and the distribution of digital products.
DM Television
Session vs JWT vs OAuth2: The Complete Authentication Strategy
Web application security depends on authentication as its fundamental element. The selection of appropriate authentication mechanisms in modern distributed and hybrid environments requires more than technical expertise because it represents a strategic decision. Whether you’re building an enterprise-grade application, a single-page web app (SPA), or a mobile-first SaaS platform, the decision between session-based authentication, token-based (JWT), and OAuth2 can significantly impact performance, scalability, user experience, and security.
This article evaluates three main authentication techniques through practical examples to support your decision-making process.
\
Session-Based Authentication: The Traditional Powerhouse How It WorksSession-based authentication follows a stateful model where the server maintains complete control over user authentication state. When a user logs in successfully, the server generates a unique session identifier, stores all session data server-side, and sends only the session ID to the client via a secure HTTP cookie.
Architecture Overview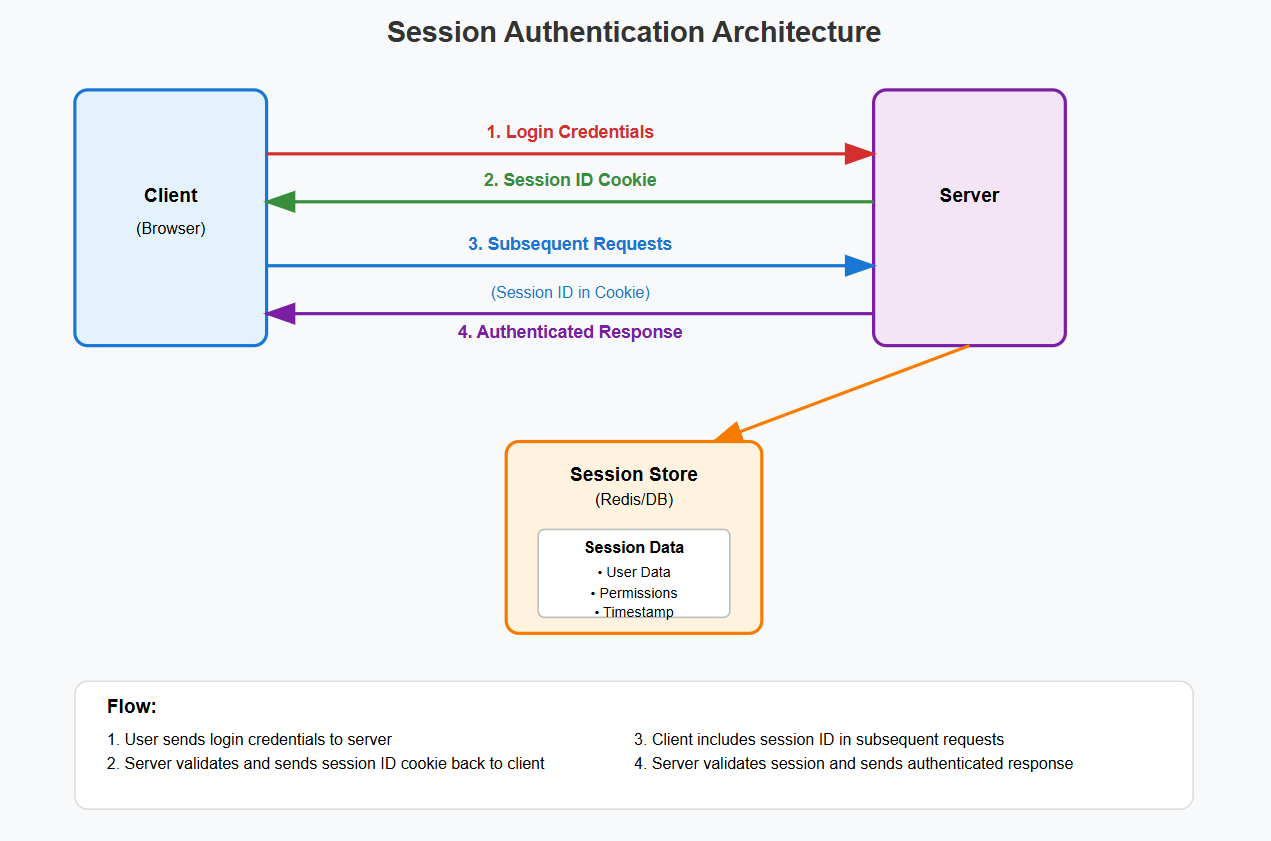
- Simple Implementation: Straightforward to implement and debug.
