and the distribution of digital products.
Deductive Verification with Natural Programs: Case Studies
:::info Authors:
(1) Zhan Ling, UC San Diego and equal contribution;
(2) Yunhao Fang, UC San Diego and equal contribution;
(3) Xuanlin Li, UC San Diego;
(4) Zhiao Huang, UC San Diego;
(5) Mingu Lee, Qualcomm AI Research and Qualcomm AI Research
(6) Roland Memisevic, Qualcomm AI Research;
(7) Hao Su, UC San Diego.
:::
Table of LinksMotivation and Problem Formulation
Deductively Verifiable Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Conclusion, Acknowledgements and References
\ A Deductive Verification with Vicuna Models
C More Details on Answer Extraction
E More Deductive Verification Examples
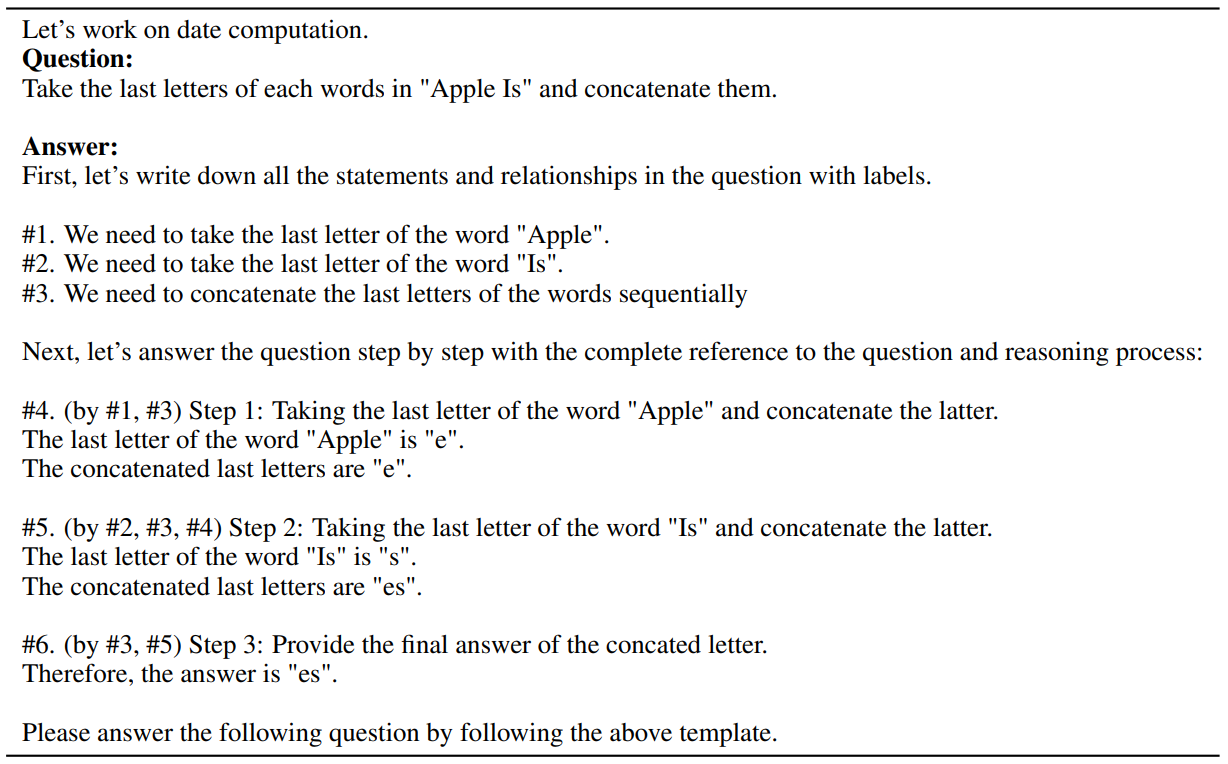
E More Deductive Verification ExamplesIn this section, we present more deductive verification examples using our Natural Program-based approach on single reasoning steps.
\ In Tab. 18, we demonstrate that the language model (ChatGPT) not only successfully identifies ungrounded information, but also identifies logical errors within the given solutions.
\ In Tab. 19, we illustrate a case where the language model fails to detect ungrounded premise numbers, mistakenly assuming that these numbers can be derived from grounded ones.
\ Lastly, in Tab. 20, we illustrate a case where the language model is sometimes unable to correctly identify grounded numbers.
\

\

\

\

\
\

\

\

\

\
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.