and the distribution of digital products.
State of Cosmos Hub Q2'24
- Governance played a crucial role in shaping the network’s Q2’24 development, with 11 of 14 proposals being passed while the Atom Accelerator DAO approved four new grants valued at $395,000, a 32% QoQ increase.
- The Cosmos Hub experienced a halt in block production for several hours following the V17 upgrade due to a bug in the ICS provider module. The network was back online after a patch was created and distributed across the 180 validators.
- Cosmos Hub's real yield growth of 8.9% QoQ outpaced the 1.1% QoQ increase in inflation, mitigating dilution effects and enhancing value for ATOM holders despite the 45.3% QoQ decline in price and market cap.
- A 20.7% QoQ increase in Average Daily IBC Transfers-In,contrasted with a 45.6% QoQ decrease in Average Daily IBC Transfers-Out. This dynamic suggests Cosmos Hub is attracting and retaining more value within its Interchain ecosystem.
- Cosmos Hub expanded its relations to include a $500,000 investmentinto Elys Network as well as onboarding DAODAO, an open-source, governance-focused protocol.
Cosmos Hub (ATOM) is an individual appchain focused on interoperability and security. It is a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) sovereign blockchain with an account-based accounting model and no native smart contract functionality. Cosmos Hub pioneered technologies such as Cosmos SDK, CometBFT (Tendermint), ABCI, and IBC, which were later used by many Interchain networks. The Interchain consists of sovereign networks connected by the common interoperability protocol: IBC. The Interchain is also referred to as the Cosmos Ecosystem.
Cosmos Hub was launched in 2019, leveraging technologies built by the Interchain Foundation and Ignite (also known as Tendermint). Various groups continue to support the development of Cosmos Hub and the Cosmos tech stack, including the Interchain Foundation, Binary Builders, Atom Accelerator DAO, Informal Systems, Strangelove, and others. The Interchain is home to over 100 independent networks, each with its own unique supporting entities.
The Atom Economic Zone (AEZ) is an ATOM-aligned ecosystem set, which includes networks with various affiliations and integrations with the ATOM token. Networks that rent security from Cosmos Hub validators, i.e., Consumer Chains, are part of the AEZ. Replicated Security (formerly referred to as Interchain Security) refers to the sharing of the full Cosmos Hub validator set with another chain, permissioned by a governance vote. For a full primer on Cosmos Hub, refer to our Initiation of Coverage report.
Website / X (Twitter) / Telegram
Key Metrics Financial Analysis
Financial Analysis
ATOM price declined 45.3% QoQ from $12.63 to $6.73 in Q2’24, aligning with the broader contraction in altcoin markets. This decline followed a period of ATOM price increase of 46.6% from $7.2 to $12.30 in Q4’23.
ATOM circulating market cap contracted 45.3% QoQ, falling from $4.8 billion to $2.6 billion in Q2’24. Consequently, ATOM’s market cap rank fell QoQ from 28 to 32.
Revenue figures reflect a divergence between USD and ATOM denominations. USD revenue decreased by 47.9% QoQ from $634,000 to $330,000 in Q2’24. ATOM-denominated revenue decreased by 34.6% QoQ from 59,200 to 38,700 in Q2’24. This disparity was largely caused by the decline in ATOM price.
The annualized real yield marginally increased from 4.1% to 4.4% in Q2’24. Annualized inflation remained relatively stable, increasing from 11.7% to 11.8% in Q2’24. The percentage of eligible supply staked decreased by 2.7% QoQ from 65.3% to 63.6% in Q2’24. The stability in the inflation rate, juxtaposed with declining market metrics, suggests adherence to an updated monetary policy of stabilizing inflation rate to 10% regardless of short-term market fluctuations and reallocation of assets by stakers.

In Q2’24, ATOM price and revenue (USD), which is derived from total transaction fees, significantly declined QoQ. ATOM price declined 45.3% QoQ from $12.30 to $6.73 in Q2’24.
This divergence between ATOM- and USD-denominated revenue figures can be attributed to the network’s fee adjustment mechanism, which adjusts fees in ATOM to maintain a stable USD-denominated cost per transaction. The decrease in ATOM price amplified the reduction in USD revenue relative to ATOM-denominated revenue.
