and the distribution of digital products.
DM Television
Frax Finance Fully Explained! (Use Code – FREE)
In simple layman’s terms, stablecoins are crypto assets pegged to the U.S. dollar.
This is done to ensure price stabilization in the crypto market.
However, recent events due to UST and USDD crashes have created a new fear, and the crypto community is now pondering: Are Stablecoins really stable?
As a result, many attempts have been made to construct more scalable and capital-efficient stablecoins.
Frax Finance is one such project. In this article, we will get a complete idea of Frax Finance.
Summary- Frax Finance is the world’s first fractional-algorithmic stablecoin, where crypto is partially backed by collateral and partially stabilized algorithmically.
- It is an open-source, permissionless, and entirely on-chain, currently on Ethereum and 12 other chains.
- FRAX can be minted and redeemed from the system for $1 of value, allowing arbitragers to balance the demand and supply of FRAX in the open market.
- FRAX can maintain its peg through the expansion and contraction of the supply of the FRAX token. (Similar to Terra/Luna)
- Frax Shares (FXS) is the governance and utility tokens of the entire Frax ecosystem.
- Frax Price Index (FPI) is the second stablecoin of the Frax Finance ecosystem. It is also the first stablecoin that is pegged to the US CPI.
- FPI uses the CPI-U unadjusted 12-month inflation rate reported by the US Federal Government.
- Frax Price Index Share (FPIS) is the governance token of the Frax Price Index (FPI) stablecoin.
- Fraxswap is the first constant automated market maker with an embedded time-weighted average market maker (TWAMM) for conducting large trades fruitlessly over a long period of time.
- Fraxlend is a lending platform that allows anyone to create a market between a pair of ERC-20 tokens.
Frax Finance has described itself to be the world’s first fractional-algorithmic stablecoin where crypto is partially backed by collateral and partially stabilized algorithmically.
It is an open-source, permissionless, and entirely on-chain, currently on Ethereum and 12 other chains. The end goal of the protocol is to provide highly scalable, decentralized, algorithmic money.
Frax ecosystem comprises two stablecoins, i.e., FRAX, which is pegged to the US dollar, and FPI, which is pegged to the US CPI.
Frax Finance Economy comprises its two stablecoins, a native AMM known as Fraxswap and a lending facility known as Fraxlend.
Frax Share (FXS) is the governance token of the entire Frax ecosystem of smart contracts, which accrues fees, profits earned, and excess collateral value.
FPIS is the governance token of the FPI, i.e., Frax Price Index.
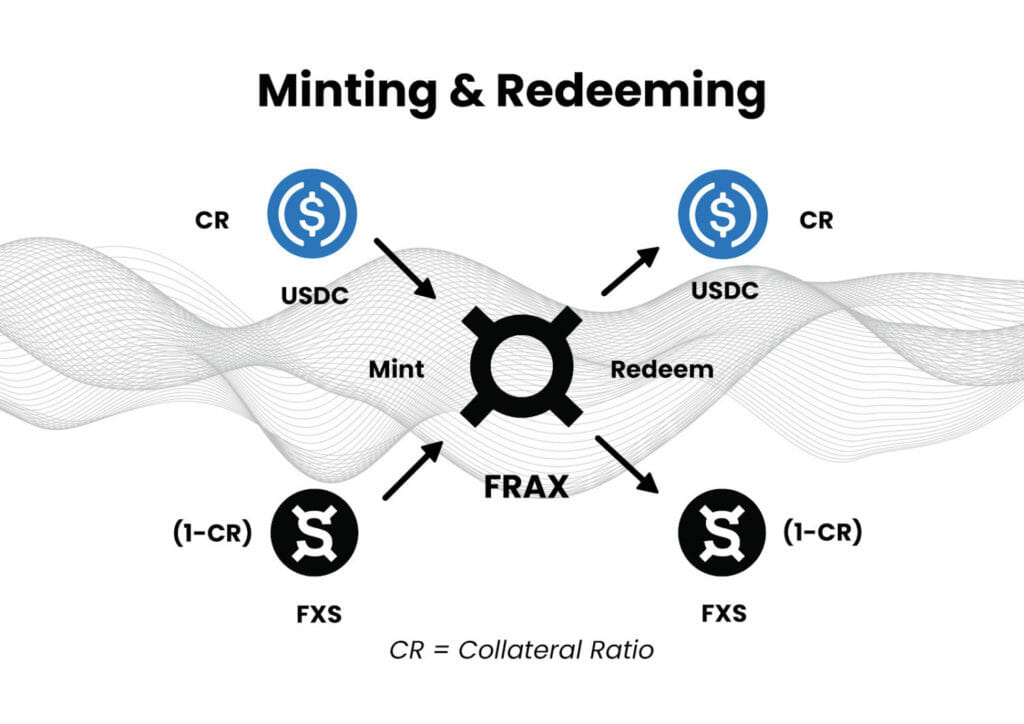
How does Frax Finance Work?FRAX can be minted and redeemed from the system for $1 of value, allowing arbitragers to balance the demand and supply of FRAX in the open market. To mint new FRAX, a user must place $1 worth of value into the system.
