and the distribution of digital products.
DM Television
Behind Every Question-Answer AI Is a Data Pipeline Built for Scale — Here's How to Build Your Own
In this article, we’ll explore how to build a data pipeline that continuously indexes document embeddings into a Redis vector database. This solution leverages various Google Cloud services, including Cloud Storage, CloudSQL, Cloud Composer (Airflow), and Cloud Run, along with LangChain, OpenAI, and Redis as the vector store. The indexed documents can then be utilized in an RAG based question-answering system.
Section 1: Solution Overview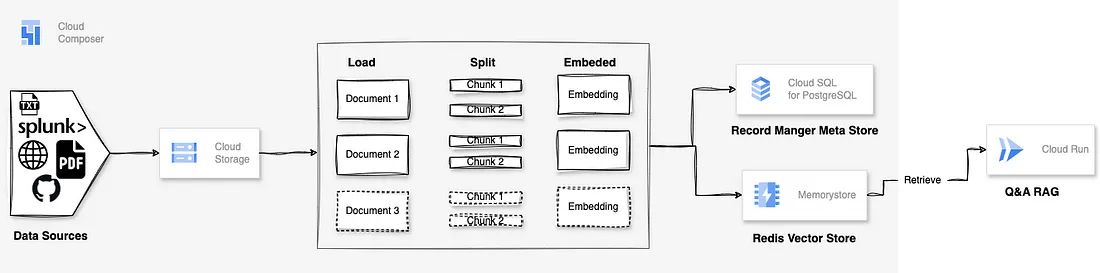
- GCP Storage Bucket: Serves as the central repository for all document types, such as PDFs, text files, and HTML .
- Document Ingestion: Collects newly created documents and stores them in the GCP Storage bucket.
- Airflow (Cloud Composer) as the Orchestrator: Automates and manages the entire workflow on a daily basis. Tasks are implemented using Google Cloud Run Operators.
\ Airflow Tasks:
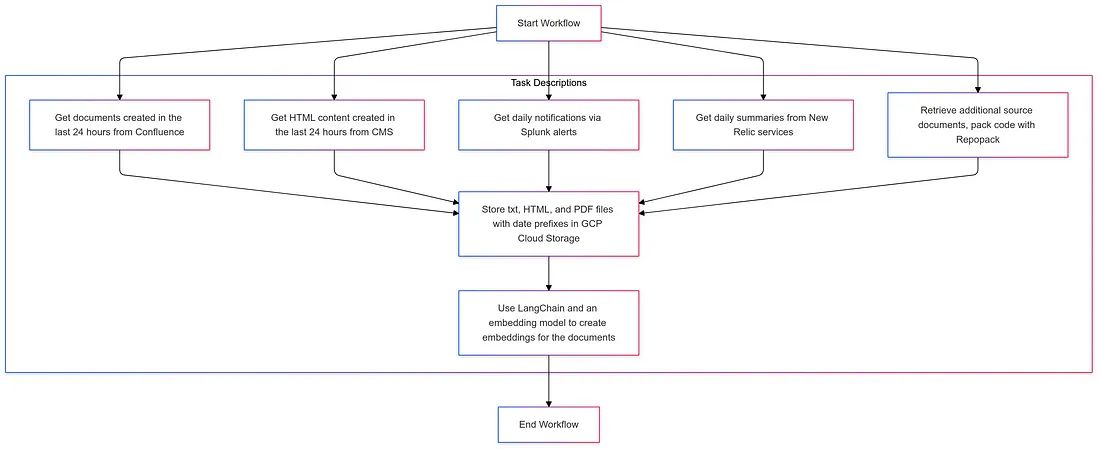
- Get documents from Confluence created in the last 24 hours.
- Get HTML content created from the organization’s CMS in the last 24 hours.
- Get daily process notifications from Splunk alerts (webhook).
- Get daily summaries from specific services in New Relic.
- Retrieve documents from additional sources, such as source code from git repo, and use Repopack to bundle each repository’s code (*.py , *.java) into a single txt file.
- Save txt, html, and pdf files generated from the above tasks in GCP Cloud Storage with daily or hourly date-time prefixes.
- Use LangChain and an embedding model (e.g. OpenAI’s embedding API) to create embeddings for the documents.
