and the distribution of digital products.
State of Chronicle Q2 2024
- Between February and June 2024, the fees paid in USD per Chronicle oracle update decreased by 51% and 95% on Ethereum and Layer-2s, respectively.
- Using the respective ETH/USD oracle as a proxy, Chronicle updates on Ethereum were 79% more computationally efficient than Chainlink updates. In Q2, Chronicle updates averaged 68,000 gas units of computational effort, while Chainlink updates averaged 327,000 gas units.
- Computational effort measured in gas units for Chronicle updates on Ethereum ranged between 53,000 and 76,000 on average throughout February and June 2024. This stayed within the range for ERC-20 transfers, which tend to oscillate between 45,000 and 100,000 gas units.
- Customer integrations on Chronicle grew 157% MoM, reaching 18 total integrations by the end of June 2024.
- Chronicle added support for four more chains (Base, Scroll, ZKsync, and Optimism) in Q2 2024, also launching the RWA Oracles and the Yield Rate Oracle with top teams in the industry (i.e., Circle, M^0, Spark, and Block Analitica).
Chronicle Protocol is an oracle network focused on providing transparent, verifiable, and cost-efficient price feed oracles to blockchains. Oracles are middleware that enable blockchains to access data from other systems and networks. Chronicle secures roughly $5 billion in assets on DeFi protocols today and has served MakerDAO and its ecosystem since 2017, when it invented Ethereum’s first onchain oracle. It originated from the Oracles Core Unit at MakerDAO, which was born out of the work of Niklas Kunkel and Mariano Conti.
Chronicle is expanding outside of the MakerDAO ecosystem. Its clever implementation of advanced cryptographic concepts has enabled the protocol to scale its supply side without increasing costs. Additionally, while many competitors tend to operate systems based on trust, Chronicle addresses this lack of transparency with end-to-end verifiability, where every piece of data can be traced back to each data feed’s original data source queries. For a full primer on Chronicle, refer to our Initiation of Coverage report.
Website / X (Twitter) / Discord
Key Metrics Performance AnalysisTotal Value Secured
Performance AnalysisTotal Value SecuredTotal value secured (TVS) represents the cumulative value of assets covered by an oracle network. When an oracle provides the necessary data for operating a DeFi platform, such as prices for assets being used as collateral, TVS would include the value of the assets in contracts reliant on the oracle's data.
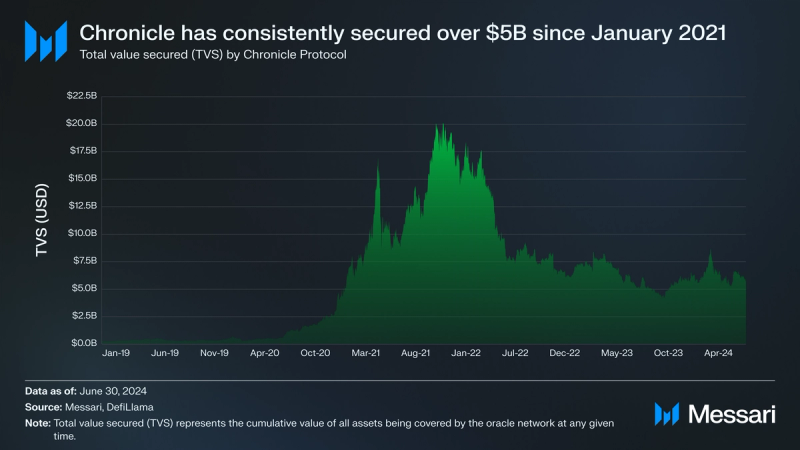
Chronicle launched Ethereum’s first onchain oracle as a part of MakerDAO in 2017. Although it only started offering a public oracle product within the past year, it has consistently secured over $5 billion since January 2021, peaking at just over $20 billion in December 2021. Chronicle’s historical TVS data is largely composed of only MakerDAO; however, as of recently, it also includes KEEP Network, which is only a fraction of a percentage of total TVS.
DefiLlama’s methodology results in the platform not covering all of Chronicle’s integrations. Chronicle increased application integrations from 3 to 18 between February and June 2024; TVS should see a rise in protocols under its coverage. Some of the new applications Chronicle is supporting include Term Finance, BadgerDAO, Morpho, and Mountain Protocol.
SignersSigners are validators on oracle networks that are tasked with sourcing raw data and submitting it to the protocol. They sign the data with a digital signature to attest to its integrity and to enable the protocol to identify the data the validator submitted. The number of signers for any given oracle transaction is always smaller than the size of the entire validator set. The number of signers is a proxy for the security of the oracle price feed. Having more signers leads to higher security, given the increased difficulty of validator collusion to manipulate the oracle reported values.