So, if we consider USDC as the collateral, then we can say that FRAX is the stablecoin partially collateralized with USDC and algorithmically stabilized by Frax Share (FXS).
The Collateral Ratio (CR) of USDC to FXS is adjusted according to the market demand of FRAX. When FRAX is in the 100% collateral phase, all of the value used to mint FRAX is collateral.
As the protocol moves into the fractional state, some of the value that enters the system during minting becomes Frax Share (FXS), which is then burned.
For example, in a 90% collateral ratio, every FRAX minted requires $0.90 of collateral and burning $0.10 of FXS. Here is a quick illustration that explains the minting and redeeming of Frax.
 Frax
Frax
All FRAX tokens are fungible with one another and entitled to the same proportion of collateral no matter what collateral ratio they were minted at.
FRAX can maintain its peg through the expansion and contraction of the supply of the FRAX token.
- Expansion: If the market price of FRAX is above the price target price of $1, then there is an arbitrage opportunity to mint FRAX with USDC and FXS according to the Collateral Ratio and market and then sell the FRAX. As a result, this increases the supply of FRAX in the market. Here, extra profit is distributed to FXS holders. Also, the protocol will decrease the Collateral Ratio, which reduces the amount of FRAX backed by USDC.
- Contraction: If the market price of FRAX is below the target price of $1, then there is an arbitrage opportunity to buy FRAX and redeem the FRAX for USDC and newly minted FXS according to the Collateral Ratio. As a result, this reduces the supply of FRAX on the market. Also, the protocol will increase the Collateral Ratio, increasing the amount of FRAX backed by USDC. So, each FRAX must be supported by a higher percentage of collateral, i.e., USDC. This action increases market confidence that Frax can maintain its backing, causing the price to rise.
Frax Shares (FXS) is the governance and utility token of the entire Frax ecosystem. It is also used for the algorithmic stabilizing of the FRAX price peg. As demand increases for FRAX, more FXS will be burnt than minted, which results in FXS supply being deflationary. However, the opposite can also happen where demand for FRAX decreases, and more FXS will be minted, resulting in FXS supply being inflationary.
Frax funnels the profits directly into the FXS token that the protocol generates from seigniorage, i.e., profit generated by Frax Finance by issuing Frax, which is the difference between the actual market value and production costs. As we know, FXS’s price is volatile, but its supply is hard capped to 100 million.
Therefore, this funneling of profit will increase the FXS price in the long run. So, if there is an increase in FRAX liquidity and usage in the DeFi space, its profit will increase. As a result, the price of FXS will also increase.
veFXS is a vesting & yield system which is based on Curve’s veCRV mechanism. Users can lock their FXS for up to 4 years four times & the amount of veFXS, i.e., 100 FXS locked for four years, will return 400 veFXS. However, it is not a transferable token, nor does it trade on liquid markets.
