and the distribution of digital products.
State of Babylon Q4 2024
- Phase-1 attracted cumulative deposits totaling 57,290 BTC, or 0.29% of Bitcoin’s circulating supply. Compared to Bitcoin ETFs, Babylon's protocol had accumulated the third-highest amount of Bitcoin, behind Blackrock and Fidelity.
- By the end of 2024, 41,032 BTC had been liquid staked, an increase of 181.7% QoQ. Lombard continued to be Babylon’s leading liquid staking protocol, ending Q4’24 with a TVL of 15,959 BTC, up 157.5% QoQ as LBTC became the 5th largest bitcoin derivative.
- Bitcoin liquid staking protocols announced fundraises totaling over $24 million in Q4’24, with announcements from Solv, PumpBTC, Allo, and Lombard.
- By the end of 2024, Babylon’s top three Finality Providers by delegation amount were liquid staking protocols, accounting for 68.5% of total delegations. These protocols included Lombard, Solv, and PumpBTC.
- In December 2024, Babylon Foundation launched a Delegation Program that will delegate stake toward Babylon Genesis validators. This will help diversify the active validator set once Babylon Genesis launches and Phase-2 commences.
Babylon was founded in 2022 by David Tse and Dr. Fisher Yu. Their original inspiration stemmed from a research paper on Bitcoin security co-authored with the founder of EigenLayer, Sreeram Kannan. Babylon plans to offer a security-sharing protocol that leverages Bitcoin's security to secure Bitcoin Secured Networks (BSNs), such as Layer-1 proof-of-stake (PoS) networks, data availability (DA) protocols, and oracles. The protocol will be facilitated through a Layer-1 network (“Babylon Genesis”) on Cosmos.
Through Babylon, bitcoin tokenholders that desire yield can deposit (stake) bitcoins to provide security for BSNs, which will include Babylon Genesis itself. Staked bitcoins are delegated to Finality Providers (FPs), which will serve as the validators that secure BSNs. Despite Bitcoin’s lack of smart contracts, Bitcoin’s scripting language is used to engineer stake slashing to punish misbehaving FPs. For a full primer on Babylon, refer to our Initiation of Coverage report.
Babylon’s roadmap consists of three Phases. Phase-1 attracted bitcoin deposits but did not implement stake slashing. Phase-1 consisted of three capped deposit rounds and saw an ecosystem of liquid staking protocols emerge, including leaders like Lombard and Solv. Phase-2 will introduce stake slashing with the launch of Babylon Genesis as the first BSN secured by Babylon, and is planned for Q1 2025. Phase-3 will launch Babylon’s full security sharing capabilities as other BSNs become secured by Babylon.
Babylon has raised $96.8 million to fund its vision. In May 2023, Babylon raised $8.8 million in a seed round led by IDG and Breyer Capital. In December 2023, Babylon raised $18 million in a Series A led by Polychain Capital and Hack VC. In May 2024, Babylon raised $70 million in a Series B led by Paradigm. A full list of investments in Babylon can be found here.
Website / X / Discord / Telegram / Docs / GitHub / Forum
Phase-1 Deposits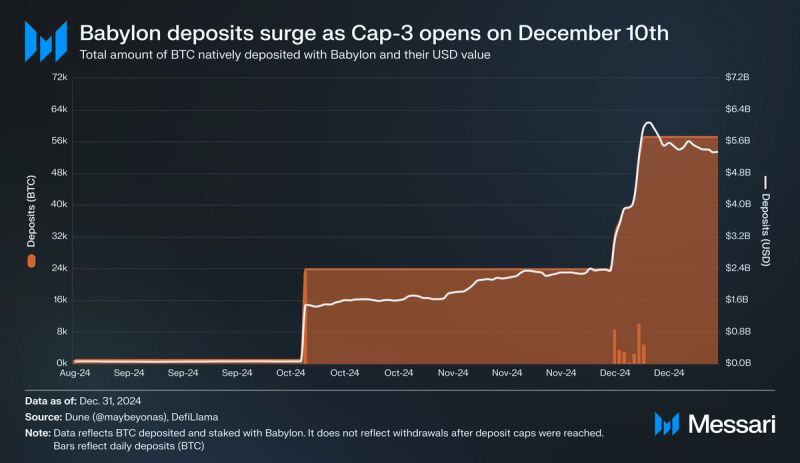
Leading up to the launch of Babylon Genesis, Babylon has attracted bitcoin deposits through three capped deposit rounds across Phase-1. Throughout Phase-1, stakers and Finality Providers (FPs) have earned points at varying rates, which reflect each user’s contribution to Babylon. Notably, Phase-1 did not implement stake slashing, which is planned to be activated in Phase-2 upon the launch of Babylon Genesis.