In Q4’23, the launch of the CRC-20 inscriptions standard on Cosmos Hub resulted in sporadic transaction spikes driven by inscription-based transaction activity, which persisted through Q1’24. In Q2’24, the network shifted to lower and more stable transaction activity, though activity levels stayed higher than those observed before the introduction of inscriptions. While ATOM price and revenue significantly contracted in Q2’24, other networks experienced similar declines QoQ, suggesting factors beyond Cosmos Hub's ecosystem were at play.
Tokenomics
ATOM’s inflation marginally increased by 1.1% QoQ, from 11.7% to 11.8% in Q2’24. The diluting effects of this inflation were minimized by the growth in real yield, which rose 8.9% QoQ, from 4.1% to 4.4% in the same period. This net-positive divergence reduced the effective tax on non-stakers and enhanced value for all ATOM holders.
Compared to H1’24, nominal yield and inflation rates have decreased by comparable percentages during H2’24, while the real yield rate continued to incrementally increase. This trend reflects the implementation of recent governance proposals and ongoing adjustments to ATOM’s tokenomics model.
ATOM’s relatively stable inflation rate is a result of a continued effort due to Proposal 848, which passed in Q4’23. The proposal aimed to balance ecosystem growth, improve ATOM's competitiveness in IBC DeFi, and optimize network security by reducing the maximum inflation rate from 20% to 10%. The proposal was controversial, generating the highest turnout in Cosmos Hub Governance history. Blockworks Research’s study determined that Cosmos was overpaying for security. Its findings suggested transitioning to a fixed supply schedule, given nearly all 180 validators break even or are profitable at a 10% inflation rate from commission alone. Validators retain the option of increasing their commission rate to help cover operational expenses. Post proposal approval, ATOM inflation rate dropped from 20% in Q3’23 to 10% early Q1’24 before stabilizing to 12% in Q2’24.
Q4’23 introduced a second influential proposal: Proposal 826, which sought to improve network security, infrastructure, and operational capacity by implementing a global minimum commission of 5% for validators, increasing their revenue and reinvestment capacity. Since its approval, staking APR decreased by 1% MoM in December ‘23 and ended Q2’24 at at 16.93%.
As of Q2’24, ATOM is subject to three types of deflationary mechanisms:
- Fee Burning
The Cosmos Hub has integrated a fee-burning mechanism similar to EIP-1559 by adopting the Skip Protocol’s Software Development Kit (SDK). This mechanism burns the base fees on transactions, permanently removing the burned ATOM from the circulating supply.
- Slashing
Validator nodes risk having their ATOM rewards slashed for infractions such as double-signing transactions or prolonged offline periods. The slashed rewards are burned. - Governance Burning
The Cosmos Hub employs an onchain governance mechanism enabling ATOM tokenholders to participate in network decision-making processes. Tokenholders can vote and issue proposals adjusting consensus parameters and the allocation of community pool funds. To submit a proposal, a minimum deposit of 250 ATOM is required from any tokenholder. In instances where a proposal is vetoed, the deposited ATOM is burned.
ATOM 2.0The ATOM 2.0 proposal aimed to fundamentally transform the tokenomics of ATOM by systematically reducing its issuance over a multi-year period, with the ultimate goal of eliminating inflation. The proposal outlined a plan to enhance ATOM’s capital efficiency and position the token as the Interchain reserve asset through liquid staking.
Despite its comprehensive vision, the initial ATOM 2.0 proposal was rejected in Q2’22, possibly due to its broad scope and rapid introduction. However, key components of the proposal advanced as separate, more focused initiatives. Among these, the passed proposals included ones to increase the treasury size and implement a liquid staking mechanism to improve ATOM's capital efficiency. Other significant elements, such as permissionless shared security models and governance hubs for Interchain technologies (e.g., IBC or CosmWasm) are still under active discussion.
In Q3’23, the Atom Accelerator DAO (AADAO) engaged Blockworks Research, Binary Builders, and RMIT University to develop a comprehensive tokenomics overhaul for ATOM, referred to as the Tokenomics RFP. This initiative produced eight proposals addressing critical areas: governance structures, liquid staking, treasury management, public funding mechanisms, relationships within the Atom Economic Zone, and ATOM issuance. The Cosmos Hub community is still discussing these proposals, with efforts underway to bring some of them to an onchain governance vote shortly.