Frax Finance: What is an AMO?AMO stands for Algorithmic Market Operations Controller, i.e., an autonomous contract(s) that can perform open market operations algorithmically to maintain FRAX’s peg. It cannot arbitrarily mint FRAX from thin air and break its peg. Also, this keeps FRAX’s base layer stability mechanism pure and untouched.
In Frax v1, there was only a single AMO, referred to as a base stability mechanism. In Frax v1, the collateral ratio of the protocol was dynamically rebalanced based on the market price of the FRAX stablecoin. If the price of FRAX was above $1, then the collateral ratio decreases, i.e., decollateralization. If the price of FRAX is below $1, then the CR increases, i.e., recollateralization. This decollateralization and recollateralization help find an equilibrium reserve requirement for the protocol to keep a very tight peg and maximize the capital efficiency of money creation.
In Frax v2, we have multiple AMOs, where each AMO is like a central bank money lego with 4 properties;
- Decollateralization (if FRAX>$1): – Lowers the Collateral Ratio
- Equilibrium (if FRAX=$1): – Doesn’t change the Collateral Ratio
- Recollateralization (if FRAX<$1): – Increases the Collateral Ratio
- FXS1559: It calculates all excess value in the system above the collateral ratio and uses this value to buy FXS for burning.
Curve is an AMM that specializes in stablecoin liquidity pools. According to DeFiLama, it currently holds around $6.04 billion in TVL, which is the 4th highest among all the DeFi protocols, i.e., just after MakerDAO, LiDO, and Uniswap.
Hundreds of liquidity pools have been launched through Curve’s factory and incentivized by Curve’s DAO. Users rely on Curve’s proprietary formulas to provide high liquidity, low slippage, and low fee transactions among ERC-20 tokens.
Curve has created a business model of liquidity as a service. It incentivizes liquidity by offering high APY to stablecoin holders in exchange for staking their coins on Curve.
It offers yield for stablecoin staking up to 20% in the form of its native token CRV, which can then be staked for a compounded yield of up to 50% or locked for a period of time to earn reCRV, i.e., the Curve’s governance token.
Governance votes in Curve decide which stablecoin pools receive the highest APY yield. A higher APY incentivizes more people to stake their assets in that pool and increase its liquidity.
Convex Finance is the most dominant on Curve Finance as it has the largest share of the CRV token, which is used to vote on which pools get the highest APY rewards. It uses Votium, which allows protocols to pay bribes to CVX holders in exchange for their votes to direct APY to the liquidity pool of choice.
FRAX pays more bribes on Votium than any other stablecoin protocol. As a result, Frax is using Curve to increase the APY of FRAX pools to increase its liquidity. More liquidity means less slippage and lower costs for trading their token. In addition, maintaining large liquidity pools of FRAX with attractive APY rewards helps maintain the coin’s peg to the USD.
Frax Finance: Frax Price Index (FPI)Frax Price Index (FPI) is the second stablecoin of the Frax Finance ecosystem.
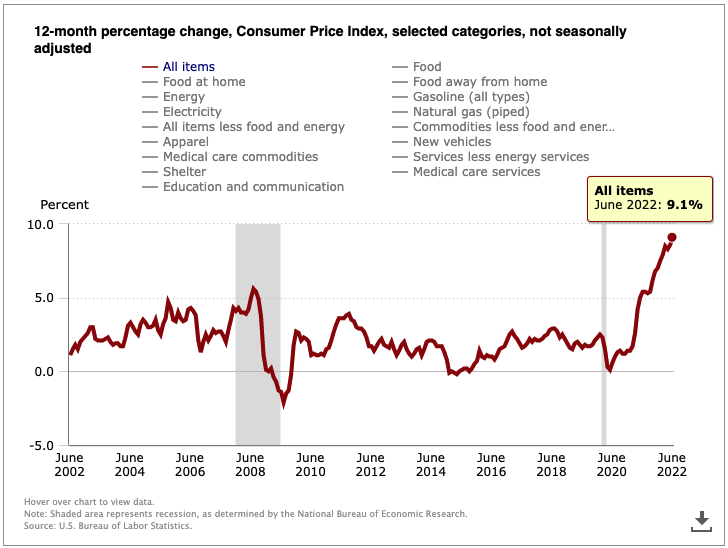
It is also the first stablecoin that is pegged to the US CPI. Consumer Price Index or CPI is a measure of the average change over time in the prices urban consumers pay for a market basket of consumer goods and services.