During Phase-1, deposited bitcoins are considered to be staked. Stakes last a maximum of 64,000 Bitcoin blocks (~15 months), after which they are considered to be expired and can be withdrawn. Notably, depositors can elect to unbond their bitcoins at any time. After an unbonding period of 1,008 blocks (~seven days), the stake is considered to be expired and can be withdrawn. This process is manually performed by a Covenant Committee that operates within a 6-of-9 multi-signature scheme that approves unbonding transactions.
Cap-1Cap-1 launched on Aug. 22, 2024, with a staking capacity of 1,000 BTC. The round attracted 1,000 BTC from 12,720 unique addresses. An estimated 80% of deposits came from Babylon’s ecosystem of liquid staking protocols, while the rest was natively staked.
During Cap-1, users could deposit between 0.005 and 0.05 BTC per transaction. The round operated on a first-come-first-served (FCFS) basis, and was open for six Bitcoin blocks (~74 minutes) before reaching capacity. While the round was open for deposits, 3,125 points were distributed between stakers and FPs per Bitcoin block.
Cap-2Cap-2 launched on Oct. 8, 2024. The round attracted 22,891 BTC from 12,590 unique addresses. This round did not feature a hard cap on deposits. Instead, it was duration-based, accepting deposits for 10 Bitcoin blocks (~two hours). Users could deposit between 0.005 and 500 BTC per transaction. While the round was open for deposits, 10,000 points were distributed between stakers and FPs per Bitcoin block, inclusive of stake from Cap-1.
Cap-3
Cap-3 launched on Dec. 10, 2024. The round attracted 33,399 BTC from 109,980 unique addresses. Once again, this round was duration-based, accepting deposits for 1,000 Bitcoin blocks (~seven days) until Dec. 17, 2024. Notably, an anonymous user deposited a total of 10,000 BTC, worth over $1 billion, across three transactions on Dec. 15, 2024.
Users could deposit between 0.005 and 5,000 BTC per transaction. For the first 300 Bitcoin blocks, 100,000 points were distributed between stakers and FPs per block, inclusive of stake from Cap-1 and Cap-2. For the final 700 Bitcoin blocks, points per block were reduced to 21,000.
Cap-3 also saw the following developments occur:
- Cap-3 introduced Babylóóng, Babylon’s dragon mascot. Users that natively staked at least 0.005 BTC during Cap-3 were eligible to receive special roles in Discord. A related contest is slated to run from Jan. 22, 2025, to March 17, 2025.
- On Dec. 9, 2024, Binance introduced “On-chain Yields.” The product’s first offering allowed users to stake bitcoins with Babylon directly on Binance.
- On Nov. 21, 2024, Anchorage Digital introduced support for bitcoin staking for institutions.