- Immediate Revocation: Sessions can be instantly invalidated server-side.
- Secure by Default: Sensitive data never exposed to client.
- Framework Support: Excellent built-in support in most web frameworks.
- Scalability Limitations: Requires session synchronization across servers.
- Memory Overhead: Server must store state for all active users.
- Mobile Challenges: Cookie-based approach doesn't work well with mobile apps.
- Load Balancer Complexity: Requires sticky sessions or shared storage.
- Traditional server-rendered web applications.
- Admin dashboards and internal tools.
- Applications requiring immediate session control.
\
JWT Authentication: The Stateless Solution How It WorksJSON Web Tokens provide a completely stateless authentication mechanism. All user information and permissions are encoded directly into a digitally signed token. The server doesn't maintain any session state, everything needed for authentication is contained within the token itself.
Architecture Overview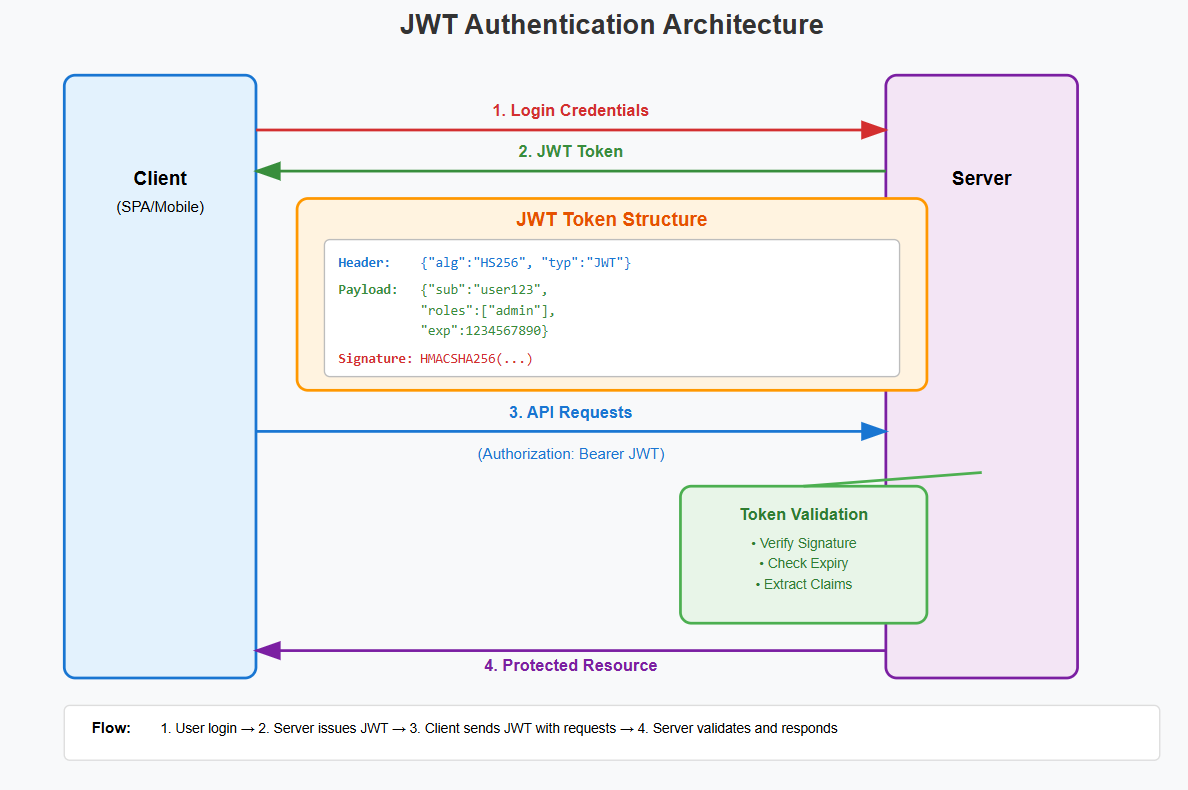
- Stateless: No server-side storage required.