Network Analysis
Average daily new addresses declined by 42% QoQ from 5,700 to 1,600 in Q2’24. Average daily transactions exhibited a greater decline of 56.2% QoQ falling from 151,000 to 66,000 in Q2’24. This contraction aligns with broader macroeconomic trends affecting other networks in Q2’24, suggesting systemic factors beyond Cosmos Hub's ecosystem at play.
While the average ATOM-denominated transaction fee increased 49.5% QoQ from 0.0043 ATOM to 0.0064 ATOM in Q2’24, the average USD-denominated transaction fee increased by 19% QoQ from $0.046 to $0.055 in Q2’24. This divergence between ATOM- and USD-denominated transaction fees may be attributed to the network’s fee adjustment mechanism. The mechanism works by adjusting fees in ATOM to maintain a stable USD-denominated cost for users, maintaining economic stability while preventing spam transactions.
Active validator count remained stable at 180 QoQ, suggesting validator confidence post Proposal 848 approval.
Whereas Total Staked (ATOM) marginally increased by 2.4% QoQ from 250.8 million to 256.9 million in Q2’24; Total Staked (USD) decreased by 26.2% QoQ from $2.3 billion to $1.7 billion in Q2’24. This disparity between ATOM- and USD-denominated stake may be attributed to the decline in ATOM’s price by 45.3% QoQ.
Inscriptions
Inscription-based transaction activity in Q2’24 exhibited significant shifts in both volume and frequency compared to the previous two quarters. Whereas Q4’23 and Q1’24 experienced sporadic and volatile transaction spikes, Q2’24 saw a transition to lower and less volatile transaction activity. That said, transaction activity was still elevated compared to pre-inscriptions deployment despite a notable decline in active addresses QoQ.
Inscriptions — digital artifacts that can be tracked and transferred by attaching arbitrary data to blocks — were introduced to Cosmos Hub following the rejection of Proposal 856 in Q4’23. This proposal sought to use the community spending pool to fund the development of COSS (CRC-20), an inscription meta-protocol for integrating trading, minting, and indexing inscriptions. Despite the proposal's rejection, COSS (CRC-20) launched shortly thereafter in Q4’23, immediately generating 3.5 million transactions.
Asteroid, built by Delphi Labs, was responsible for the multi-day frenzy in January, spiking transactions to a high of 1.1 million. Asteroid activity stabilized at lower levels throughout Q1’24. In Q2’24, Asteroid released their roadmap and received a $105,000 grant from Neutron Grants and AADAO.
Inscriptions Use CaseInscriptions' primary use case on Cosmos Hub facilitates data storage by combining inscribed data with offchain indexing to create token standards. Unlike platforms with native smart contract networks, Cosmos Hub does not support smart contract functionality and thus relies on meta-protocols like COSS to achieve similar smart contract outcomes. This enables the creation and management of assets, supports community organization, and enhances the network's role in the Interchain. Along with IBC connectivity, Cosmos Hub sports cheaper and faster transactions compared to Bitcoin, further integrating these new assets within DeFi. Given ATOM's broad community, inscriptions can unlock diverse and find sustainable use cases on Cosmos Hub.
Staking
In Q2’24, the engaged staking rate continued its QoQ decline, dropping from a high of 66% to 63.6% in Q2’24. This decline occurred despite the total staked ATOM remaining stable at 240 million, suggesting newly minted ATOM tokens likely being kept available to cover validators' operational expenses.
Staking on Cosmos Hub serves to secure the network. With a staking rate of 63.6%, Cosmos Hub ranks among the highest compared to other Layer-1 networks, making it an attractive option in terms of network security. Tokenholders can stake ATOM to become validators or delegate their tokens to active validators. Validators, who must meet specific system requirements, play a crucial role in maintaining network security and receive rewards for their efforts. Tokenholders can delegate a minimum of 1 ATOM to validators, sharing in the rewards generated by the validator. Rewards for delegators are proportional to the amount of ATOM staked, minus a commission fee determined by the validator.