\
 4. Document Embeddings with LangChain and OpenAI: Embed and index documents using LangChain’s RecordManager in incremental mode. LangChain’s RecordManager offers two modes for indexing: incremental and full. Both modes provide automated cleanup:
4. Document Embeddings with LangChain and OpenAI: Embed and index documents using LangChain’s RecordManager in incremental mode. LangChain’s RecordManager offers two modes for indexing: incremental and full. Both modes provide automated cleanup:
- If the content of the source document or derived documents has changed, both incremental and full modes will clean up (delete) previous versions of the content.
- If the source document has been deleted (meaning it is not included in the documents currently being indexed), the full cleanup mode will delete it from the vector store correctly, but the incremental mode will not.
- Redis Vector Store: Store the embeddings for future search and retrieval tasks.
- Web App hosted in Cloud Run:
- Use LangChain and Streamlit to build a question-answering web app based on the indexed documents.
- Utilize a document retriever and a LLM model (e.g ChatGPT) to generate answers.
To test this document indexing and Q&A approach locally, we’ll set up a Docker environment with Redis and PostgreSQL as the core storage components. This PoC will include scripts to simulate data ingestion, embedding, and retrieval functionalities. Additionally, we’ll create sample documents in a dedicated folder to act as the initial content, simulate data ingestion from Confluence with a fetch_confluence_pages.py script, index documents with document_indexer.py, and implement a basic Q&A functionality using main.py.
\n Project Structure
Here’s how the project structure will look:
project-folder/ ├── docker-compose.yml ├── documents/ │ ├── doc1.html │ ├── doc2.txt │ └── doc3.txt ├── fetch_confluence_pages.py ├── document_indexer.py └── main.py Step 1: Create Sample DocumentsCreate a local directory named documents and place some sample text files there.
mkdir documents cd documents echo "This is a sample document about AI." > doc2.txt echo "Another document related to machine learning." > doc3.txt cat <Understanding LLM Parameters
LLM parameters, often referred to as weights, are crucial for the model's ability to understand and generate human-like text. They are fine-tuned during training to minimize errors in predictions, ensuring that the model responds accurately to a wide range of inputs.
EOF Step 2: Set Up Docker Compose for Redis and PostgreSQLTo create the local environment, use Docker Compose to set up Redis and PostgreSQL. This setup will help you test the document indexing pipeline with vector embedding storage and metadata storage for RecordManager.
Create a docker-compose.yml file:
version: '3.8' services: postgres: image: postgres:15 container_name: local-postgres restart: always environment: POSTGRES_USER: myuser POSTGRES_PASSWORD: mypassword POSTGRES_DB: mydb ports: - "5432:5432" volumes: - postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data networks: - app-network redis: image: redis/redis-stack:latest container_name: local-redis restart: always ports: - "6379:6379" volumes: - redis_data:/data networks: - app-network volumes: postgres_data: driver: local redis_data: driver: local networks: app-network: driver: bridgethen run:
docker-compose up -d Step 3: Install Required Libraries langchain==0.3.4 langchain-community==0.3.3 langchain-core==0.3.13 langchain-openai==0.2.3 langchain-redis==0.1.1 psycopg2-binary pypdf dotenv unstructured #rank_bm25 Step 4: fetch_confluence_pages.py – Data ingestion from Confluence (optional)This script fetches documents from Confluence and stores them in the documents folder. It connects to Confluence’s REST API to retrieve pages created within the last 24 hours.
