and the distribution of digital products.
DM Television
Automate Infrastructure and Secure Your App with Terraform and Cognito
Terraform is an open-source tool that allows you to define and provision infrastructure using code. It allows you to describe the desired state of your infrastructure, and Terraform figures out how to achieve it. This enables you to automate infrastructure provisioning, manage complex environments efficiently, and collaborate effectively with your team.
\ Amazon Cognito is an AWS service that simplifies user authentication and authorisation for your web and mobile applications. It manages user sign-up, sign-in, and data securely, allowing you to focus on building your core application features. Cognito also provides features like multi-factor authentication and integration with social identity providers, enhancing the security and convenience of your user experience.
Infrastructure as code (IaC)Infrastructure as code (IaC) is a practice where infrastructure and services are defined and provisioned through code instead of manual processes. This approach allows you to manage and automate the creation, configuration, and updates of your infrastructure resources like servers, networks, and storage. IaC enables consistency, repeatability, and version control for your infrastructure, making it easier to manage and scale your systems. There are a couple of other tools that currently help with IaC; these include:
\
AWS CloudFormation
Ansible
Puppet
Chef
\
In this tutorial, we aim to create an AWS Cognito user pool manually through the AWS web interface and also create a similar user pool with Terraform. This is generally a beginner’s introduction to how Terraform can help automate the creation of resources on AWS programmatically.
\
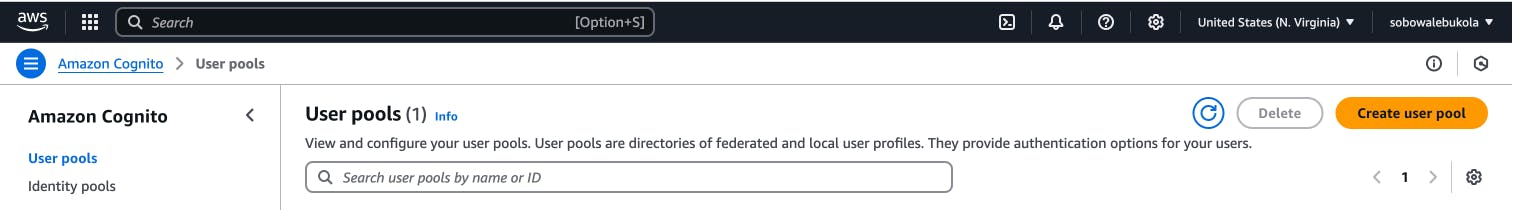
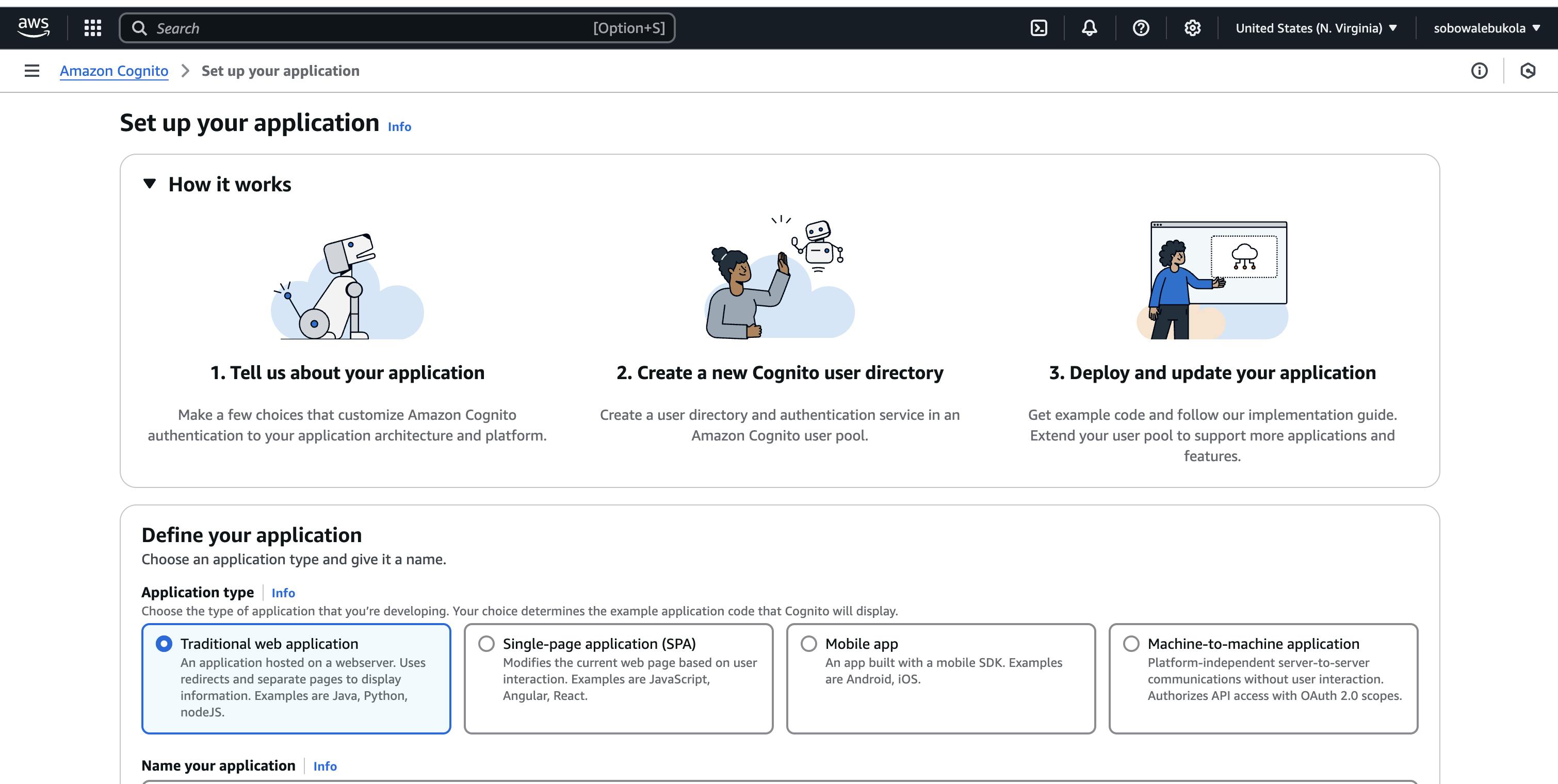
We will be creating an AWS Cognito user pool with the AWS console as follows:
Sign in to the AWS console.