Only the top 180 validators, ranked by combined self-staked and delegated ATOM, are eligible to earn rewards. Among these validators, the top seven validators control 34% of the total stake, resulting in a Nakamoto coefficient of 7. This structure ensures that both validators and delegators are incentivized to contribute to the network's security and decentralization.
IBC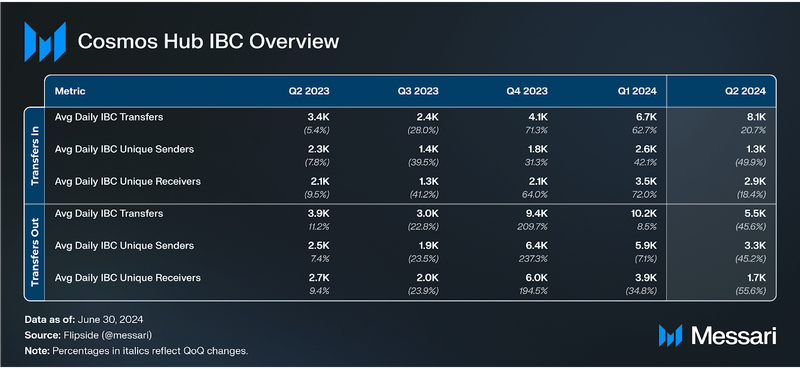
In Q2’24, a notable divergence emerged in IBC transfer volumes despite the sharp QoQ decline in average daily IBC unique senders and receivers for both inbound and outbound IBC transfers. Average Daily IBC Transfers-In increased 20.7% QoQ, rising from 6,700 to 8,100 in Q2’24. In contrast, Average Daily IBC Transfers-Out decreased 45.6% QoQ, dropping from 10,200 to 5,500 in Q2’24.

This divergence reflects a trend where interchain interactions through inbound transfers increased 20.7% QoQ, going from 6,700 to 8,100 in Q2’24, despite the decline in daily active addresses. Moreover, the contrasting trends between inbound and outbound IBC transfers suggest that fewer daily active addresses are engaging in more frequent inbound transactions. They are also becoming more strategic in their interchain activities, focusing on specific use cases offered by the connected chains. Meanwhile, outbound activity is becoming more concentrated and less frequent.
As of Q2’24, Cosmos Hub had 67 IBC peers (distinct counterparties of Cosmos Hub with established IBC connectors) and 463 IBC channels (the total number of routes available through connectors).
In previous quarters, inbound and outbound transfers were closely aligned, particularly in Q3’23. However, between Q4’23 through part of Q1’24, outbound transfers consistently exceeded inbound transfers. This trend reversed between Q1’24 and Q2’24, with inbound transfers surpassing outbound transfers, suggesting that Cosmos Hub is increasingly able to attract and retain value within its ecosystem.
Proposal 862 was passed to provide a fee-grant support system covering gas fees for IBC relaying activities. This temporary solution was proposed by Cosmos Hub relayers, who aimed to prevent service degradation and preserve efficient IBC operations. A multisig group will manage the distribution of the FeeGrants to vetted relayers, with various onboarding requirements detailed in the forum post.
Network HaltThe Cosmos Hub experienced a halt in block production at block 20,740,969 on June 5, 2024, following the scheduled V17 upgrade. The halt occurred due to a bug triggered when a validator left the active set and another took its place. This bug halted the chain for approximately 4 hours and 40 minutes. The issue was reported by the Informal Staking team and resolved by the Cosmos Hub team in coordination with Hypha and Binary Builders, allowing the chain to resume on June 6, 2024.
The root cause was identified as a bug in the ICS provider module, which executes logic during the AfterUnbondingInitiatedHook hook. This logic caused the number of validators to exceed the MaxValidators parameter whenever changes to the active set occurred within the same block.
The team acknowledged the need for improvements in their testing processes. They chose to set the MaxValidators parameter lower than the number of validators during tests and optimize the code to query only necessary data. The team plans to collaborate with the Cosmos-SDK team to address potential inconsistencies in hooks and improve documentation.