fetch_confluence_pages.py
import os from dotenv import load_dotenv import logging import requests from google.cloud import storage from datetime import datetime, timedelta from typing import List, Dict, Optional, Tuple import base64 from urllib.parse import quote from pathlib import Path load_dotenv() # Configure logging logging.basicConfig( level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s' ) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) CONFLUENCE_DOMAIN = os.getenv('CONFLUENCE_DOMAIN') CONFLUENCE_API_USER = os.getenv('CONFLUENCE_API_USER') CONFLUENCE_EMAIL = os.getenv('CONFLUENCE_EMAIL') CONFLUENCE_API_TOKEN = os.getenv('CONFLUENCE_API_TOKEN') GCP_BUCKET_NAME = os.getenv('GCP_BUCKET_NAME') google_credentials_path = os.getenv('GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS') LOCAL_DOCUMENTS_DIR = 'documents' CONFLUENCE_BASE_URL = f"https://{CONFLUENCE_DOMAIN}" def get_auth_headers(): """Generate the authentication headers for Confluence API.""" auth_string = f"{CONFLUENCE_EMAIL}:{CONFLUENCE_API_TOKEN}" auth_bytes = auth_string.encode('ascii') base64_auth = base64.b64encode(auth_bytes).decode('ascii') return { 'Authorization': f'Basic {base64_auth}', 'Accept': 'application/json' } def validate_environment() -> bool: """Validate that all required environment variables are set.""" required_vars = [ 'CONFLUENCE_DOMAIN', 'CONFLUENCE_EMAIL', 'CONFLUENCE_API_TOKEN', 'GCP_BUCKET_NAME', 'GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS' ] missing_vars = [var for var in required_vars if not os.getenv(var)] if missing_vars: logger.error( f"Missing required environment variables: {', '.join(missing_vars)}") return False return True def get_storage_client() -> Optional[storage.Client]: """Initialize and return GCP storage client.""" try: return storage.Client() except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Failed to initialize GCP storage client: {str(e)}") return None def get_date_folders() -> Tuple[str, str]: """ Get the folder paths for storing files. Returns both the GCS path and the date string for the CQL query. """ yesterday = datetime.now() - timedelta(days=1) folder_date = yesterday.strftime('%Y-%m-%d') gcs_folder = f"documents/{folder_date}" return gcs_folder, folder_date def fetch_new_confluence_pages() -> None: """Fetch new Confluence pages and save them to GCP Storage.""" if not validate_environment(): return storage_client = get_storage_client() if not storage_client: return try: # Get folder paths gcs_folder, query_date = get_date_folders() # Get bucket and list existing pages bucket = storage_client.bucket(GCP_BUCKET_NAME) logger.info(f"Storing files in folder: {gcs_folder}") # Construct CQL query cql_query = quote(f"type=page and created >= '{query_date}'") url = f"{CONFLUENCE_BASE_URL}/wiki/rest/api/content/search?cql={cql_query}&expand=body.storage" logger.info(f"Requesting URL: {url}") # Using headers for authentication headers = get_auth_headers() response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=30) # Debug logging logger.info(f"API Response Status: {response.status_code}") if response.status_code != 200: logger.error(f"API Response: {response.text}") response.raise_for_status() pages = response.json().get('results', []) logger.info(f"Found {len(pages)} pages to process") processed_count = 0 skipped_count = 0 for page in pages: try: was_processed = process_single_page( page, bucket, headers, gcs_folder) if was_processed: processed_count += 1 else: skipped_count += 1 except Exception as e: logger.error( f"Failed to process page {page.get('id', 'unknown')}: {str(e)}") continue logger.info( f"Processing complete. Processed: {processed_count}, Skipped: {skipped_count}") except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e: logger.error(f"Failed to fetch Confluence pages: {str(e)}") logger.error( f"Response content: {getattr(e.response, 'text', 'No response content')}") except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Unexpected error: {str(e)}") def process_single_page(page: Dict, bucket: storage.Bucket, headers: Dict, folder_path: str) -> bool: """ Process a single Confluence page and save it to GCP Storage. Returns True if page was processed, False if skipped. """ page_id = page['id'] title = page['title'] # Sanitize filename safe_title = "".join(c for c in title if c.isalnum() or c in (' ', '-', '_')).rstrip() filename = f"{safe_title}.html" logger.info(f"Processing page: {safe_title} (ID: {page_id})") content_url = f"{CONFLUENCE_BASE_URL}/wiki/rest/api/content/{page_id}?expand=body.storage" content_response = requests.get(content_url, headers=headers, timeout=30) content_response.raise_for_status() content = content_response.json()['body']['storage']['value'] # Save content to GCP Storage with metadata blob = bucket.blob(f"{folder_path}/{filename}") # Add metadata metadata = { 'confluence_id': page_id, 'original_title': title, 'backup_date': datetime.now().isoformat(), 'content_type': 'confluence_page' } blob.metadata = metadata blob.upload_from_string(content, content_type='text/html') logger.info(f"Successfully saved page: {safe_title}") # Save content to local documents folder for local run only local_folder = Path(LOCAL_DOCUMENTS_DIR) local_file_path = local_folder / filename with open(local_file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file: file.write(content) logger.info(f"Successfully saved page to local folder: {safe_title}") return True if __name__ == "__main__": fetch_new_confluence_pages() Step 5: document_indexer.py – Index Documents Using EmbeddingsThis script will load all documents in the documents folder, split each document as needed, generate embeddings for each segment, and store them in the Redis as vector database.