- Highly Scalable: Easy horizontal scaling across multiple servers.
- Mobile-Friendly: Perfect for Single Page Applications and mobile applications.
- Cross-Domain: Works seamlessly across different domains.
- Self-Contained: All necessary information embedded in token.
- Revocation Complexity: Difficult to invalidate tokens before expiration.
- Token Size: Can become large with extensive claims.
- Security Risks: Token theft provides access until expiration.
- Key Management: Requires secure key storage and rotation.
- REST APIs and microservices.
- Single Page Applications (React, Angular) and Mobile applications.
- Cross-domain authentication.
\
OAuth2 with OpenID Connect: The Federation Champion How It WorksOAuth2 with OpenID Connect (OIDC) delegates authentication to trusted external identity providers while maintaining security and user experience. It separates authentication (who you are) from authorization (what you can access), enabling users to login with existing accounts from providers like Google, Microsoft, or GitHub.
Architecture Overview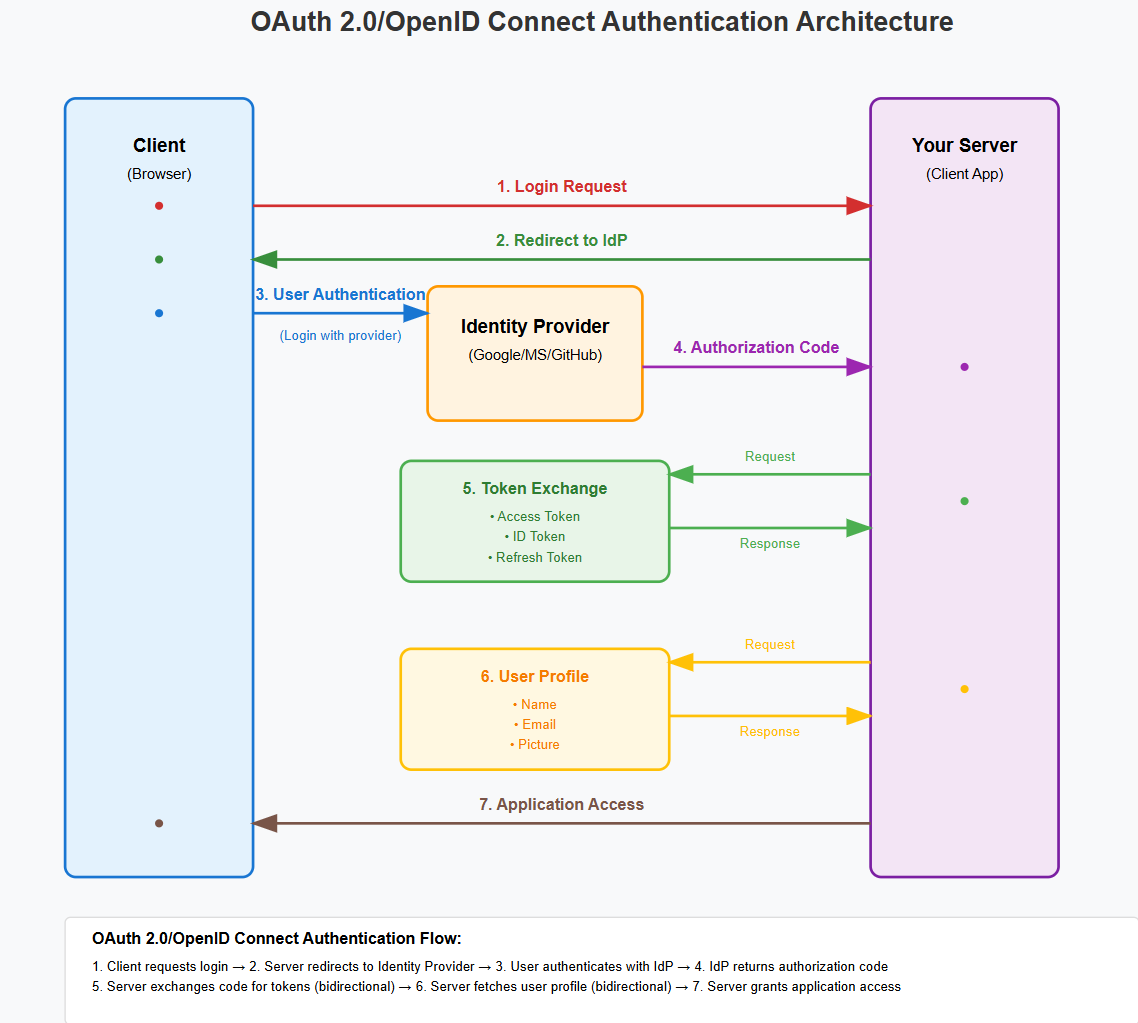
- Enhanced Security: Leverages proven identity providers.