Search for Cognito in the top left bar for services.
Create the user pool through the AWS Console user interface
\
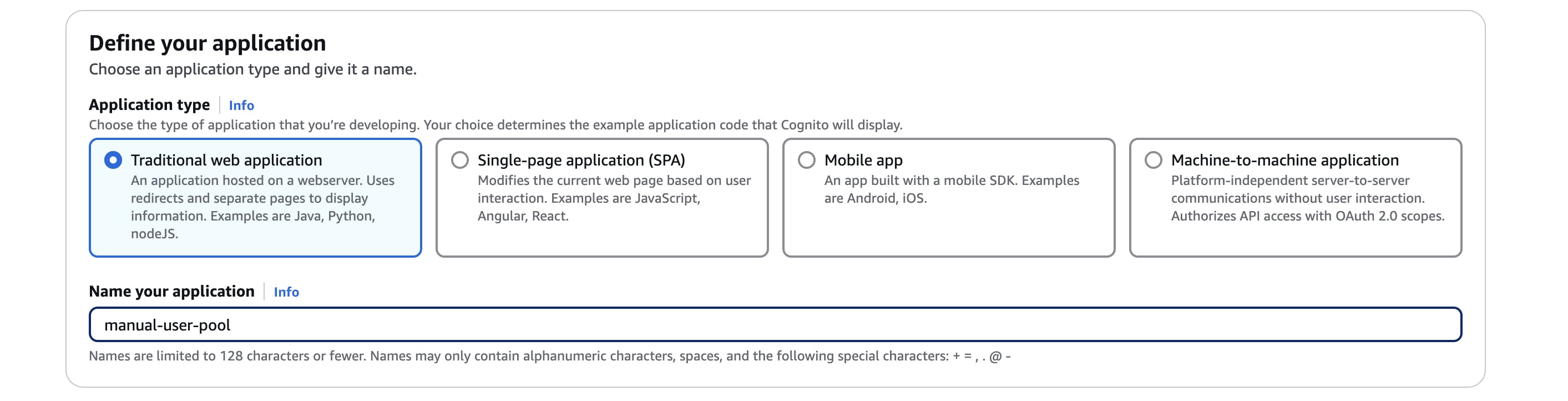
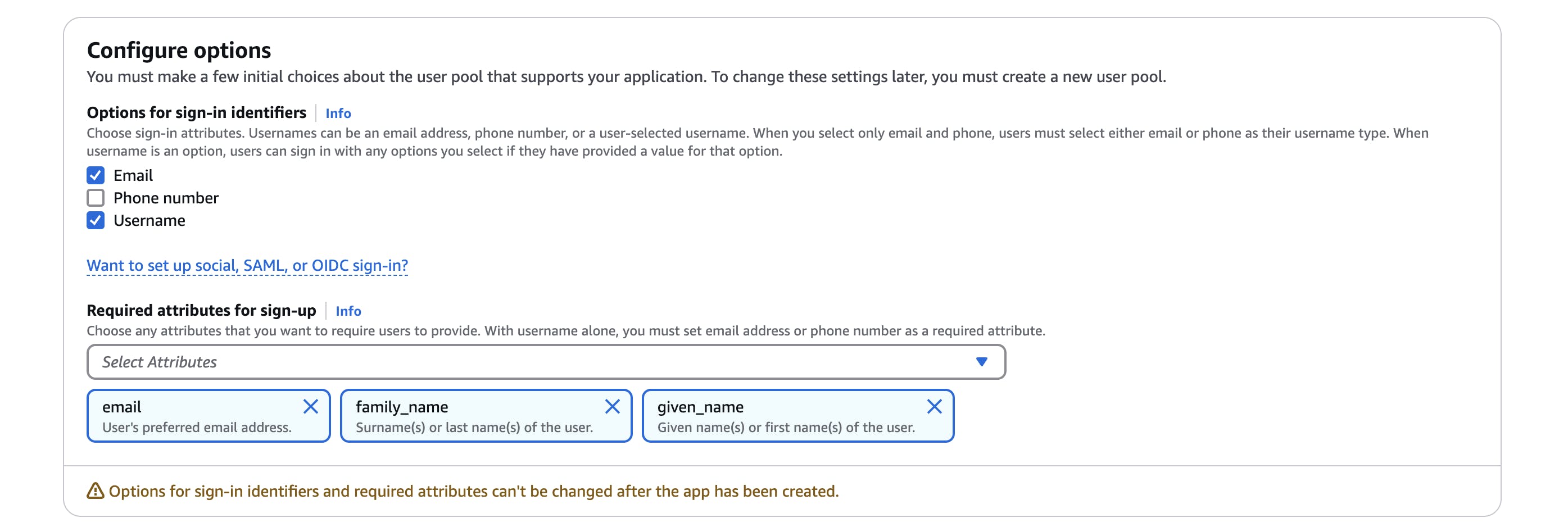
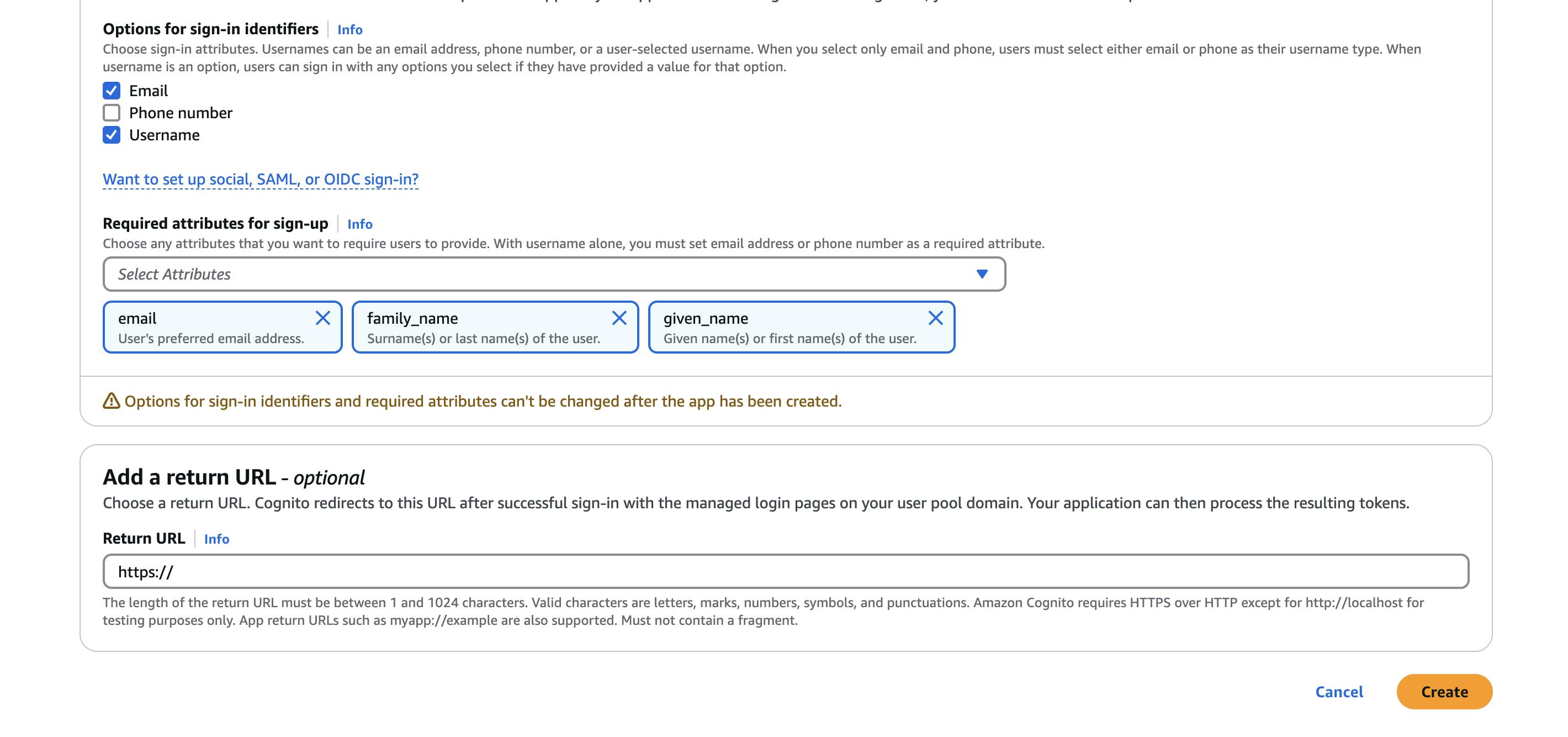
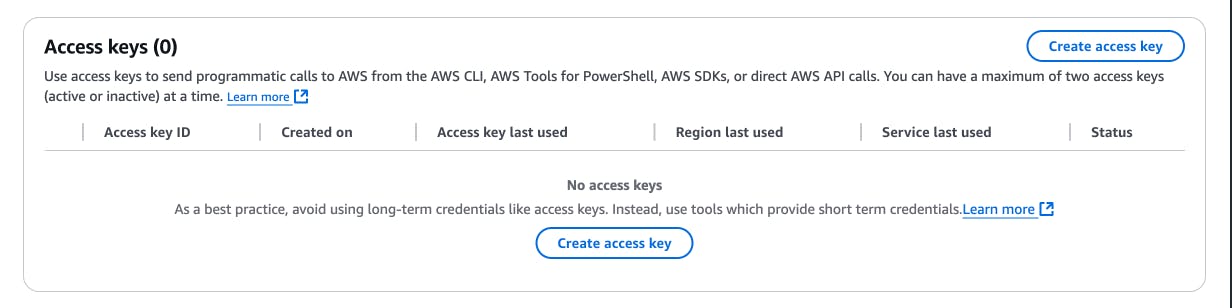