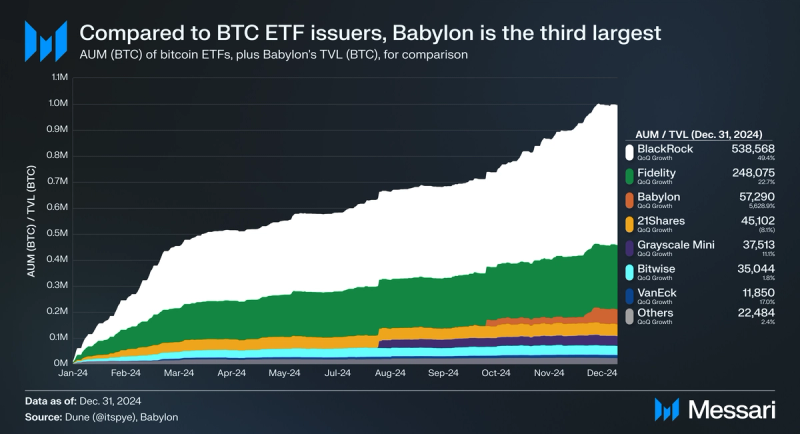
Babylon’s cumulative deposits (BTC) totaled 57,290 by the end Phase-1, worth $5.35 billion at the end of 2024. In total, Babylon’s cumulative deposits equated to 0.29% of Bitcoin’s circulating supply at the end of 2024. Notably, cumulative deposits (BTC) do not reflect bitcoin withdrawals, which have reduced Babylon’s TVL (BTC) marginally over time.
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) for bitcoin launched in January 2024. Assets under management (AUM) for these products increased throughout 2024, ending the year with a total AUM (BTC) of 938,635. As Babylon saw 57,290 BTC deposited throughout 2024, when compared to bitcoin ETFs, Babylon's protocol had accumulated the third-highest amount of Bitcoin, behind Blackrock and Fidelity.
Liquid Staking Ecosystem
A majority of Babylon’s bitcoin deposits come from its ecosystem of liquid staking protocols. These protocols accept bitcoin deposits from users regardless of whether or not Babylon is accepting additional deposits. In return, users receive liquid staking tokens that can be used across DeFi. When Babylon opens deposits, protocol-held bitcoins are natively deposited (staked) with Babylon.
By the end of 2024, approximately 41,032 BTC had been liquid staked, an increase of 181.7% QoQ up from 14,567. Lombard continued to be Babylon’s leading liquid staking protocol by a wide margin:
- Lombard (LBTC): Ended Q4’24 with a TVL of 15,959 BTC, up 157.5% QoQ. This resulted in LBTC becoming the 5th largest bitcoin derivative behind WBTC, BTCB, cbBTC, and M-BTC.
- Lombard’s growth can be largely attributed to two things, its focus on DeFi integrations and the Luminary Program that rewards users with Lux points. Lombard offers products in partnership with Berachain, BOB, Corn, SatLayer, Pendle, Morpho, Maple Finance, Euler, and more, all of which distribute Lux points.
- Lombard has led the emergence of restaked bitcoin, which is facilitated through Symbiotic and Karak. LBTC holders can mint liquid restaking tokens in partnership with Ether.Fi (eBTC).
- In December 2024, Lombard raised $1 million from Binance Labs. This comes after a $16 million seed round in July 2024.
- LBTC is natively supported on three networks. Over 93% of LBTC’s supply lives on Ethereum, though a significant portion has been minted on Base, and a lesser amount on BNB Smart Chain.
- Solv (SolvBTC.BBN): Ended Q4’24 with a TVL of 9,360 BTC, up 112.4% QoQ.
- Solv’s growth can be largely attributed to its focus on DeFi integrations and its points program that rewards users with Solv points. Solv offers products in partnership with Avalon, Pendle, Mezo, SatLayer, Corn, Sonic, and more, all of which distribute Solv points.
- Solv launched its SOLV token on Jan. 17, 2025, on Hyperliquid. The initial airdrop to Season 1 points holders totaled 7.25% of the total supply. Season 2 is now ongoing.
- In December 2024, Solv raised $11 million in a strategic funding round, bringing its total amount raised to $25 million.
- PumpBTC (pumpBTC): Ended Q4’24 with a TVL of 5,498 BTC, up 245.3% QoQ.