It is intended to keep its price constant to the price of all items within the CPI basket and thus hold its purchasing power with on-chain stability mechanisms.
Furthermore, it aims to be the first on-chain stablecoin to have its unit of account derived from a basket of goods, i.e., both crypto and non-crypto.
 CPI Graph
CPI Graph
FPI uses the CPI-U unadjusted 12-month inflation rate reported by the US Federal Government.
A specialized Chainlink oracle commits this data on-chain immediately after it is publicly released. The oracle’s reported inflation rate is then applied to the redemption price of FPI in the system contract.
This redemption price grows per second on-chain or declines in rare cases of deflation. The peg calculation rate is updated once every 30 days when bls.gov releases its monthly CPI price data.
So, when buying FPI stablecoins for another asset like SOL, the trader assumes that CPI purchasing power is growing faster over time than the sold SOL. Likewise, if selling FPI for SOL, the trader believes that SOL growth is outpacing the CPI inflation rate of the US Dollar.
Users can mint FPI with FRAX or redeem FPI for FRAX. There is a small fee associated, i.e., 0.3%. twammToPeg function is used by the protocol to introduce market pressure to bring the market price of FPI up or down to the target peg price.
Frax Price Index Share (FPIS) is the governance token of the Frax Price Index (FPI) stablecoin. Its tokens supply is hard capped to 100 million tokens. Here is the token distribution:
- 35% of FPIS is allocated to Frax Finance Treasury
- 30% of FPIS is allocated to FPI Protocol Treasury
- 25% of FPIS is allocated to Core Developers & Contributors
- 10% of FPIS is allocated to February 2022 Airdrop to FXS Holders
veFPIS is a vesting & yield system for the FPIS governance token. Users can lock their FPIS for up to 4 years for four times & the amount of veFPIS, i.e., 100 FPIS locked for four years, will return 400 veFPIS. It is not a transferable token, nor does it trade on liquid markets.
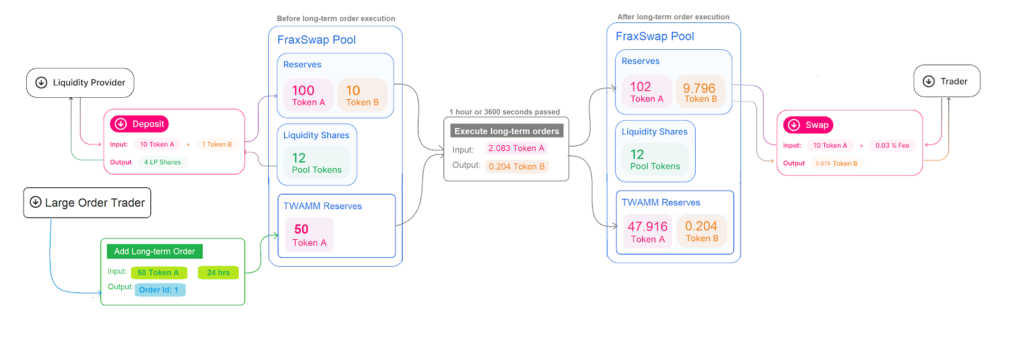
Frax Finance: FraxswapFraxswap is the first constant product automated market maker with an embedded time-weighted average market maker (TWAMM) for conducting large trades over a long period of time trustlessly.
Furthermore, it is a fully permissionless AMM, meaning other protocols can create their LP pairs in any token and use it. The core AMM is based on Uniswap V2.
The goal was to create a unique AMM with specialized features for algorithmic stablecoin monetary policy, forward guidance, and large sustained market orders to stabilize the price of one asset by contracting its supply or acquiring specific collateral over a prolonged period.
Here is a quick illustration of how Fraxswap works.
 Fraxswap
Fraxswap
Fraxswap is the first live TWAMM implementation.