Note: Analyzing signers for push oracles in isolation doesn't fully explain the security of their networks. For this reason, this analysis also looks at Chainlink signers throughout Q2 and today (August 20, 2024: the time of writing).
In Q2, Chainlink signers on Ethereum varied between 7 and 11 signers. On Layer-2s (L2s), such as Base, Optimism, Arbitrum, and Polygon zkEVM, Chainlink averaged 4 signers. The number of signers on Chainlink oracles has not changed since Q2 (example of 7 signers on Ethereum; example of 4 signers on Base).
Chronicle matched or lagged Chainlink signers on Ethereum oracles in Q2 and early Q3, until mid-August, when it started using 13 signers per oracle update (on Ethereum and L2s). However, Chronicle has consistently used significantly more signers than Chainlink on L2 oracles since launching support for them, representing a 225% higher threshold for oracle price feed manipulation as of writing
Gas and FeesGas UsageGas refers to the amount of computational work required to perform a transaction or operation on the Ethereum network. It’s a measure of the resources needed, not a currency or amount of Ether (ETH). The gas price on the Etherscan Gas Tracker is a multiplier based on network costs. When people say “gas/prices are high,” they mean the cost of compute is high. Gwei is a denomination of ETH used to specify the price per unit of gas. It's a small fraction of ETH, where 1 Gwei equals 10-9 ETH.

Because the price of gas is set by total network activity, Chronicle can’t control it and instead aims to make gas as efficient as possible. Chronicle achieves such efficient updates using Schnorr multi-signature aggregation cryptography. Generally, messages that pass more data to the EVM will require more computational effort. This results in the message requiring more gas units. To maintain security, oracle updates require signatures within transaction messages. However, these signatures often come at the cost of adding data to the message (oracle update), where more signatures imply more data. Schnorr enables Chronicle validators to sign a single aggregated signature, leading to significant data compression with an increasing validator set and, therefore, increased oracle feed security.
Chronicle’s clever implementation of this cryptographic primitive has led to oracle updates on Ethereum and L2s requiring a small number of gas units. On Ethereum, ETH transfers are the cheapest transaction type, requiring 21,000 gas units. ERC-20 transfers often use between 45,000 and 100,000 gas units, and DEX trades can range between 100,000 and 500,000 gas units. (Gas consumed for operations on Ethereum can be viewed on Etherscan.) Meanwhile, Chronicle updates are relatively efficient (at 53,000–76,000 gas units between February and June 2024) compared to many operations that can be executed on Ethereum.
FeesFees measured in USD are what ultimately get paid out by protocols using push oracles. If the gas price is 1.5 Gwei, the gas used is 50,000 for an update, and the ETH price is $2,500, a protocol would pay $0.1875 for the transaction. Below is a breakdown of the calculation:
- Calculate Gas Price in Gwei: 1.5 Gwei × 50,000 units = 75,000 Gwei
- Convert Gwei to ETH: 75,000 Gwei = 75,000 × 10-9 ETH = 0.000075 ETH
- Convert ETH to USD: 0.000075 ETH × 2,500 USD/ETH = 0.1875 USD

Between February and June 2024, despite a 25% increase in ETH price and a 29% rise in the computational effort (gas units) for updating Chronicle oracles on Ethereum, the fees paid for updates fell by 51%. This paradoxical outcome occurred when users began setting a significantly lower gas price (in gwei) for transactions, likely due to reduced network congestion or lower transaction demand (a potential result of Dencun), which more than offset the increase in both ETH price and gas usage. Even with ETH's value rising, fees in fiat terms decreased sharply.
Chainlink Comparison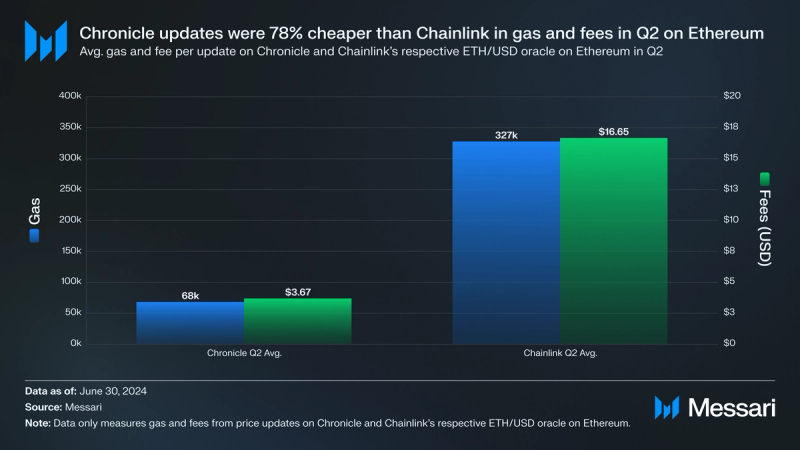
Using Chronicle’s and Chainlink’s respective ETH/USD oracles as a proxy, Chronicle outperformed Chainlink in computational efficiency and update price in USD on Ethereum. On average in Q2, Chronicle’s ETH/USD oracle used 68,000 gas units at $3.67 per update. Compared to Chainlink’s ETH/USD oracle, which used 327,000 gas units at $16.65 per update, Chronicle’s oracle was 79% more computationally efficient and 78% less expensive. Gas and fees for oracles are important because they represent necessary costs to the protocols using them. DeFi projects (or oracle protocols) typically seek grants to subsidize oracle updates for integrated applications. The profit that DeFi applications accrue, or the grants that they win, can be more efficiently utilized when oracle operating prices are more economical.