GovernanceCosmos Hub employs a combination of offchain and onchain governance mechanisms. Offchain discussions, typically held in the Cosmos governance forum, serve as the primary means for designing and debating network improvement proposals and parameter changes. Community members can propose network or treasury management initiatives and participate in these discussions. Users can submit network change requests to the Cosmos Hub's onchain governance system as formal proposals. Once onchain, ATOM stakers vote on the proposed changes.
In Q2, 11 of 14 total proposals passed. The passed proposals include:
- Proposal 895 Signaling: Permissioned CosmWasm - Following the rejection of Proposal 893 for permissioned CosmWasm, a detailed forum discussion was initiated, leading to a more refined definition of its parameters. This proposal aims to introduce programmability to the Cosmos Hub.
- Proposal 897 Signaling ICS 2.0: Partial Set Security - This proposal introduces a new form of Shared Security for AEZ chains.
- Proposal 899 DCF Agoric Cosmos Hub - This proposal activates idle ATOM in the Cosmos Community Pool, allocating an initial 4% (eventually increasing to 10%) of the pool's ATOM to generate value for the Cosmos Hub. The ATOM would be staked through stATOM and stkATOM.
- Proposal 912 DCF Agoric Community Spend - This proposal executes Proposal 899 through the community’s multisig.
- Proposal 914 Gaia V16 Software Upgrade - A mandatory upgrade for all validators and full node operators, executed at block height 20,440,500 on May 15, 2024. Key features include:
- The IBC rate limit module: prevents large inflows or outflows of IBC tokens within a short time frame, providing additional protection for IBC transfers.
- The ICA controller sub-module: enables users to perform cross-chain actions using their Hub accounts.
- The IBC fee middleware: authorizes the creation of IBC channels with in-protocol incentivization for relayers.
- Proposal 917 DoraHacks AEZ Quadratic Funding Program - This proposal authorized the distribution of 80,000 ATOM to DoraHacks and Dora Factory to conduct 10 quadratic funding (QF) rounds, in conjunction with the Atom Accelerator DAO, over the next 24 months. The objective of these rounds is to fund public goods and developer teams that add value to the Atom Economic Zone.
- Proposal 920 AADAO Oversight Election: Vote for Grace - This proposal elected Grace Yu to the Atom Accelerator DAO (AADAO)’s Oversight Committee. The committee is tasked with ensuring that all AADAO members act in the best interests of the ATOM community and serve as a counterbalance to the Strategy Committee.
- Proposal 922 AADAO Oversight Election: Vote for Clyde Carver - This proposal elected Clyde Carver to the AADAO’s Oversight Committee. The final selection of Oversight Member was based on the candidate who received the most ATOM votes. While Clyde’s proposal “passed,” Proposal 920 to elect Grace had more Yes votes, resulting in Grace’s selection.
- Proposal 924 Gaia V17 Software Upgrade - This upgrade integrates ICS 2.0, also known as Partial Set Security (PSS), into Gaia. PSS allows consumer chains to utilize only a subset of validators from the provider chain, offering greater flexibility than the traditional Replicated Security model. Each consumer chain can select the desired level of security by adjusting the top_N parameter.
- Proposal 926 Signaling: Expedited Software Upgrade - This proposal introduces “Expedited Proposals,” a new type of proposal with shorter voting durations and a higher tally threshold. If an expedited proposal (7 days as opposed to 14) does not meet the threshold within the shorter voting duration, it converts to a regular proposal, and voting restarts under normal conditions. An immediate application is to reduce the voting duration of Software Upgrade proposals to expedite the upgrading of the Cosmos Hub.
- Proposal 927 Funding 3rd-Party Audit of Hydro/ATOM Wars Platform - This proposal allocates community pool funds to commission a third-party audit for the Hydro/ATOM Wars codebase. Hydro is a bidding and governance platform designed to efficiently deploy liquidity across the Interchain.
In Q2, AADAO approved four new grants valued at $395,000, a 32% increase over Q1’s grant value of $300,000. YTD, AADAO has allocated $1 million to six recipients, raising total grant issuance to $4.8 million across 45 recipients since the program’s inception in 2023. AADAO was funded with 976,000 ATOM ($5.85 million) for 2024 via Proposal 865. In Q2, the second batch of 2024 grants was awarded to:
- Pro Delegators - Pro Delegators, a cross-chain validator, received $15,000 to enhance economic understanding of Interchain Security 2.0 (PSS) among validators and consumer chains.