Time-Weighted Automated Market Maker (TWAMM) is to help traders execute large orders with minimal slippage and low gas fees.
Let’s see an example to understand how it works. So, when large traders want to buy an asset, like $20 million worth of Shiba INU coin, they cannot just execute that as one trade as it will increase the market price by a large number. But, they will use a trading desk or an algorithm to break down the $20 million order into smaller orders of $1,000 across many hours or days to have less impact on price in the market.
The TWAMM tries to emulate this strategy by breaking up orders into a combination of an almost infinite number of small orders via an automated market maker (AMM) over a period of time.
However, this method can also result in prices deviating from the crypto market as a whole. So, it relies on arbitrage traders to mitigate this issue by trading against the AMM’s price to return it to the market price, ensuring effective execution for long-term orders.
This new approach will help traders execute large orders efficiently over hours, weeks, or days without going to a CEX or some trading desk.
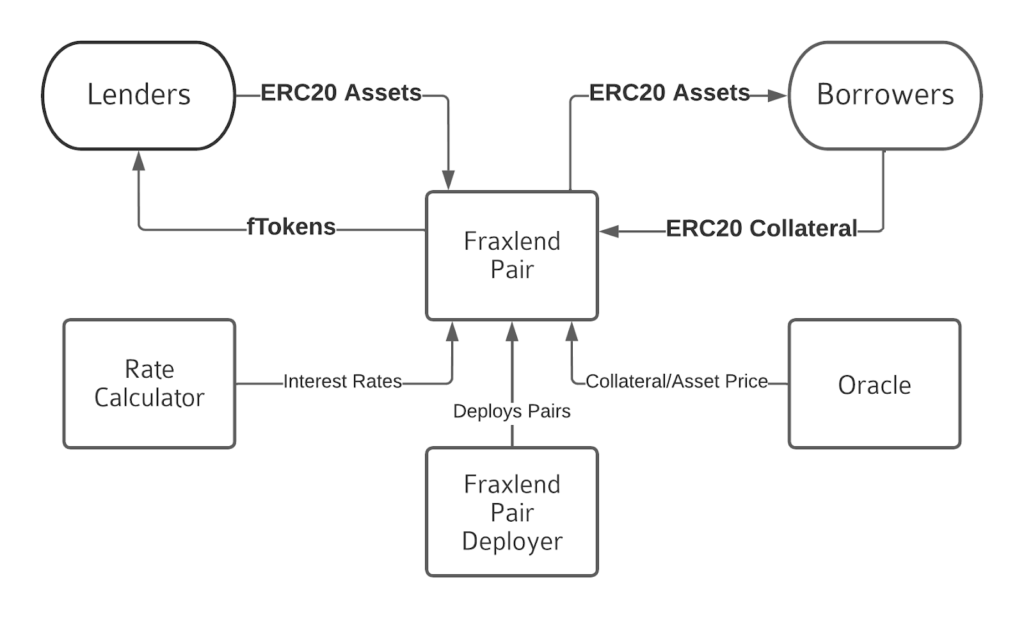
Frax Finance: FraxlendFraxlend is a lending platform that allows anyone to create a market between a pair of ERC-20 tokens. Any token part of a Chainlink data feed can be lent to borrowers or used as collateral.
It also adheres to the EIP-4626: Tokenized Vault Standard. This standard allows for implementing a standard API for tokenized Vaults representing shares of a single underlying ERC-20 token.
It is an extension of the ERC-20 token standard that provides basic functionality for depositing and withdrawing tokens and reading balances. Here is a quick illustration below to understand how Fraxlend works.
 Fraxlend
Fraxlend
- Step 1: Lenders deposit Asset Tokens into the Pair and receive fTokens. fTokens are ERC-20 tokens and are redeemable for Asset Tokens. At any time, a Lender can exchange their fTokens for the underlying Asset Tokens at the rate given by the current price. The fToken Share Price increases as more interest are accrued.