- Superior UX: Users can use existing accounts (Google, Microsoft, etc.).
- Industry Standard: Based on well-established protocols.
- Reduced Liability: Offloads sensitive user data to specialized providers.
- Global Scale: Supports enterprise federation and SSO.
- Implementation Complexity: More complex setup and debugging.
- External Dependencies: Relies on third-party service availability.
- Limited Control: Less control over authentication flow and user data.
- Privacy Concerns: Some users prefer not to use third-party authentication.
- Consumer-facing applications.
- B2B SaaS platforms.
- Enterprise applications requiring SSO.
- Applications needing social login.
- Multi-tenant platforms.
\
Comparison Matrix| Aspect | Session-Based | JWT | OAuth2/OIDC | |----|----|----|----| | Architecture | Stateful | Stateless | Stateless | | Scalability | Medium | High | High | | Token Revocation | Immediate | Complex | Provider-Dependent | | Mobile Support | Limited | Excellent | Excellent | | API Integration | Poor | Excellent | Excellent | | Security Level | High | Medium-High | High | | Implementation | Simple | Medium | Complex | | Best For | Web Apps | APIs/SPAs | Federated Identity | | Storage Requirements | High (Server) | None | Minimal | | Cross-Domain | Limited | Excellent | Excellent | | Maintenance | Low | Medium | Medium-High |
\
Framework for Choosing the Right Strategy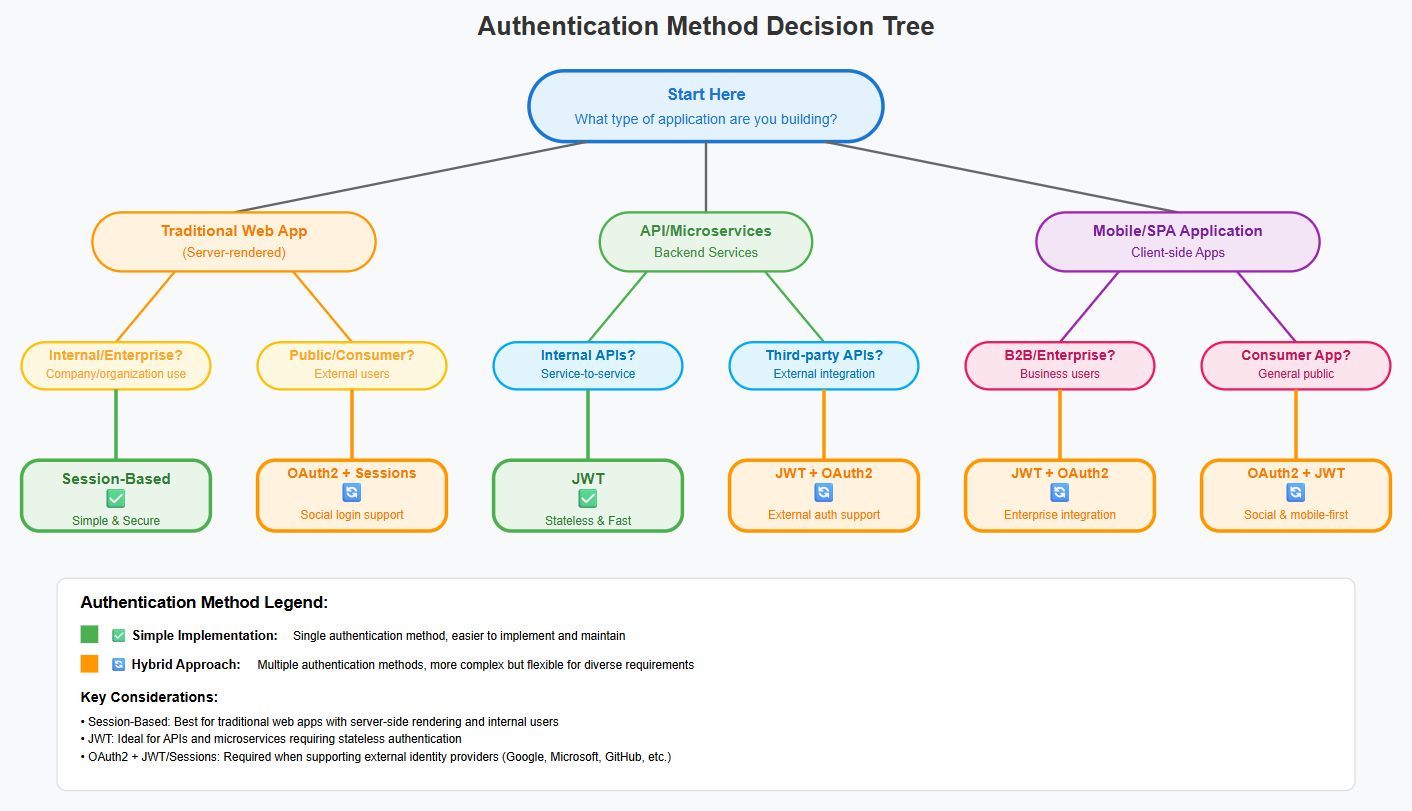
\
- Use Session-Based Auth for traditional MVC apps, secure environments, and where session revocation is critical.
- JWT is ideal for REST APIs, SPAs, mobile apps, and microservices needing stateless and scalable auth.
- OAuth2/OIDC is best for social logins, SSO, and enterprise systems using external identity providers.
- Session-based auth works well when infrastructure supports shared storage and user scale is predictable.