The manual creation process is as shown below:
\
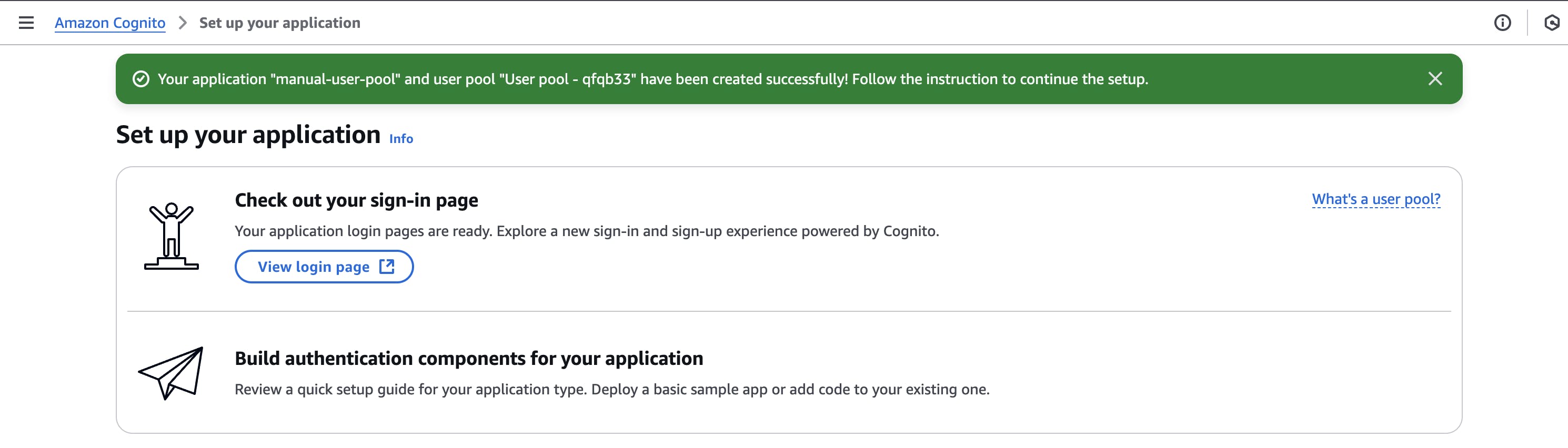
You should notice I added some attributes as required for sign-up (email, familyname, givenname). We have just created an AWS Cognito user pool that provides an authentication service for any web or mobile application.