- Step 2: Borrowers can borrow Asset Tokens by depositing a different ERC-20 token, i.e., known as the Collateral Token. To receive their collateral back, a borrower must return the original loan amount plus all accrued interest.
All these processes can be performed with three essential elements. These three elements are:
- Chainlink Oracles: It helps to determine the current market rate for both the Asset Token and the Collateral Token.
- Rate Calculator: It calculates the interest rate.
- Fraxlend Pair Deployer: The contract helps in the deployment of pairs.
The supply of the FRAX stablecoin is dynamic and constantly changing to keep the price at $1 due to its fractional-algorithmic monetary policy. But, the Frax Shares (FXS) tokens supply is hard capped to 100 million tokens. Here is the Frax Shares (FXS) token distribution:
- 65% of FXS, i.e., 65 million FXS is for the Community: DeFi Protocols have used liquidity programs to jumpstart growth and distribute protocol tokens to community members. Out of these, 65%;
- 60% of FXS is used by Liquidity Programs, Farming & Community
- 5% of FXS is used on Project Treasury, Grants, Partnerships & Security-Bug-Bounties via Team and Community discretion.
- 35% of FXS, i.e., 35 million FXS, is for the Team & Investors: Out of these 35%;
- 20% of FXS is allocated to Team, Founders & Early Project Members who have been involved in the project since 2018.
- 3% of FXS is allocated to Strategic Advisors & Outside Early Contributors who helped in legal, technical, and business efforts to advance the adoption of the Frax Finance.
- 12% of FXS is allocated to accredited Private Investors.
Frax Finance was audited in November 2020 by the Certik Team. Certik Team has given them a trust score of 88/100, security score of 86/100, and market & community score of 95/100. So, according to Certik Team Project is Relatively Decentralized.
Later, Frax Finance was audited two times by Trail of Bits in June and December 2021. This project is now under an ongoing audit by the Trail of Bits and Shipyard Team, which started in April 2022.
Frax Finance also provides one of the largest bounties. The bounty is calculated as the lower value of 10% of the total possible exploit or $10M paid in FRAX and FXS, which is evenly split. This bounty does not cover any front-end bugs. It is only for smart contract code.
Frax Team is also offering a bug bounty of up to 15% of the TVL at risk, which is payable in FRAX to anyone that discovers and discloses a catastrophic bug that causes any infinite mints, Insta-drain of FraxSwap TWAMM token0/token1 reserves and Insta-drain of FPIControllerPool FRAX reserves in FraxSwap or FPI.
How to Buy Frax on a Crypto Exchange like Gate.io?Gate.io is one of the earliest crypto exchange platforms, which provides traders with numerous options for cryptocurrencies and various other financial services like margin lending or borrowing. In this section, we will learn how to buy Frax on a Centralized Exchange like Gate.io.
- Step 1: Go to the official Gate.io website and Create an account with an email id and phone number. Then, complete the verification process to log into the account successfully.
 Login/Signup
Login/Signup
- Step 2: Now, Click on Trade and then, Click on Spot.
 Click on Spot
Click on Spot
- Step 3: We will be directed to the Trade BTC/USDT page. So before buying FRAX, we should have USDT or ETH in our wallet. Now, Search Frax with a search option on the left-hand side of the screen.
 Search FRAX
Search FRAX
- Step 4: Now, our trade pair will be changed to Trade FRAX/USDT. Now, we can easily buy or sell FRAX with USDT or ETH.
 Buy/Sell FRAX
How to Buy Frax on a Decentralized Exchange Like Uniswap?
Buy/Sell FRAX
How to Buy Frax on a Decentralized Exchange Like Uniswap?
Uniswap is one of the most popular Decentralized exchanges. In this section, we will learn how to buy Frax on a Decentralized Exchange like Binance.
- Step 1: We need an Ethereum Wallet like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, etc., and some ETH. Go to the Uniswap interface. Then, click the Connect Wallet option in the upper right corner and log in with the wallet.
 Connect Wallet
Connect Wallet
- Step 2: We will see four wallet options, i.e., MetaMask, WalletConnect, Fortmatic, and Coinbase Wallet. This article will use MetaMask Wallet, one of the most widely used crypto wallets. Now, Click on Select a token.