- PumpBTC’s growth can be largely attributed to its focus on DeFi integrations and its points program that rewards users with PumpBTC points. PumpBTC offers products in partnership with Berachain, Corn, Core, Zircuit, Swell, Pendle, and more, all of which distribute PumpBTC points. Notably, the snapshot for Season 1 was completed on Jan. 1, 2025.
- In December 2024, PumpBTC raised $10 million in a seed round.
- In October 2024, PumpBTC launched its PumpBera NFT collection as a free mint on Arbitrum.
- pumpBTC is natively supported on seven networks. Over 88% of pumpBTC’s supply lives on Ethereum, though a significant portion has been minted on BNB Smart Chain and Base.
- Obelisk (oBTC): Ended Q4’24 with a TVL of 3,583 BTC, up 35,654.2% QoQ.
- Obelisk is operated by NodeDAO, a decentralized staking operator.
Other bitcoin liquid staking protocols include Lorenzo (stBTC), Bedrock (uniBTC), Acorn (aBTC), BabyPie (mBTC), Allo (alloBTC), pSTAKE (yBTC), and Kinza (kBTC). Notably, Allo was the one project from this list that announced it had raised funds in Q4’24. It raised $2 million in a seed round and $750,000 in a Binance Labs accelerator program. In total, bitcoin liquid staking protocols announced fundraises totaling over $24 million in Q4’24.

Babylon’s liquid staking diversity score was six (i.e., the number of liquid staking protocols comprising 90% of Babylon’s liquid staking TVL) at the end of 2024. This is a 50% QoQ increase, as Obelisk and Lorenzo joined Lombard, Solv, PumpBTC, and Bedrock. Acorn, BabyPie, Allo, and Kinza made up the remaining amount at the end of 2024, while pSTAKE didn’t launch yBTC until Jan. 15, 2025.
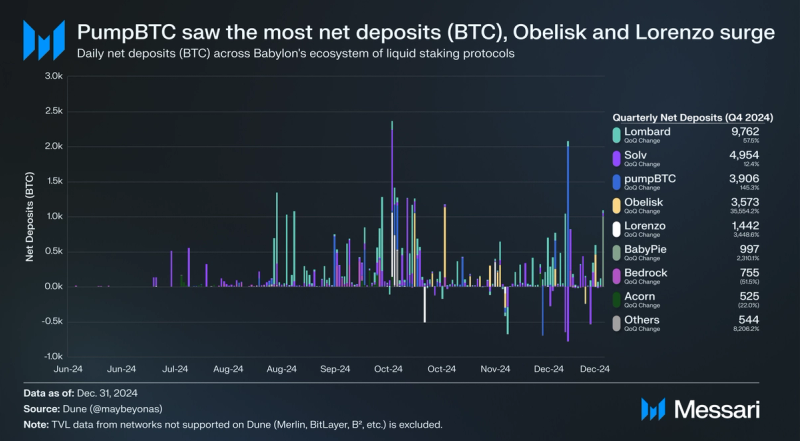
In Q4 2024, quarterly net deposits (BTC) increased for the majority of Babylon’s liquid staking protocols.
- Lombard: 9,762 BTC deposited, up 57.5% QoQ as it maintained its lead in TVL and saw the highest net deposits among all bitcoin liquid staking protocols.
- Lombard’s largest daily net deposits totaled 1,057 BTC on Oct. 4, while its largest daily net withdrawals totaled 378 BTC on Nov. 23.
- Solv: 4,954 BTC deposited, up a modest 12.4% QoQ to remain Babylon’s second largest liquid staking protocol by TVL.
- Solv’s largest daily net deposits totaled 1,170 BTC on Oct. 14, while its largest daily net withdrawals totaled 785 BTC on Dec. 17.
- PumpBTC: 3,906 BTC deposited, up 145.3% QoQ as PumpBTC jumped from 4th to 3rd place in terms of TVL across bitcoin liquid staking protocols.