Installation of TerraformTo install Terraform on your operating system, follow the installation guide here:
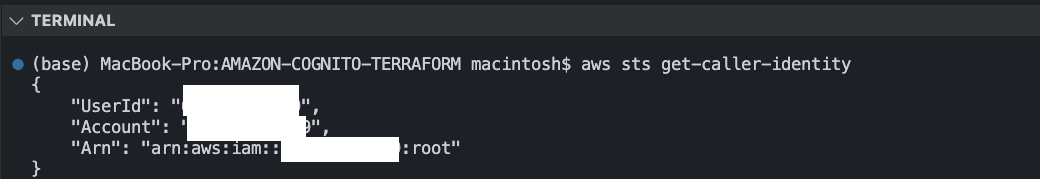
AWS ConfigurationCheck if you have configured AWS on your device before using the command below:
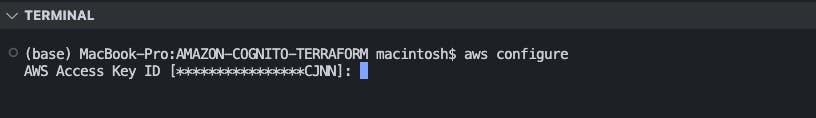
aws sts get-caller-identityIf you do not have any configured AWS credentials on your device as shown above, set up an AWS profile on your device using the command:
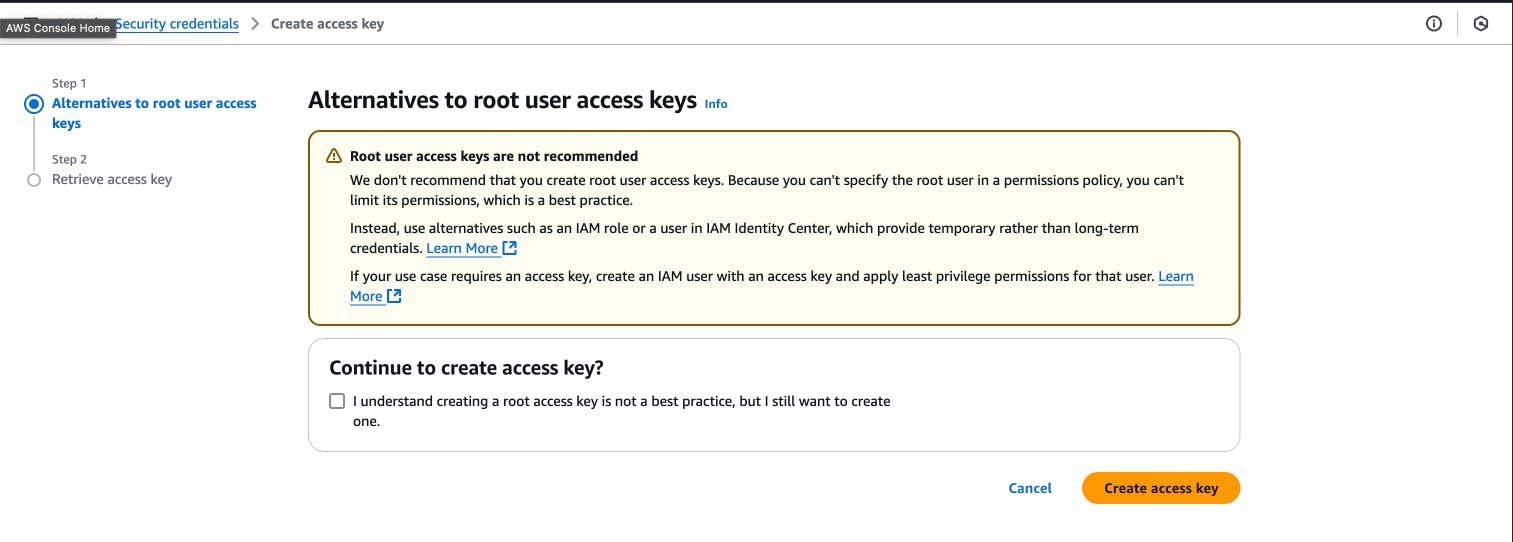
aws configureIf you do not currently have access keys configured for your account, follow the guide here to create the needed keys.
You will need to enter the following to configure your device profile:
- Access Key ID
- Secret Access Key
- Default region (e.g., us-east-1)
- Output format (e.g., json)
\ After you are done with the terminal prompt, run aws sts get-caller-identityagain and ensure it returns your AWS profile identity.
Terraform scriptCreate a folder AMAZON-TERRAFORM-COGNITO for the Terraform script and configuration files.
\ Create a file main.tf in your newly created folder.