 Select a Token
Select a Token
- Step 3: Now, Search Frax token and Click on Import via CoinmarketCap.
 Search FRAX
Search FRAX
- Step 4: Enter the amount and press the swap button. A transaction preview window will open, and we need to confirm the transaction on our MetaMask wallet. Our tokens will then appear in our MetaMask wallet. We can track its progress by copying and entering the transaction ID into Etherscan.
 Swap FRAX
Frax Finance: How to Buy Frax Shares (FXS) on a Centralized Exchange like Binance?
Swap FRAX
Frax Finance: How to Buy Frax Shares (FXS) on a Centralized Exchange like Binance?
Binance is the world’s leading centralized cryptocurrency exchange. In this section, we will learn how to buy Frax Shares (FXS) on a Centralized Exchange like Binance.
- Step 1: Go to the official Binance website and Create an account with an email id and phone number. Complete the verification process to log into the account successfully.
 Login/Signup
Login/Signup
- Step 2: Now, Click on Trade and then, Click on Spot.
 Click on Spot
Click on Spot
- Step 3: We will be directed to the Trade BTC/USDT page. So before buying Frax Shares (FXS), we should have USDT, BUSD, or BTC in our wallet. Now, Search Frax Shares (FXS) with a search option on the right-hand side of the screen.
 Search FXS
Search FXS
- Step 4: The trading pair will be changed to Trade FXS/USDT. So now, we can easily buy or sell Frax Shares (FXS) with USDT, BUSD, or ETH.
 Buy/Sell FXS
Frax Finance: How to Buy Frax Shares (FXS) on a Decentralized Exchange Like 1inch?
Buy/Sell FXS
Frax Finance: How to Buy Frax Shares (FXS) on a Decentralized Exchange Like 1inch?
1inch is a DEX aggregator that connects many DEXes into a single platform, allowing users to locate the most economical exchanging routes across all platforms. In this section, we will learn how to buy Frax Shares (FXS) on a Decentralized Exchange like 1inch.
- Step 1: We need an Ethereum Wallet like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, etc., and some ETH. Go to the 1inch interface. Then, click the Connect Wallet option in the upper right corner and log in with the wallet.

- Step 2: Click on I read and accept. Choose the Network, i.e., Ethereum and Choose the wallet, i.e., Metamask in the popup window.
- Step 3: Now, Search Frax Shares (FXS) token.
- Step 4: Enter the amount and press the swap button. A transaction preview window will open, and we need to confirm the transaction on our MetaMask wallet. Our tokens will then appear in our MetaMask wallet. We can track its progress by copying and entering the transaction ID into Etherscan.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Frax finance is a very new project and has to be battle tested. However, it successfully replicated the central banking’s fractional reserve model on the blockchain. Furthermore, because it combines both collateralized stablecoin and algorithmic stable, it hits the perfect balance of asset usability and risk associated with it. In Addition, FXS shares are not only a governance token but also accrue value from the protocol profit; therefore, if FRAX has good adoption, we will see FXS going over $100 in the next few years.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Will Frax coin suffer the same fate as UST and USDD?No one knows what will happen to Frax Finance in the future as no one expected the Terra-Luna Crash and USDD Crash. However, Frax Finance is a promising stablecoin project, and we will have to wait to see what future it will bring.
Who is behind Frax Finance?Frax Finance was created by Iranian-American Software Developer Sam Kazemian, who proposed a fractional algorithmic stablecoin in 2019. The founding team also includes Travis Moore and Jason Huan.
Is it possible to use Frax on Polkadot?Frax team has deployed their protocol to Moonbeam, i.e., the Ethereum-compatible smart contract platform on Polkadot. After the integration, its stablecoin can be minted natively on Polkadot. This integration will allow users and teams in the Polkadot and Moonbeam ecosystems to access highly scalable, stable, and on-chain money. The addition of Frax Protocol on Moonbeam continues to solidify Moonbeam’s rapidly growing DeFi ecosystem.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.