- PumpBTC’s largest daily net deposits totaled 2,000 BTC on Dec. 17, while its largest daily net withdrawals totaled 700 BTC on Dec. 7.
- Obelisk: 3,573 BTC deposited, up 8,695.5% QoQ as the protocol emerged to become Babylon’s fourth largest liquid staking protocol by TVL.
- Obelisk’s largest daily net deposits occurred on Oct. 17 (1,050 BTC) and Oct. 29 (1,000 BTC).
- Lorenzo: 1,442 bitcoins deposited, up 3,448.6% QoQ as the protocol emerged to become Babylon’s fifth largest liquid staking protocol by TVL.
- Lorenzo’s Q4’24 net deposits originated largely from two consecutive days. Net deposits totaled 912 and 710 BTC on Oct. 8 and Oct. 10, respectively.
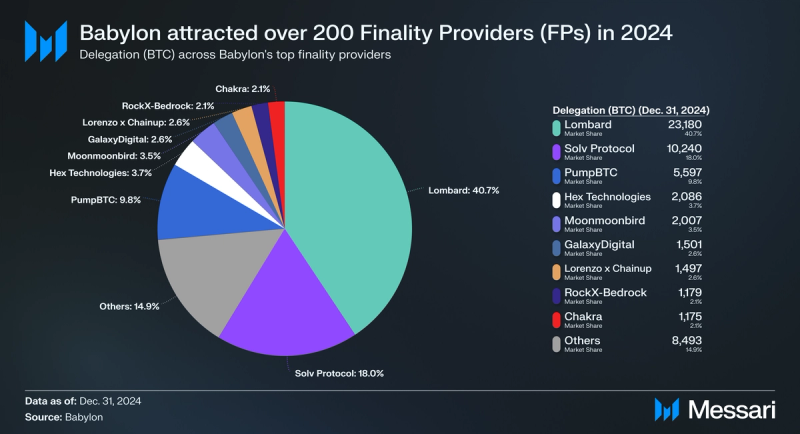
Babylon attracted over 200 Finality Providers (FPs) that garnered delegations in 2024. By the end of the year, the top three FPs were liquid staking protocols that made up 68.5% of Babylon’s total delegated bitcoins. Three of these protocols have garnered significantly more delegations than their own TVL, indicating confidence from users aside from the benefits that liquid staking tokens provide.
- Lombard: Ended Q4’24 with a delegation (BTC) of 23,180 and a delegation dominance of 40.7%. As Babylon’s largest liquid staking protocol by TVL, Lombard is also the FP with the most delegations.
- Lombard’s delegation (BTC) is 45.2% higher than its TVL (BTC) of 15,959, indicating a level of trust placed in the protocol by those that choose to native stake and forego minting LBTC.
- Solv: Ended Q4’24 with a delegation (BTC) of 10,240 and a delegation dominance of 18%.
- Solv’s delegation (BTC) is 32.7% higher than its TVL (BTC) of 7,714, indicating a level of trust placed in the protocol by those that choose to native stake and forego minting SolvBTC.BBN.
- PumpBTC: Ended Q4’24 with a delegation (BTC) of 5,597 and a delegation dominance of 9.8%.
- PumpBTC’s delegation (BTC) is only 1.8% higher than its TVL (BTC) of 5,498, indicating the vast majority of users prefer to mint pumpBTC to earn points and leverage it in DeFi.
Babylon’s Finality Provider diversity score was 13 (i.e., the number of Finality Providers receiving 90% of delegations) at the end of 2024. Real-time TVL data across Babylon, inclusive of all FPs and their delegation amounts, can be seen on the Babylon Staking Dashboard.
Babylon Foundation Delegation ProgramIn December 2024, Babylon Foundation launched a Delegation Program. Babylon Foundation’s Delegation Program will support validators that wish to secure Babylon Genesis upon its launch as Phase-2 commences. Babylon Foundation will delegate stake toward accepted validators, helping to diversify the active set which will comprise the top 100 validators by delegated stake.