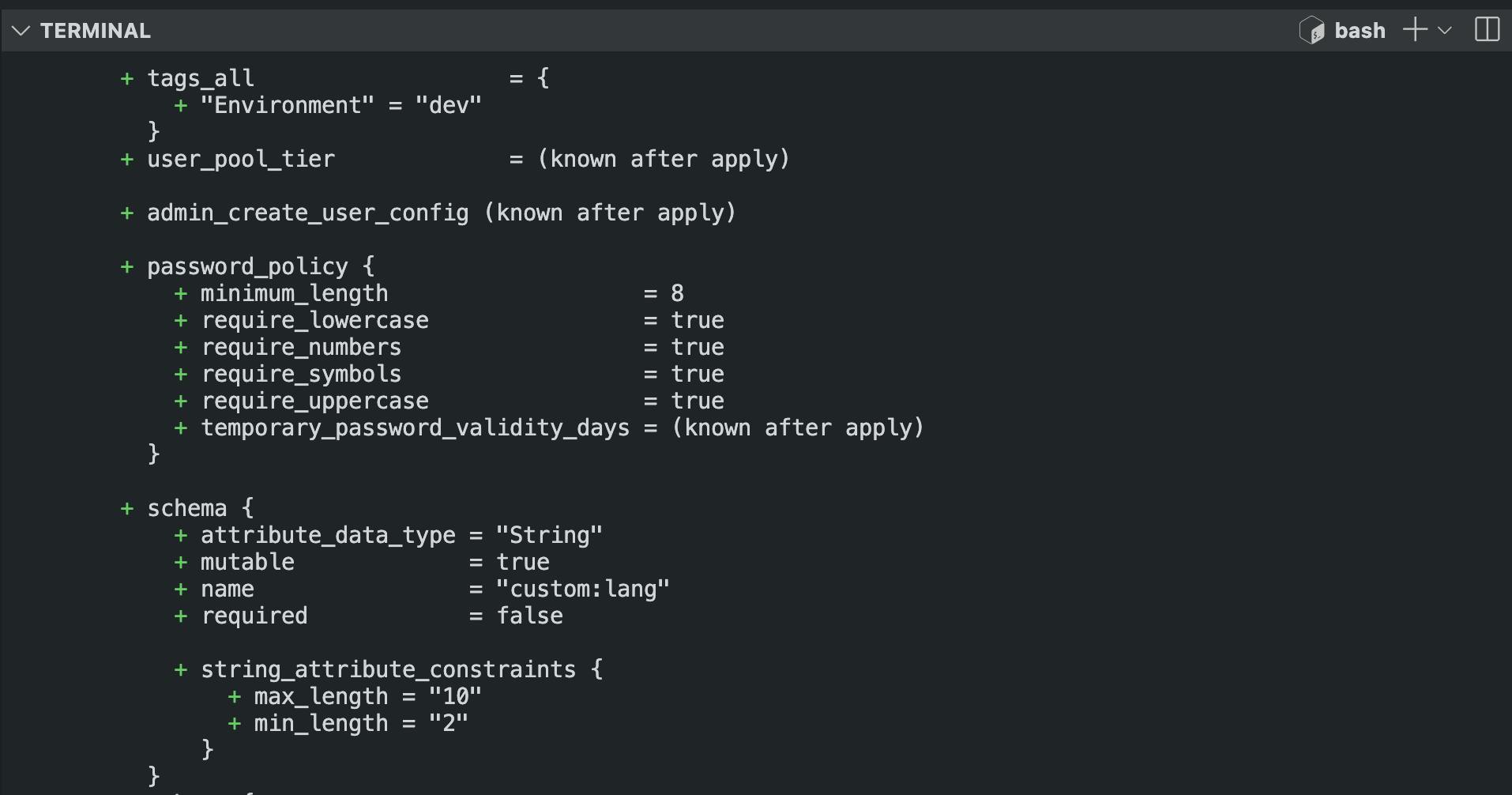
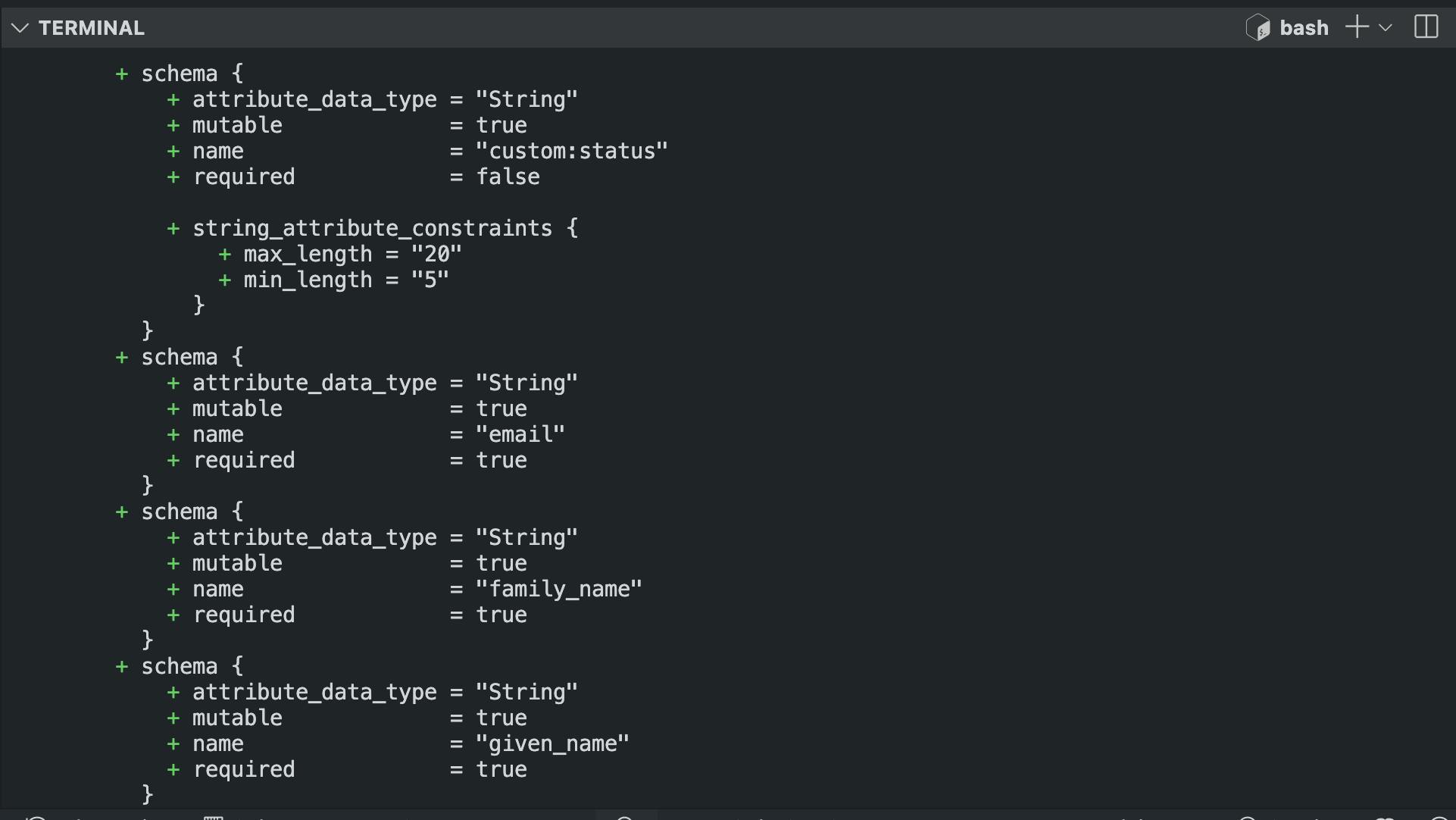
provider "aws" { region = "us-east-1" # Replace with your desired AWS region } # Create a Cognito User Pool resource "aws_cognito_user_pool" "main" { name = "terraform-user-pool" # Custom attributes with shorter names schema { name = "custom:lang" attribute_data_type = "String" mutable = true required = false string_attribute_constraints { max_length = 10 min_length = 2 } } schema { name = "custom:status" attribute_data_type = "String" mutable = true required = false string_attribute_constraints { max_length = 20 min_length = 5 } } # Standard attributes schema { name = "email" attribute_data_type = "String" mutable = true required = true } schema { name = "family_name" attribute_data_type = "String" mutable = true required = true } schema { name = "given_name" attribute_data_type = "String" mutable = true required = true } # Password policy password_policy { minimum_length = 8 require_lowercase = true require_uppercase = true require_numbers = true require_symbols = true } # Tags for resources tags = { Environment = "dev" } } # Create a User Pool Client resource "aws_cognito_user_pool_client" "main" { name = "terraform-user-pool-client" user_pool_id = aws_cognito_user_pool.main.id generate_secret = false explicit_auth_flows = [ "ALLOW_USER_PASSWORD_AUTH", "ALLOW_REFRESH_TOKEN_AUTH", "ALLOW_CUSTOM_AUTH", "ALLOW_USER_SRP_AUTH" ] } # Output User Pool and Client IDs output "user_pool_id" { value = aws_cognito_user_pool.main.id } output "user_pool_client_id" { value = aws_cognito_user_pool_client.main.id }Open a terminal in the current working directory and run the three terminal commands as shown below:
\ Command:
\
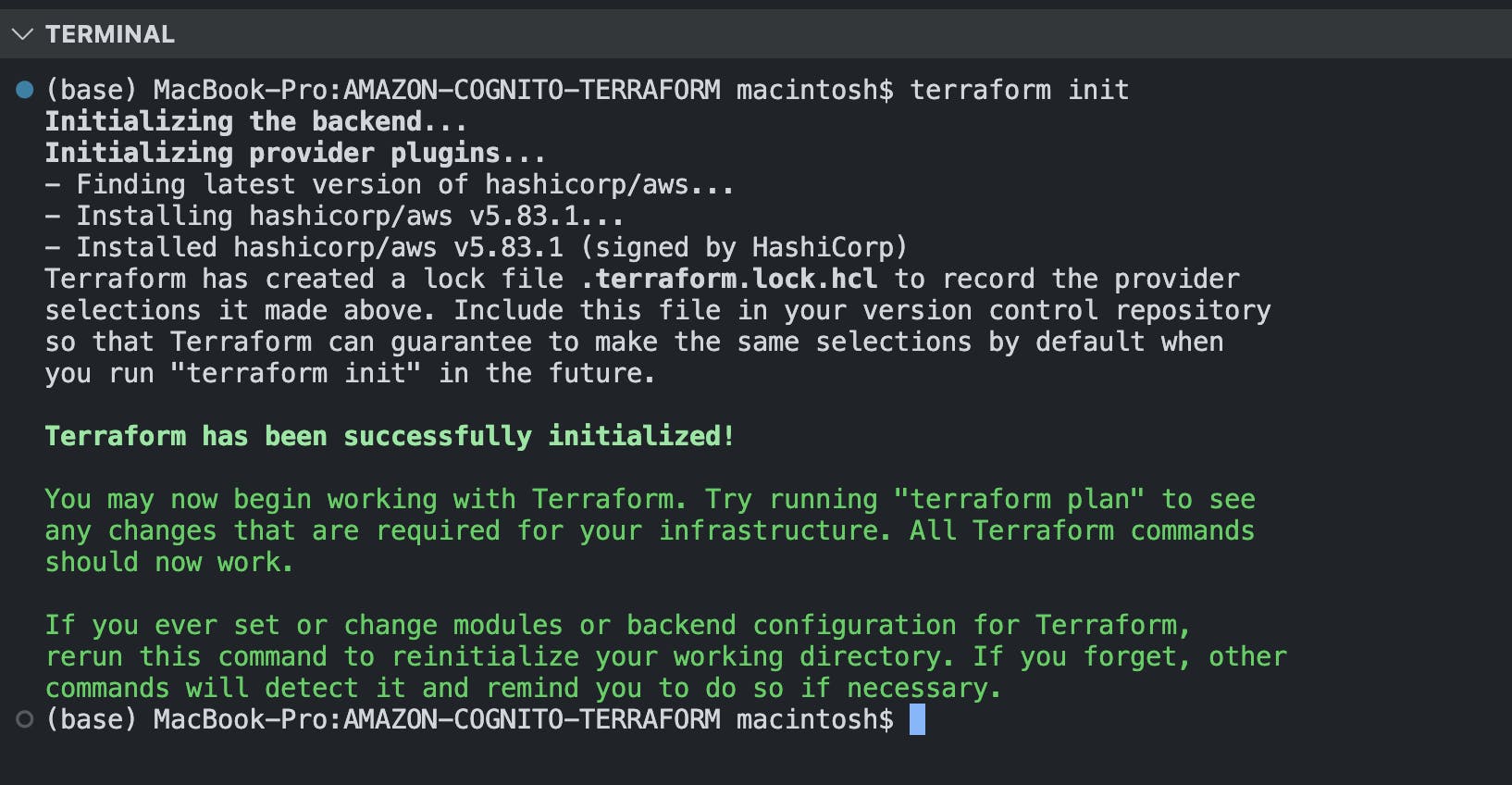
terraform init\ Result:
\
Command:
\
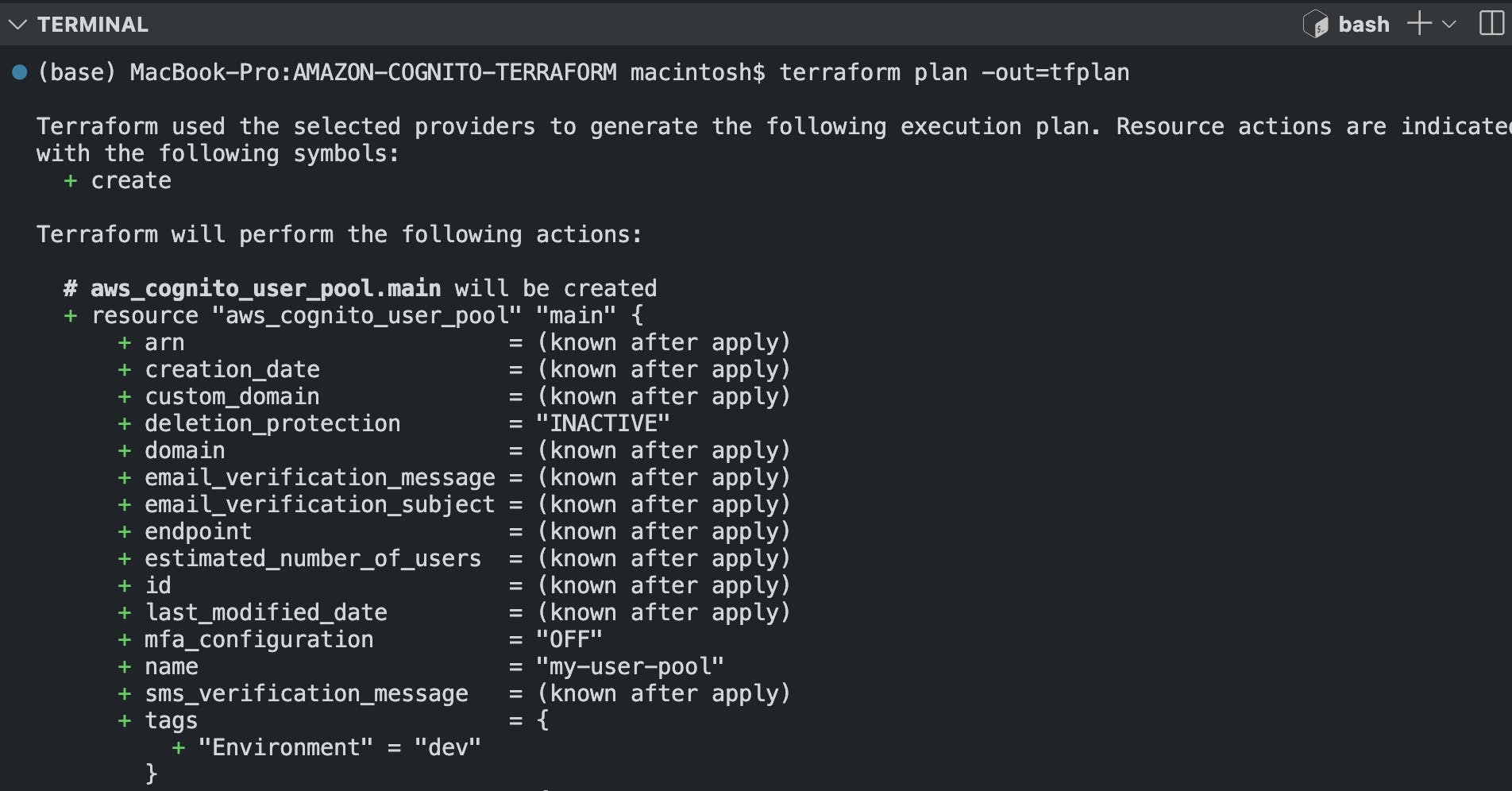
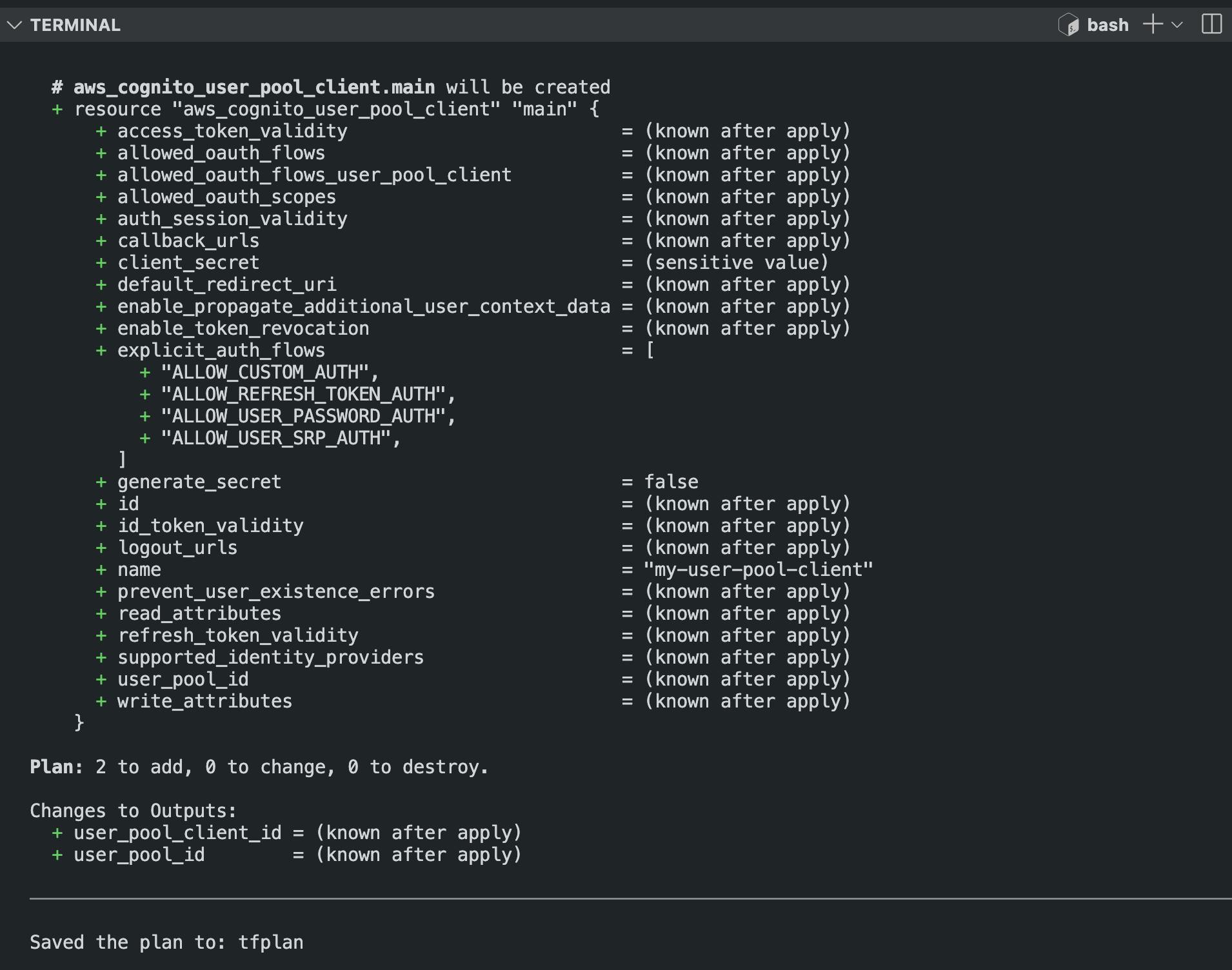
terraform plan -out=tfplan\ Result:
\
Command:
\
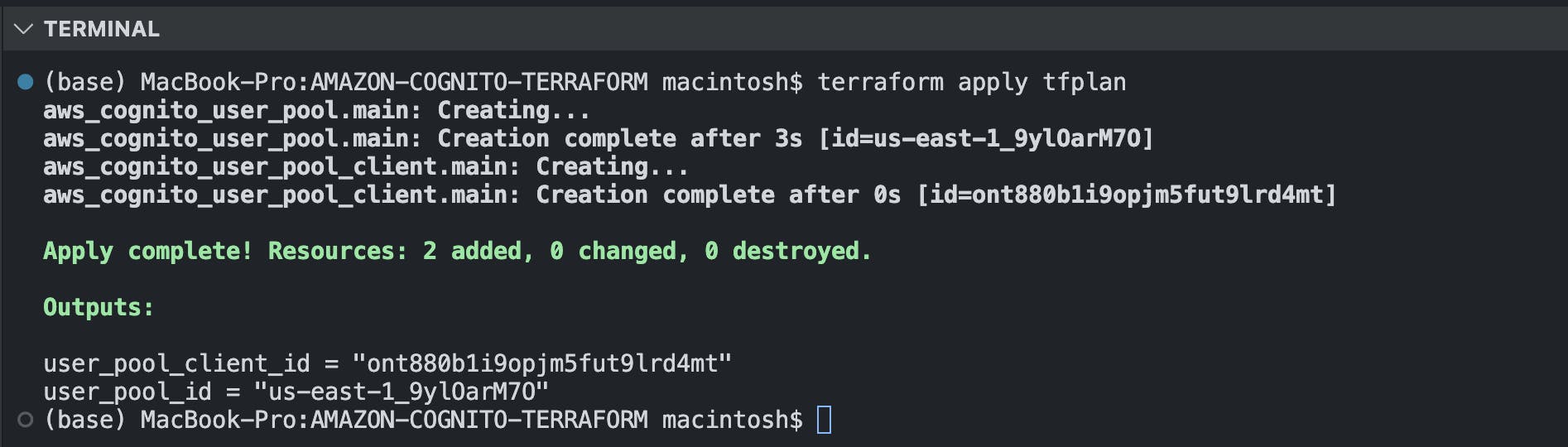
terraform apply tfplan\ Result:
\
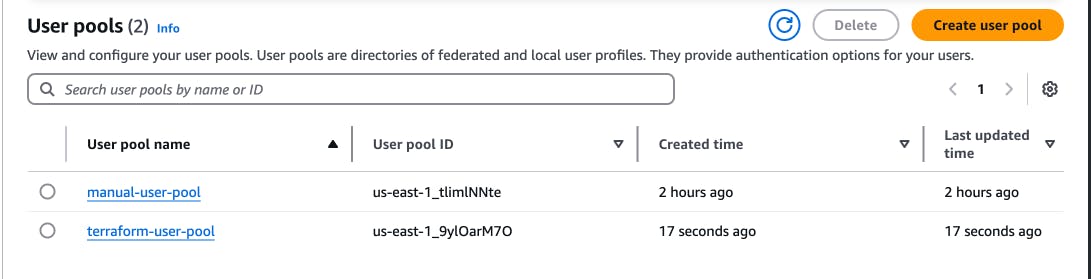
\ Visit your Amazon Cognito page on the console and observe the new terraform-user-pool you created with Terraform. You have been able to successfully provision a Cognito service without doing it manually through the AWS console!
\
Imagine configuring the over 200 Amazon Web Services with Infrastructure as Code. Terraform can handle complex scenarios like multi-region deployments, intricate networking topologies, and serverless architectures. It integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines and leverages advanced features like modules and workspaces for efficient infrastructure management. By utilising Terraform's capabilities, we can automate complex deployments, ensure consistency, and enhance the reliability of our AWS infrastructure.
\ If you've followed this tutorial to this point, congratulations! You've successfully provisioned an AWS Cognito service using Terraform. Keep exploring Terraform’s capabilities to further enhance your cloud infrastructure, and don’t hesitate to experiment as you refine your skills. Happy provisioning!
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.