Langchain RecordManager checks the metadata in the Postgres db upsertion_record table before indexing, tracking each document’s last modification date. When run for the first time, it indexes all documents and updates the metadata. For subsequent runs, it only indexes new or modified documents.
document_indexer.py
import os import logging from typing import List, Dict, Optional from dataclasses import dataclass from pathlib import Path from datetime import datetime from dotenv import load_dotenv from langchain.indexes import SQLRecordManager, index from langchain.schema import Document from langchain_community.document_loaders import ( TextLoader, UnstructuredHTMLLoader, PyPDFLoader ) from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings from langchain.vectorstores import Redis from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter logging.basicConfig( level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s', handlers=[ logging.FileHandler('document_indexing.log'), logging.StreamHandler() ] ) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) @dataclass class IndexingConfig: """Configuration for document indexing system.""" documents_dir: str redis_host: str redis_port: int postgres_host: str postgres_port: int postgres_db: str postgres_user: str postgres_password: str openai_api_key: str chunk_size: int = 1000 chunk_overlap: int = 200 @property def redis_url(self) -> str: return f"redis://{self.redis_host}:{self.redis_port}" @property def postgres_url(self) -> str: return f"postgresql+psycopg2://{self.postgres_user}:{self.postgres_password}@{self.postgres_host}:{self.postgres_port}/{self.postgres_db}" @classmethod def from_env(cls) -> 'IndexingConfig': """Create configuration from environment variables.""" load_dotenv() return cls( documents_dir=os.getenv('DOCUMENTS_DIR', 'documents'), redis_host=os.getenv('REDIS_HOST', 'localhost'), redis_port=int(os.getenv('REDIS_PORT', '6379')), postgres_host=os.getenv('POSTGRES_HOST', 'localhost'), postgres_port=int(os.getenv('POSTGRES_PORT', '5432')), postgres_db=os.getenv('POSTGRES_DB', 'mydb'), postgres_user=os.getenv('POSTGRES_USER'), postgres_password=os.getenv('POSTGRES_PASSWORD'), openai_api_key=os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY'), chunk_size=int(os.getenv('CHUNK_SIZE', '1000')), chunk_overlap=int(os.getenv('CHUNK_OVERLAP', '200')) ) class DocumentProcessor: """Handles document loading and processing.""" SUPPORTED_EXTENSIONS = { '.txt': TextLoader, '.html': UnstructuredHTMLLoader, '.htm': UnstructuredHTMLLoader, '.pdf': PyPDFLoader } def __init__(self, config: IndexingConfig): self.config = config self.splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter( separators=["\n\n", "\n", " ", ""], chunk_size=config.chunk_size, chunk_overlap=config.chunk_overlap, length_function=len ) def load_documents(self) -> List[Document]: """Load documents from the specified directory.""" documents = [] directory_path = Path(self.config.documents_dir) if not directory_path.exists(): logger.error(f"Directory not found: {directory_path}") raise FileNotFoundError(f"Directory not found: {directory_path}") for file_path in directory_path.iterdir(): if not file_path.is_file(): continue ext = file_path.suffix.lower() loader_class = self.SUPPORTED_EXTENSIONS.get(ext) if not loader_class: logger.warning( f"Skipping unsupported file format: {file_path.name}") continue try: logger.info(f"Loading document: {file_path.name}") loader = loader_class(str(file_path)) docs = loader.load() # Add metadata for doc in docs: doc.metadata = {"source": file_path.name} documents.extend(docs) except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Failed to load {file_path.name}: {str(e)}") continue logger.info(f"Successfully loaded {len(documents)} documents") return documents class DocumentIndexer: """Handles document indexing and embedding storage.""" def __init__(self, config: IndexingConfig): self.config = config self.processor = DocumentProcessor(config) def initialize_components(self): """Initialize embeddings, vectorstore, and record manager.""" try: self.embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings( openai_api_key=self.config.openai_api_key) self.vectorstore = Redis( redis_url=self.config.redis_url, index_name='document_embeddings', embedding=self.embeddings ) self.record_manager = SQLRecordManager( namespace="redis/document_embeddings", db_url=self.config.postgres_url ) # Create the schema if it doesn't exist self.record_manager.create_schema() logger.info("Successfully initialized all components") except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Failed to initialize components: {str(e)}") raise def process_and_index_documents(self): """Process and index documents with error handling and logging.""" try: documents = self.processor.load_documents() if not documents: logger.warning("No documents were loaded") return logger.info("Splitting documents into chunks...") chunks = self.processor.splitter.split_documents(documents) logger.info( f"Created {len(chunks)} chunks from {len(documents)} documents") # Index documents logger.info("Indexing documents...") result = index( chunks, self.record_manager, self.vectorstore, cleanup="incremental", source_id_key="source", ) logger.info("Indexing completed successfully") logger.info(f"Indexing results: {result}") return result except Exception as e: logger.error( f"Error during document processing and indexing: {str(e)}") raise def main(): """Main function to run the document indexing process.""" try: config = IndexingConfig.from_env() indexer = DocumentIndexer(config) indexer.initialize_components() # Process and index documents result = indexer.process_and_index_documents() logger.info("Document indexing process completed successfully") return result except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Document indexing process failed: {str(e)}") raise if __name__ == "__main__": main()Expected Output on First and Subsequent Runs
- First Run: Since there’s no existing metadata, all documents will be indexed.
- Subsequent Runs: If there are no new or modified documents, the output will indicate that all documents were skipped.
\n Step 6:main.py – Set Up Q&A Retrieval with LangChain
The script provides a simple interface to query documents in Redis using LangChain to respond to user questions.
main.py
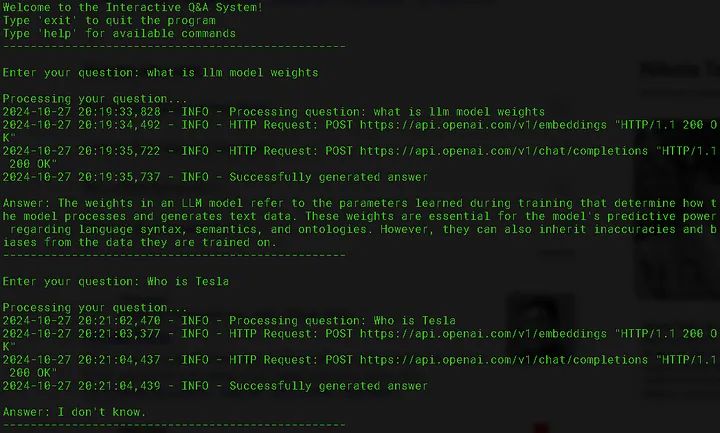
import os import logging from typing import List, Optional, Dict from dataclasses import dataclass from langchain.vectorstores import Redis from langchain.schema import Document from dotenv import load_dotenv from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings from langchain_openai.chat_models import ChatOpenAI from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser from langchain_core.retrievers import BaseRetriever logging.basicConfig( level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s' ) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) @dataclass class Config: """Configuration class for the application.""" redis_host: str redis_port: int = 6379 redis_index_name: str = "document_embeddings" retriever_k: int = 2 max_retries: int = 3 temperature: float = 0 @property def redis_url(self) -> str: return f"redis://{self.redis_host}:{self.redis_port}" @classmethod def from_env(cls) -> 'Config': """Create configuration from environment variables.""" load_dotenv() return cls( redis_host=os.getenv('REDIS_HOST', 'localhost'), redis_port=int(os.getenv('REDIS_PORT', '6379')), redis_index_name=os.getenv( 'REDIS_INDEX_NAME', 'document_embeddings'), retriever_k=int(os.getenv('RETRIEVER_K', '2')), max_retries=int(os.getenv('MAX_RETRIES', '3')), temperature=float(os.getenv('TEMPERATURE', 0)) ) class QASystem: """Main QA system class handling document retrieval and question answering.""" DEFAULT_PROMPT_TEMPLATE = """ You are an assistant for question-answering tasks. Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer the question. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know. Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer concise. Question: {question} Context: {context} Answer: """ def __init__(self, config: Config): self.config = config self.embedding = OpenAIEmbeddings() self.initialize_components() def initialize_components(self): """Initialize Redis vectorstore, retriever, and QA chain.""" try: self.redis_vectorstore = Redis( redis_url=self.config.redis_url, index_name=self.config.redis_index_name, embedding=self.embedding ) logger.info( f"Successfully connected to Redis at {self.config.redis_url}") self.retriever = self.initialize_retriever() self.qa_chain = self.create_qa_chain() except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Failed to initialize components: {str(e)}") raise def initialize_retriever(self) -> BaseRetriever: """Initialize the Redis retriever.""" return self.redis_vectorstore.as_retriever( search_kwargs={"k": self.config.retriever_k} ) @staticmethod def format_docs(docs: List[Document]) -> str: """Format the retrieved documents into a single string.""" return "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs) def create_qa_chain(self): """Create the question-answering chain.""" prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(self.DEFAULT_PROMPT_TEMPLATE) llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=self.config.temperature) return ( { "context": self.retriever | self.format_docs, "question": RunnablePassthrough(), } | prompt | llm | StrOutputParser() ) def answer_question(self, question: str, max_retries: Optional[int] = None) -> str: """ Answer a question using the QA chain with retry mechanism. Args: question: The question to answer max_retries: Maximum number of retry attempts Returns: str: The answer to the question """ max_retries = max_retries or self.config.max_retries retry_count = 0 while retry_count < max_retries: try: logger.info(f"Processing question: {question}") answer = self.qa_chain.invoke(question) logger.info("Successfully generated answer") return answer except Exception as e: retry_count += 1 if retry_count < max_retries: logger.warning( f"Attempt {retry_count} failed: {str(e)}. Retrying...") else: logger.error( f"Failed to answer question after {max_retries} attempts") raise RuntimeError(f"Failed to answer question: {str(e)}") def get_document_count(self) -> int: """Get the number of documents in the Redis vectorstore.""" try: # Using a broad search to get document count docs = self.redis_vectorstore.similarity_search("", k=1) return len(docs) except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Failed to get document count: {str(e)}") return 0 def interactive_qa(self): """ Run an interactive Q&A session where users can input questions until they type 'exit'. """ print("\nWelcome to the Interactive Q&A System!") print("Type 'exit' to quit the program") print("Type 'help' for available commands") print("-" * 50) while True: try: # Get user input question = input("\nEnter your question: ").strip() # Check for exit command if question.lower() == 'exit': print("\nThank you for using the Q&A system. Goodbye!") break # Check for help command elif question.lower() == 'help': print("\nAvailable commands:") print("- 'exit': Quit the program") print("- 'help': Show this help message") print("- 'count': Show number of documents in the system") continue # Check for count command elif question.lower() == 'count': doc_count = self.get_document_count() print(f"\nNumber of documents in the system: {doc_count}") continue # Skip empty questions if not question: print("Please enter a valid question.") continue # Get and display answer print("\nProcessing your question...") answer = self.answer_question(question) print("\nAnswer:", answer) print("-" * 50) except KeyboardInterrupt: print("\n\nProgram interrupted by user. Goodbye!") break except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Error processing question: {str(e)}") print( "\nSorry, there was an error processing your question. Please try again.") def main(): """Main function to run the QA system.""" try: config = Config.from_env() qa_system = QASystem(config) doc_count = qa_system.get_document_count() logger.info(f"System initialized with {doc_count} documents in Redis") qa_system.interactive_qa() except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Application error: {str(e)}") raise if __name__ == "__main__": main()After running the optional fetch_confluence_pages.py (to pull recent documents from Confluence) and executing document_indexer.py to embed and index documents in Redis, you can start the interactive Q&A interface by running main.py.
\ Once you run main.py, you will be prompted to enter a question. The system uses embeddings to find relevant information from the indexed documents and then leverages LangChain and ChatGPT to generate a response.
\
\
SummaryThat’s about it! From this article, you should have a basic understanding of building a solution for continuous document indexing. For the steps outlined, you can implement a similar pipeline, adapt it to your needs, and scale it to handle large volumes of documents and user queries.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.