Prospective validators were able to apply for delegation by Jan. 31, 2025. The duration of delegation will be six months, after which extensions can be requested for outstanding performers. Notably, validators that operate exclusively as liquid staking protocols, and any validators with delegations that exceed 10% of total delegated amount, are ineligible to join or remain in the program.
Bitcoin Secured NetworksBabylon’s network of Bitcoin Secured Networks (BSNs) continues to grow, reaching 25 in 2024. In Q4 2024, Babylon announced it will be investing in prospective BSNs, and introduced the following BSNs:
- In December 2024, Babylon introduced BOB as a BSN. BOB is an Ethereum Layer-2 network focused on bitcoin-based DeFi with $220 million in TVL (USD) at the end of 2024. BOB’s architecture also leverages BitVM to enable trust-minimized bridges that inherit security from Bitcoin and facilitate interoperability with other Layer-1 networks.
- In December 2024, Babylon introduced Manta Network as a BSN. Manta is a general-purpose Ethereum Layer-2 network with $65 million in TVL (USD) at the end of 2024.
- In December 2024, Babylon introduced BirdLayer (formerly DODOchain) as a BSN. Birdlayer is a trading-focused Arbitrum Layer-3 network with $23 million in TVL (USD) at the end of 2024.
- In December 2024, Babylon introduced LayerEdge as a BSN. LayerEdge is a proof aggregation layer for Bitcoin, aiming to leverage Bitcoin to secure and verify complex computations without executing them directly.
- In November 2024, Babylon introduced Sui as a BSN. Sui is a general-purpose Layer-1 network with $1.7 billion in TVL (USD) at the end of 2024. Sui is based on the MoveVM, whose core technical differentiation is the replacement of accounts with objects.
- In November 2024, Babylon introduced Pell Network as a BSN. Pell Network is an omnichain restaking protocol with $385 million in TVL (USD) at the end of 2024. Pell Network allows liquid staked bitcoin to be restaked to secure Decentralized Validated Services (DVS).
- In October 2024, Babylon introduced Corn as a BSN. Corn is an Ethereum Layer-2 network with $2 million in TVL (USD) at the end of 2024. Corn is focused on bitcoin-based DeFi and utilizes BTCN, a tokenized version of bitcoin, as the network’s gas and rewards token.
- In October 2024, Babylon introduced SatLayer as a BSN. SatLayer is an omnichain restaking protocol that allows liquid staked bitcoin to be restaked to secure Bitcoin Validated Services (BVS).
In Q4 2024, Babylon concluded Phase-1 after opening for bitcoin deposits during Cap-2 and Cap-3. In total, Phase-1 attracted cumulative deposits totaling 57,290 BTC, or 0.29% of Bitcoin’s circulating supply. Compared to bitcoin ETFs, Babylon's protocol had accumulated the third-highest amount of Bitcoin, behind Blackrock and Fidelity.
The majority of Babylon’s bitcoin deposits came from its ecosystem of liquid staking protocols. bitcoin liquid staking protocols announced fundraises totaling over $24 million in Q4’24, with announcements coming from Solv, PumpBTC, Allo, and Lombard. By the end of 2024, 41,032 BTC had been liquid staked, an increase of 181.7% QoQ. Lombard continued to be Babylon’s leading liquid staking protocol, ending 2024 with a TVL of 15,959 BTC, up 157.5% QoQ as LBTC became the 5th largest bitcoin derivative.
By the end of 2024, Babylon’s top three Finality Providers by delegation amount were liquid staking protocols, accounting for 68.5% of total delegations. These protocols included Lombard, Solv, and PumpBTC. In December, Babylon Foundation launched a Delegation Program that will delegate stake toward Babylon Genesis validators. Users can look forward to the commencement of Phase-2 as Babylon Genesis launches and becomes the first Bitcoin Secured Network (BSN).
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.