- JWT enables cross-domain auth and suits microservice architectures with minimal backend state.
- OAuth2/OIDC supports multi-source authentication, ideal for consumer-facing and federated identity systems.
- Hybrid strategies are often optimal; combine session, JWT, and OAuth2 based on app modules and user needs.
\
Security Best Practices- Always use HTTPS to encrypt all authentication data in transit.
- Enable rate limiting to block brute force and credential stuffing attacks.
- Implement MFA to add an extra layer of authentication security.
- Log and monitor auth events to detect and respond to suspicious activity.
- Conduct regular security audits to identify and fix vulnerabilities.
- For sessions: Use HttpOnly and Secure flags, enforce timeouts, and prevent fixation.
- For JWT/OAuth2: Use strong signing keys, short expiry, PKCE (OAuth2), and validate state/scope.
\
ConclusionThe selection of appropriate authentication methods remains essential for developing applications which are both secure and scalable and provide good user experience. Traditional web applications require session-based authentication because it provides strong session control and revocation capabilities. The stateless authentication method known as JWT provides scalable authentication solutions which work well for APIs and SPAs and mobile applications. OAuth2/OIDC serves as the ideal solution for SSO and social logins and external identity provider integration.
There’s no universal solution, each method serves different needs:
- Hybrid approaches often provide the best mix of control, scalability, and user experience.
- Always enforce HTTPS, use MFA, and monitor auth events to stay secure.
- Build security into your design, not as an afterthought.
- Review and update your auth strategy regularly based on evolving threats.
- Choose wisely, implement securely, and keep user trust at the core.
\
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.