- La Multisig - La Multisig, a Web3 content hub, was granted $12,000 to enhance user and developer onboarding for the Cosmos ecosystem in Latin America, with a particular emphasis on Argentina.
- Hypha Workers Co-op - Hypha Workers Co-op was awarded two grants: $50,000 for the ISLE Testnet and $77,000 for the Testnet Incentives Program.
- The ISLE Testnet, which returned $20,000 of unused funds, educates and incentivizes PSS and ISC 2.0 participation.
- The Testnet Incentives Program is designed to support validator participation in the Interchain Security testnet.
- Dora Factory / DoraHacks - Through its AEZ Quadratic Funding program, Dora Factory was awarded $200,000 for a 24-month initiative to invest in 10 quadratic funding rounds. This program was supported by Cosmos Hub governance, with the intent to sustain the development of public goods and app chains within the AEZ.
The Cosmos Hub serves as the central point for various cryptocurrency communities, acting as a Schelling point for Interchain ecosystems and modular builders. This alignment with other communities manifests through both formal and informal connections. For instance, the ecosystem demonstrated sustained ideological alignment with ATOM stakers being included in the eligibility criteria for multiple airdrops. In Q1’24, SAGA allocated a portion of its airdrop to ATOM stakers, and Aether committed to distributing 40% of its airdrop to ATOM stakers and holders of Stride stATOM. In Q2’24, the Penumbra team dedicated part of its airdrop to top contributors by code volume to select Github repos and Cosmos ecosystem users, recognizing their role in the development and growth of the Interchain.
Interchain SecurityThe Atom Economic Zone (AEZ) is an ecosystem of networks aligned with the ATOM token. It continues to expand through networks exhibiting various levels of integration with the ATOM token. In Q2’24, Replicated Security, a shared security model, remained the most actively explored AEZ strategy by the Cosmos Hub community and Interchain networks. Part of its appeal is allowing validators to use their stake to participate in the consensus of another network. Stride and Neutron, two of the earliest adopters of Replicated Security, have been joined by several new consumer chains, including Elys Network, which became the first to implement via testnet the Partial Set Security (PSS) model.
When PSS was introduced through Proposal 897, it allowed a subset of Cosmos Hub validators to opt-in to support consumer chains. Doing so provides greater flexibility and scalability compared to the original Replicated Security model. The opt-in approach enables validators to manage their hardware requirements more effectively by selectively participating in consumer chains, while still requiring governance approval to maintain alignment with the Cosmos Hub's objectives.
In addition to the progress made with PSS, Q2 saw further development of the Interchain Security (ICS) model proposed by Babylon and Informal Systems. This approach aims to leverage staked native BTC to provide security for ICS consumer chains, offering additional protection against security risks such as long-range attacks. Moreover, Babylon's proposal to utilize Bitcoin for data availability and to use the timestamping of Proof-of-Stake chains has garnered significant attention within the AEZ.
The implementation of PSS and the ongoing development of BTC-backed ICS demonstrate the Cosmos Hub's commitment to expanding and refining shared security options within the AEZ. As more consumer chains adopt these models, the Interchain ecosystem becomes increasingly robust, secure, and interconnected, with the Cosmos Hub playing a central role in facilitating this growth.
Neutron
After launching in 2023, Neutron became the first chain to leverage the Cosmos Hub's validator set and security through Replicated Security. It continued to serve as a DeFi center for the Cosmos Hub. In Q2’24, Neutron TVL decreased 39% QoQ, with the bulk of its TVL coming from Astroport, an automated market maker (AMM) that also operates on other Interchain networks such as Injective.
Notable Neutron developments include:
- Proposal 72 - Cosmos Hub allocated funding to develop Neutron.
- Proposal 819 - Reallocated funding approved in Proposal 72 directly to the Neutron Foundation to oversee the network’s development.
- Proposal 835 - Authorized the Neutron DAO to transfer 43 million unclaimed airdrop NRTN tokens to the Cosmos Hub community pool.
