Block Solutions Labs (Sony BSL). Soneium launched its mainnet in January with The Graph partnering as a launch collaborator since August 2024.
- Sebastian Lorenz New Edge & Node CTO - In January, Sebastian Lorenz joined Edge & Node, a core developer team for The Graph, as its new Chief Technology Officer (CTO).
- Kraken Launches GRT Staking - In January, crypto exchange Kraken announced it had GRT staking support for U.S. clients in 37 states and two territories.
The Graph is supported by a number of community support programs funded by The Graph Foundation. Amongst these programs, there were a number of notable events, activities, and initiatives undertaken in the fourth quarter.
- In October, The Graph India closed submissions and announced winners for its Bootcamp and Hackathon with 21 project submissions and participation from more than 120 students.
- Datapalooza, The Graph’s annual event, took place in November during Devcon in Bangkok.
- @GraphDevs, a dedicated Twitter account serving as a hub for developers, released a developer survey in December to solicit feedback.
In November, Geo, a core developer team for The Graph, proposed GRC-20, a knowledge graph data standard that aims to establish a unified, interoperable data structure for decentralized applications in Web3. GRC-20 is designed to enable the sharing and extension of information across various domains by organizing knowledge into structured components. These components include:
- Spaces: Logical groupings that represent individuals, communities, or projects acting as containers for organizing and managing knowledge graphs. Public spaces reside onchain while personal spaces can be private or selectively shared.
- Entities and Relations: Entities represent a unique concept, such as a person, place, object, or idea, while Relations define the connections between these entities, forming a graph-like structure.
- Triples: The foundational units of knowledge in GRC-20. Each triple consists of three elements—an Entity, an Attribute, and a Value (e.g., Entity: "Actor", Attribute: "Name", Value: "John Doe"). Triples can be extended, modified, and referenced across the ecosystem.
- Encoding and IDs: GRC-20 employs Protobufs for encoding data. Each entity is assigned a globally unique 22-character ID, created using Base58 encoding. These IDs ensure that data is universally accessible and free from collisions.
To date, GRC-20 remains in a draft stage as a Graph Request for Comment (GRC-0020) pending public comments. Following this stage, GRC-20 will be finalized as an initial standard that can be updated over time.
Updates to The Graph Improvement Proposal (GIP) ProcessIn January, The Graph Council voted to approve GIP-0061, simplifying The Graph Improvement Proposal (GIP) process by removing the Graph Request for Proposals (GRP) step. It also introduces clearer instructions on how to complete GIP auditing, testing, and discussion and an intake form to request actions necessary to complete such requirements.
Closing SummaryIn Q4, demand for data on The Graph reached an all-time high of over 5.9 billion queries, up 13% QoQ from 5.3 billion. Additionally, demand-side fees in USD grew by 4.3% QoQ to an all-time high of $215,000. Moreover, at the end of the fourth quarter, there were more than 11,200 active Subgraphs on The Graph, an increase of 8% QoQ from 10,400.
Beyond these metrics, a number of key developments took place. In November, The Graph team introduced GRC-20, a proposed knowledge graph standard, while in December, the final step in deprecating its Ethereum Mainnet (L1) protocol was completed, with all contracts earmarked as “end of life.” The Graph also integrated with multiple networks since Q3’24, including Boba, Unichain, and Mantra, extending its support to more than 100 chains.
As The Graph moves into its fifth year of operation, it will look to continue to expand its coverage and use via new and existing data services like Firehose, Substreams, and other to-be-launched offerings.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.