Qualitative AnalysisRWA OraclesM^0Chronicle partnered with M^0 to launch a real-world asset (RWA) oracle to verify the collateral on the M^0 protocol. M^0 is an overcollateralized stablecoin minting protocol that enables approved entities (often institutions) to mint a fungible stablecoin, M, using short-term U.S. Treasury bills as collateral. The collateral type is subject to change as directed by governance on the protocol.
Reserve, Morpho, and Re7Reserve and Re7 selected Chronicle to secure its hyUSD/eUSD market on Base via Morpho. hyUSD is a yield-bearing stablecoin created by the Reserve Protocol. Reserve enables issuers to deploy overcollateralized Reserve-based stablecoins backed by their choice of collateral assets. Re7 is a DeFi-focused R&D, risk assessment, and asset management firm. Morpho is a lending and borrowing protocol that enables anyone to permissionlessly deploy lending markets.
CircleCircle selected Chronicle as its oracle launch partner for its deployment of the EURC token on Base. EURC is an overcollateralized, euro-backed stablecoin. Circle is the company responsible for launching USDC stablecoin.
Mountain ProtocolChronicle was selected by Mountain Protocol to provide exclusive price feed support for USDM and wUSDM across multiple blockchains, including Ethereum, Base, and Polygon zkEVM. Mountain Protocol is the issuer of USDM, the first regulated permissionless yield-bearing stablecoin backed by U.S. Treasuries. With a current TVL of over $150 million, it has become the largest yield-bearing stablecoin. Mountain Protocol is a regulated entity by the Bermuda Monetary Authority.
Yield Rate OracleChronicle collaborated with Block Analitica to build an ETH staking yield rate oracle. Block Analitica is a risk management platform for DeFi protocols. The yield rate oracle tracks and delivers the value of the onchain ETH staking yield rate for Spark. The oracle enables protocols to automatically adjust lending and borrowing rates for WETH. In most lending protocols, these rates are adjusted manually via governance. The yield rate oracle facilitates a more capital-efficient system.
Expanding Scribe
In Q2, Chronicle launched Scribe on six new blockchains, including Arbitrum, Optimism, Scroll, Mantle, Base, and ZKsync Era. Scribe is Chronicle’s oracle smart contract system. It overcomes the linear relationship between security and cost that constrains other oracle protocols. Typically, when an oracle protocol increases the number of validators and, therefore, security, its costs increase due to requiring an Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) signature for each new validator. This approach fosters a one-to-one relationship between the signature and the signer — more signers lead to more signatures, which ultimately increases the data and costs of oracle updates.
However, Scribe uses a custom oracle consensus algorithm based on Schnorr multi-signature aggregation cryptography. Schnorr signatures uniquely enable multiple parties to sign a single aggregated signature. As a result, Chronicle can increase the number of signers without increasing the signature size, leading to substantial data compression. Ultimately, this results in a more secure and resilient oracle with significantly lower operating costs.
Closing SummaryChronicle had a highly productive first half of 2024, expanding its network to nine blockchains and increasing customer integrations to 18 projects by the end of Q2 (25 total as of writing). Its oracle smart contracts have proven to be 79% more computationally efficient and 78% more cost-effective in USD fees compared to Chainlink oracles. Chronicle's updates are so efficient that they often rival ERC-20 transactions in terms of computational effort measured in gas units, positioning the network positively for future scalability.
Chronicle launched new oracle primitives, including the RWA Oracle and the Yield Rate Oracle in collaboration with top industry teams such as Circle, M^0, Spark, and Block Analitica. With these advancements, Chronicle is well-positioned to capitalize on the growing DeFi market as projects seek the most robust, decentralized, and efficient oracle infrastructure available.
——
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.