- Proposal A-41 - Approved in Q3’24, authorized the upgrade to V4.0.1, which would integrate:
- Skip’s Feemarket: implements the Additive Increase Multiplicative Decrease (AIMD) feemarket similar to Ethereum EIP-1559, where the base fee adjusts according to the network's demand for block space.
- Slinky: an onchain consensus-level oracle run by chain validators.

Stride leverages Cosmos Hub’s Replicated Security to support liquid staking for various Interchain networks and assets. ATOM remains a core component of Stride’s activities. Liquid staking is a significant market, and Stride's integration within the AEZ and ATOM’s performance underscores its strategic importance.
After launching in Q1’24, stTIA was responsible for nearly all of Q1’s growth. Soon after, stTIA surpassed milkTIA as the largest staked TIA asset by market cap. In Q2’24, ATOM’s TVL dominance on Stride marginally decreased QoQ from 32.5% to 31% in Q2’24 despite Stride’s TVL sharp decline during the same period, highlighting ATOM’s strength within Stride’s ecosystem.
Stride supported several other tokens for liquid staking, including STARS, EVMOS, JUNO, and INJ. Cosmos Hub Proposal 805 (an amendment to Proposal 800 — Liquidity as a Service) will have AADAO deploy 450,000 ATOM to an ATOM/stATOM constant product pool on Astroport Neutron.
OsmosisThe Osmosis AMM DEX remains deeply integrated with Cosmos Hub and ATOM. This integration was solidified in Q4’23 with the passing of Proposal 810 on Cosmos Hub, which allowed transaction fees on Cosmos Hub to be paid with any token, leveraging Osmosis to swap these tokens for ATOM. This feature promotes flexibility in gas fee payments and enhances the utility of the Osmosis DEX within the Cosmos ecosystem.
ATOM is used as an alternative gas token on Osmosis, although much of this usage appears to be automated bot activity based on observed patterns. The ATOM/OSMO pool, the first and still the largest by TVL on Osmosis, underscores the deep liquidity relationship between ATOM and Osmosis. Furthermore, Proposal 858, which passed in Q4’23, allocated 900,000 ATOM to the ATOM/stATOM liquidity pool to stabilize the staked ATOM peg and enhance protocol revenue.
Elys NetworkElys Network is set to be the first chain to implement PSS. Elys is a DeFi-focused network that offers user experience features similar to a centralized exchange, while maintaining a noncustodial model for its AMM without requiring KYC. Additional noncustodial features include oracle-based index pools for diversified assets, native perpetual trading, leverage, borrowing, and EVM bridging.
As the network grows and accumulates more total value locked (TVL) and activity, it requires increased security. Higher network value will likely incentivize more Cosmos Hub validators to participate, thereby scaling security proportionally with network value. The flexibility of PSS provides a cost-effective approach to scaling security based on the network's needs. In Q2’24, a proposal draft explored launching Elys Network as an opt-in consumer chain, which is intended to be launched permissionlessly. However, given the current limitations of the ICS, a permissionless launch is not possible due to technical reasons involving the chain_id.
Closing SummaryIn Q2'24, Cosmos Hub demonstrated resilience and strategic growth despite market-wide financial challenges. While ATOM's price and market cap experienced declines, the network maintained stability with an 8.9% QoQ increase in real yield and stable inflation. The adoption of key governance proposals, such as ICS 2.0 and Partial Set Security (PSS), highlighted the community's proactive approach to enhancing security and scalability. Effective fee adjustment mechanisms contributed to economic stability, even as network metrics like daily new addresses and transactions aligned with broader market trends.
Cosmos Hub’s commitment to long-term growth was underscored by its strategic advancements in tokenomics, governance, and ecosystem funding. The network's adaptability was evidenced by the integration of inscriptions, enabling innovative use cases and strengthening its role within the Interchain ecosystem. Despite a decline in staking engagement, Cosmos Hub remained among the top networks in participation, ensuring robust security and decentralization. The ecosystem’s expanding capabilities were further highlighted by developments in Interchain Security, particularly BTC-backed ICS and PSS adoption. Overall, Q2'24 positioned Cosmos Hub for sustained growth and stability through strategic initiatives and strong community-driven governance.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.